Beijing Zhongguancun Life Science Park
Project Information
- Project Location:
- China Beijing
- Project Scale:
- 26 Hectares
- Design Time:
- August 2001
- Build Time:
- October 2002
- Client:
- Beijing Zhongguancun Life Science Park Development Co., Ltd.
- Award List:
- 2004 Beijing 11th Excellent Engineering Design First Prize, 2004 Capital City Environmental Excellent Design Scheme Award
- Related Papers
Project Profile
1. Project Statement
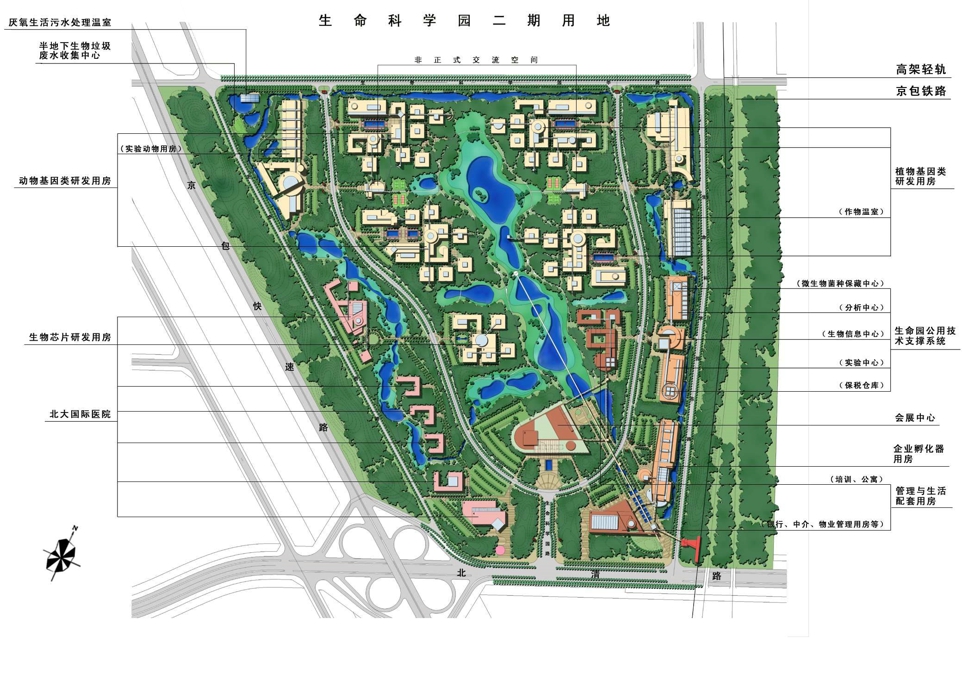
The Zhongguancun Life Science Park is a research and development campus for life sciences. An international competition was carried in late 1999 for the master plan and landscape design, and this design won the first place. This design aims at creating an ecologically and environmentally sustainable campus.
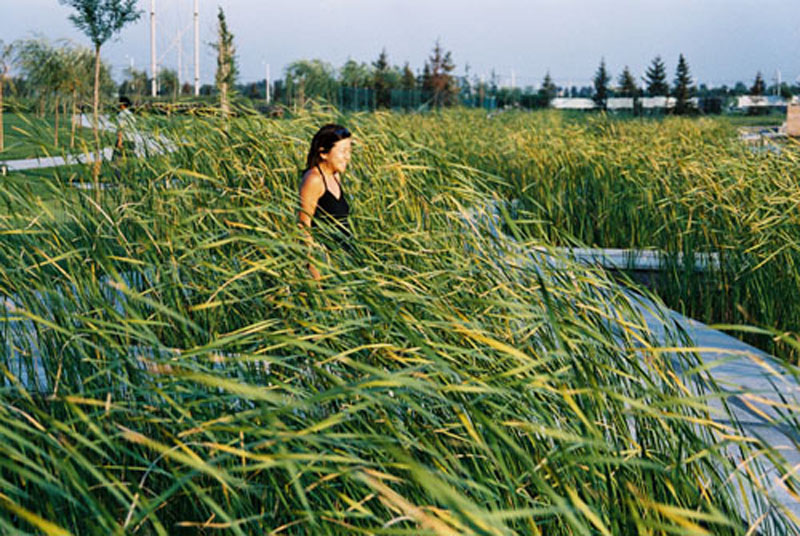
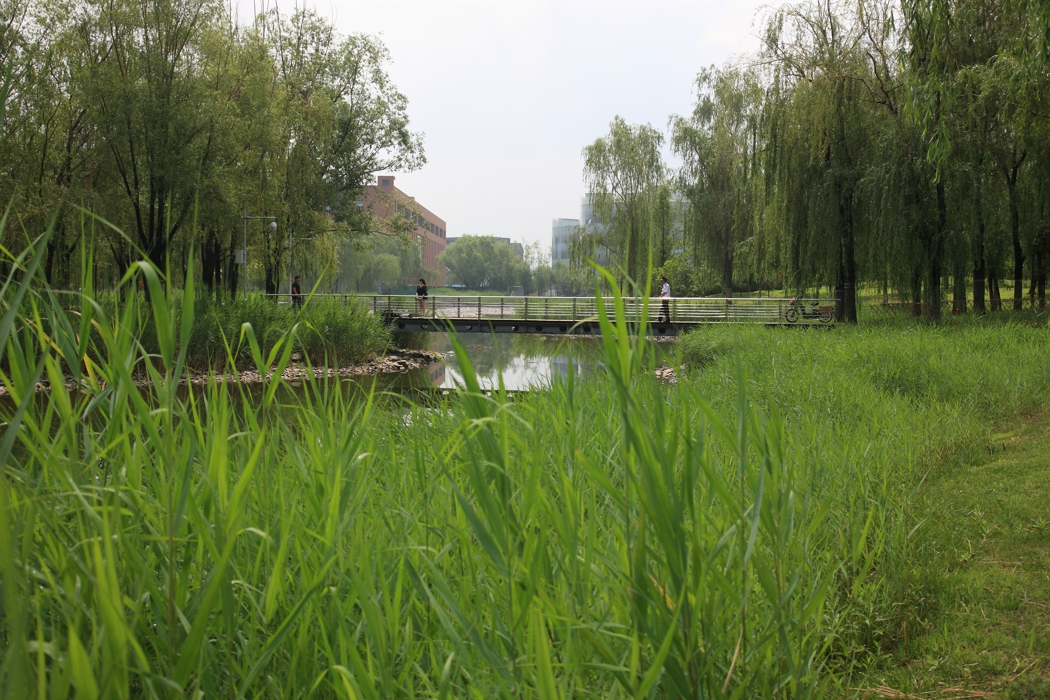
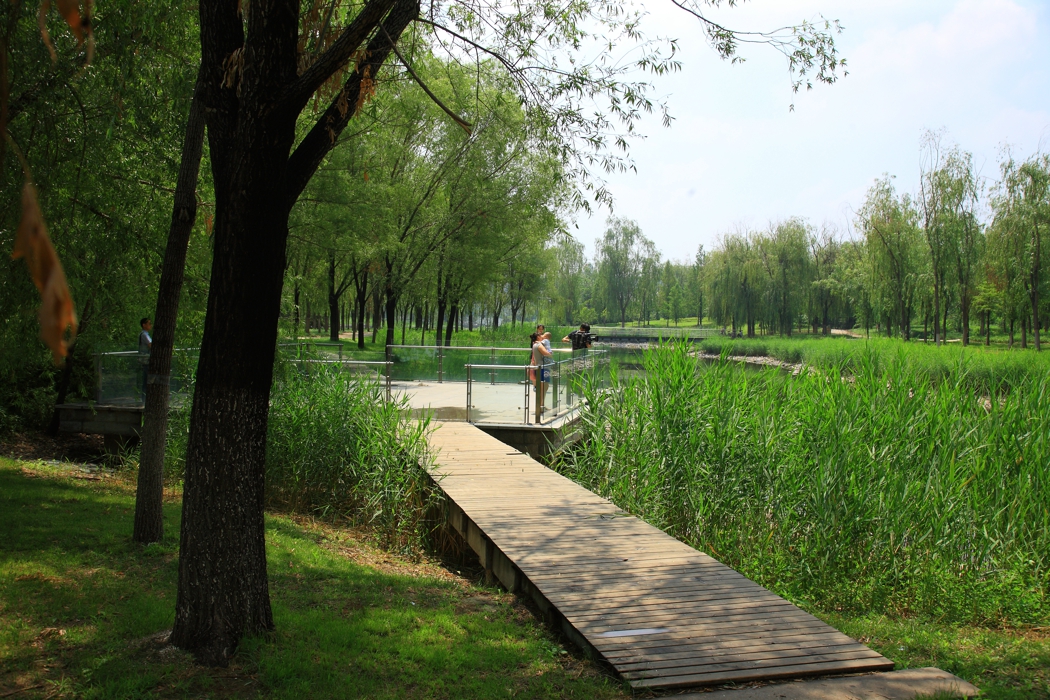
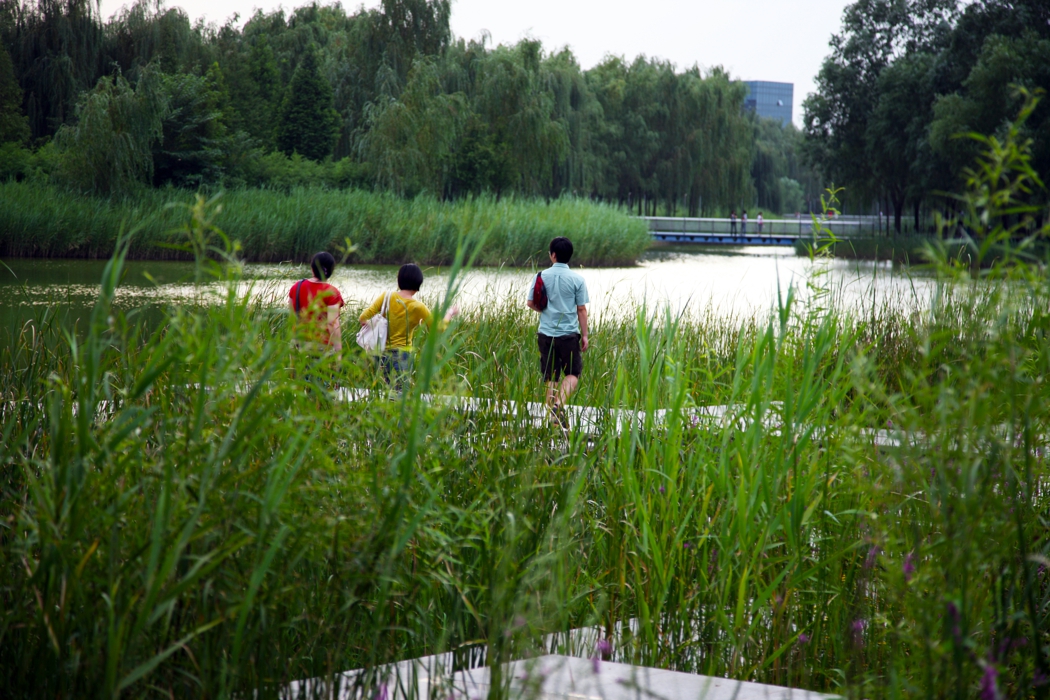
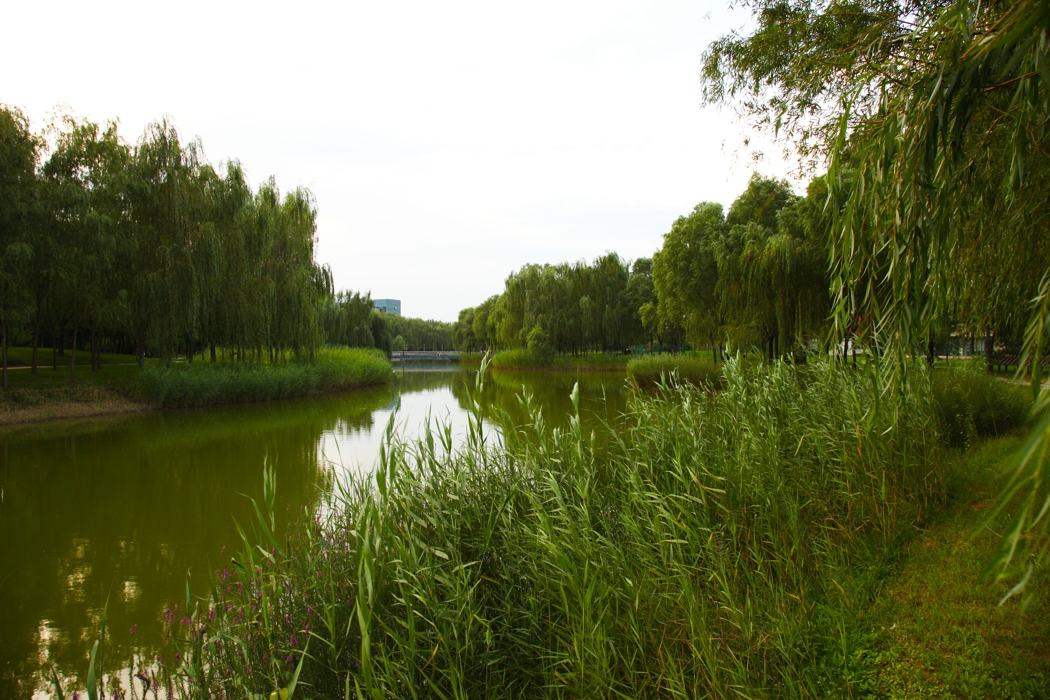
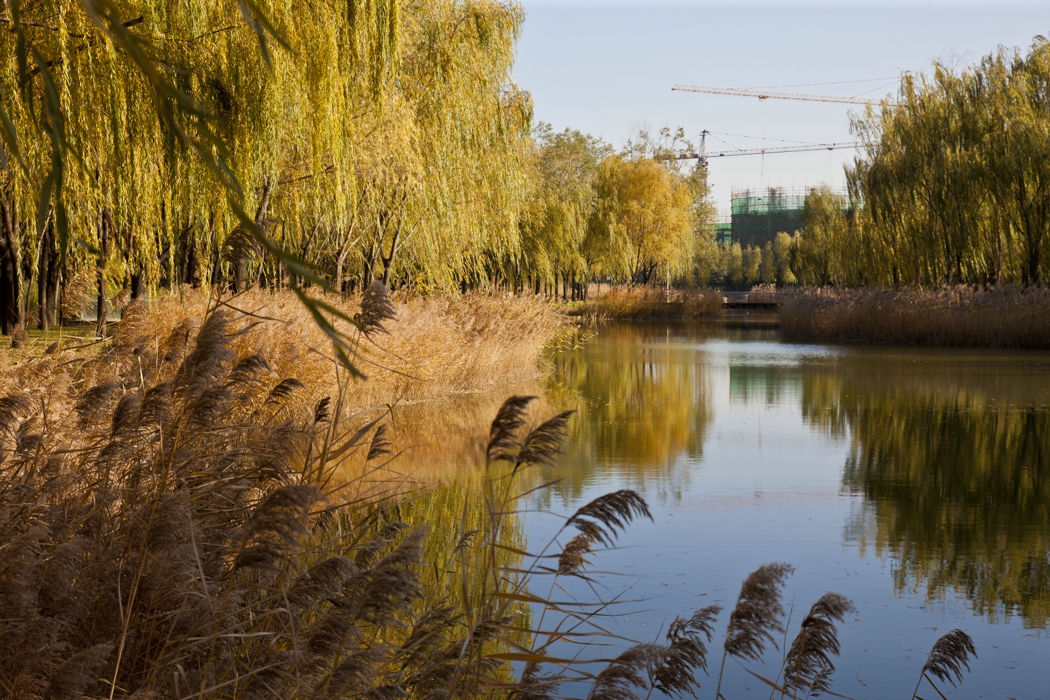
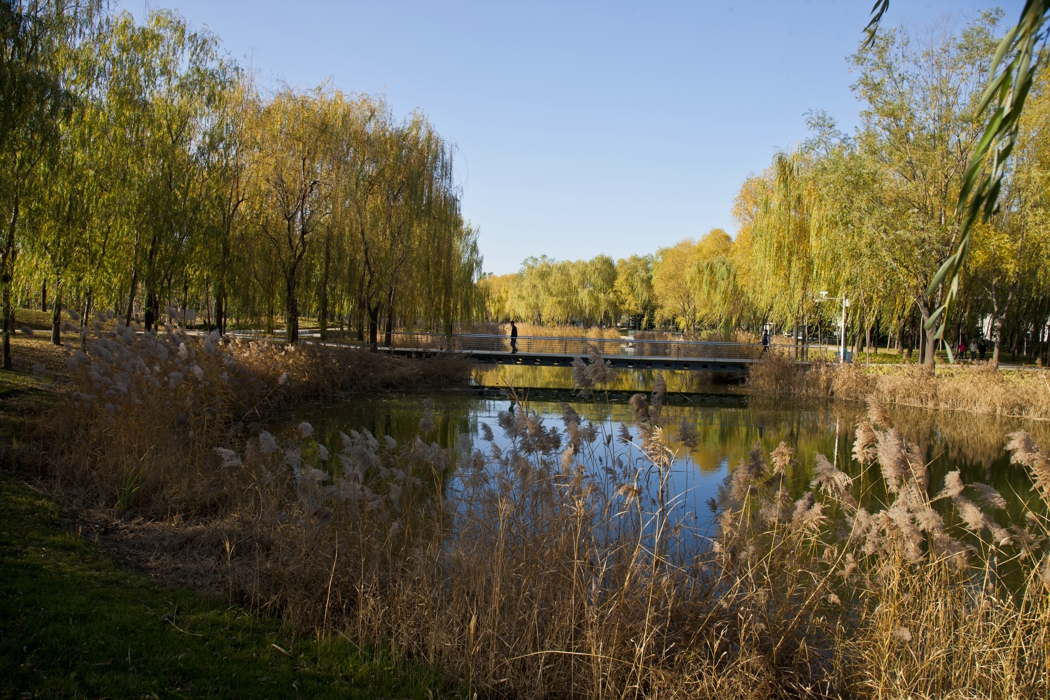
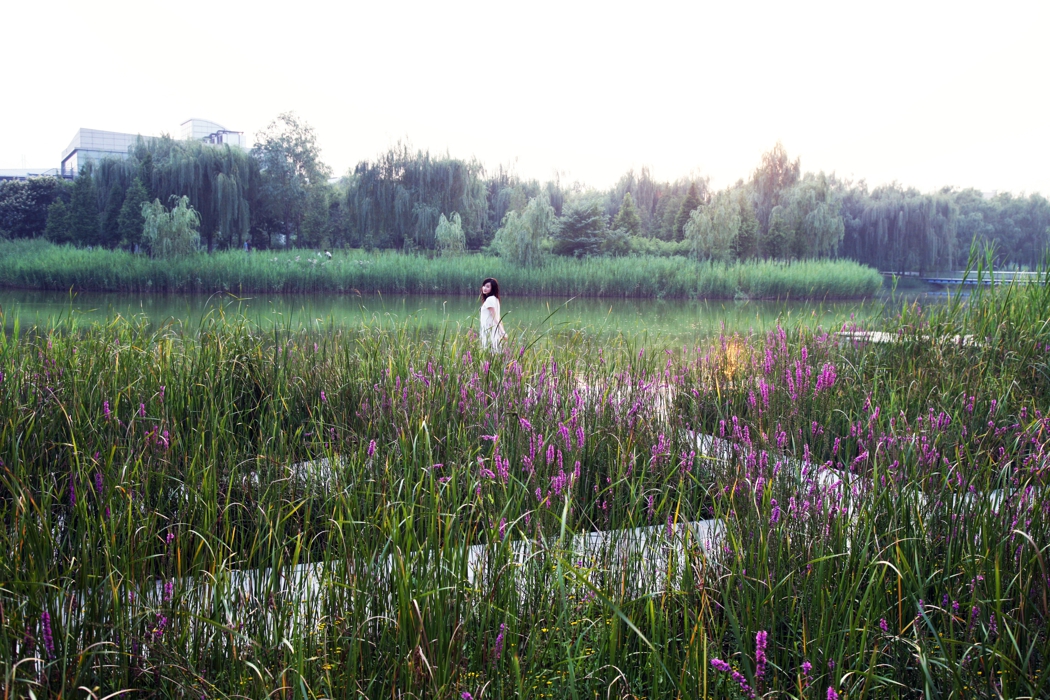
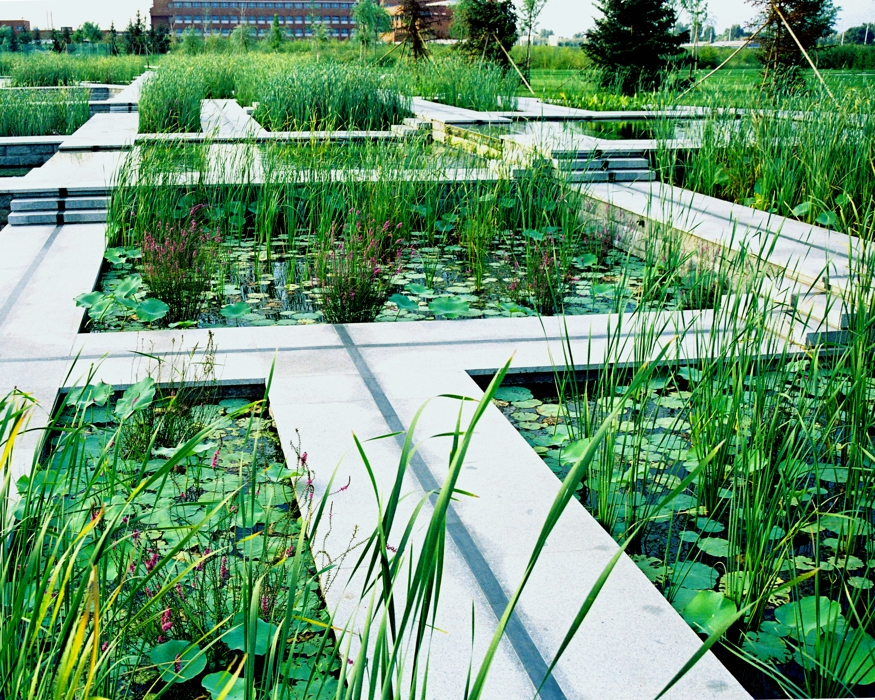
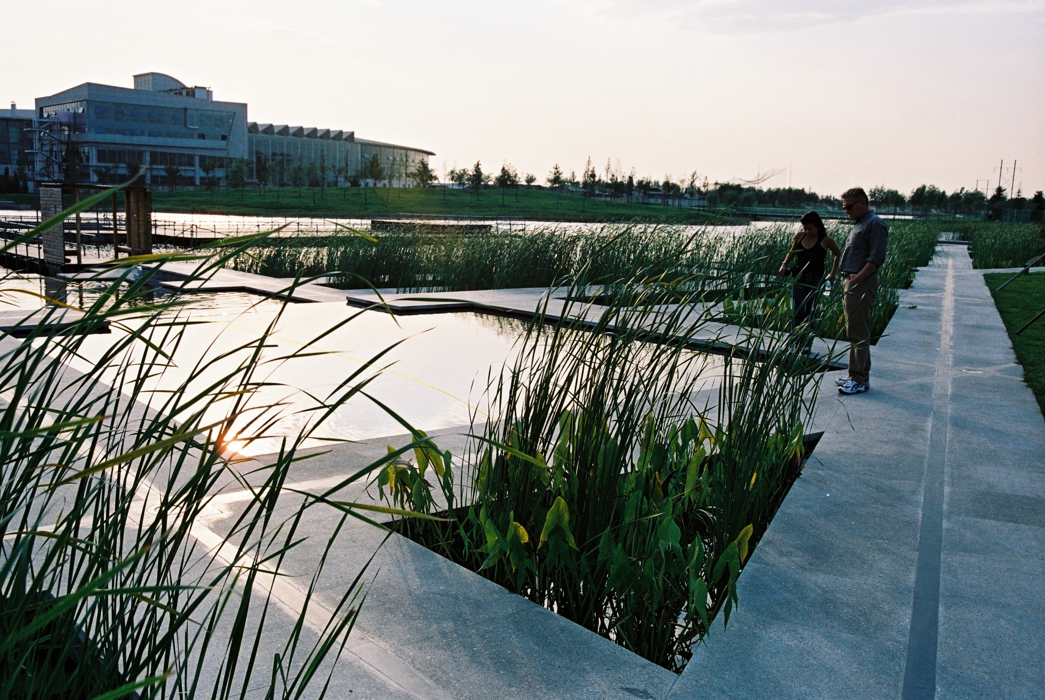
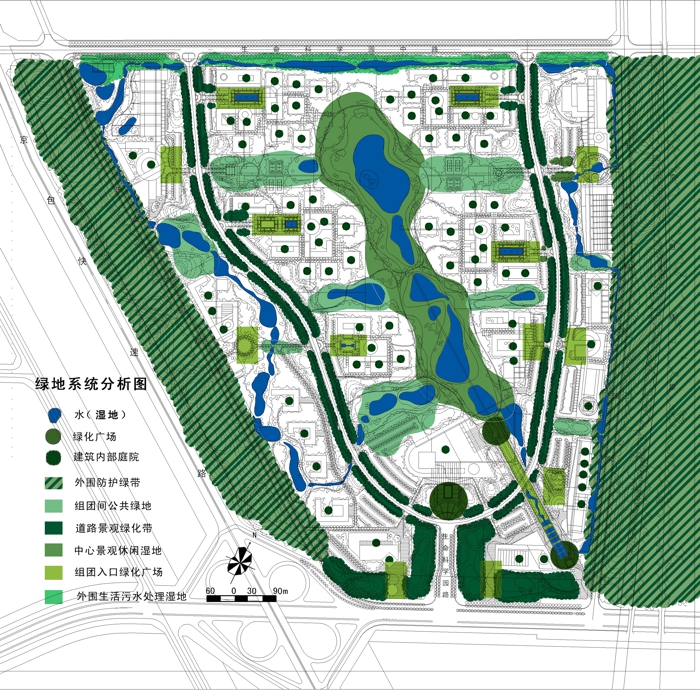
The campus is 132 Ha in area. In total 530,000 square meters of research and development buildings will be constructed. The central park of the campus, which is 10 Ha in area is featured with man made wetland and a pond, which is presented for 2004 ASLA award, was fully executed by the end of 2002.
There are many challenges that the landscape architect has to face and finally make this project executed successfully. It was these challenges and solutions that make this project special.
2. Objective and Challenge
2.1 The Communication Challenge
The first challenge was communicational and political: the landscape architect convinces the client successfully to accept the idea of collecting storm water and recycling sewage water by using man made wetland and use soft lining for the pond. It was a revolutionary way of thinking for the Chinese clients who are so much used to the traditional way of civil engineering in dealing with storm water and sewage, and using concrete lining for water features. This project becomes a good environmental education site for civil engineers.
2.2 The Technical Challenge
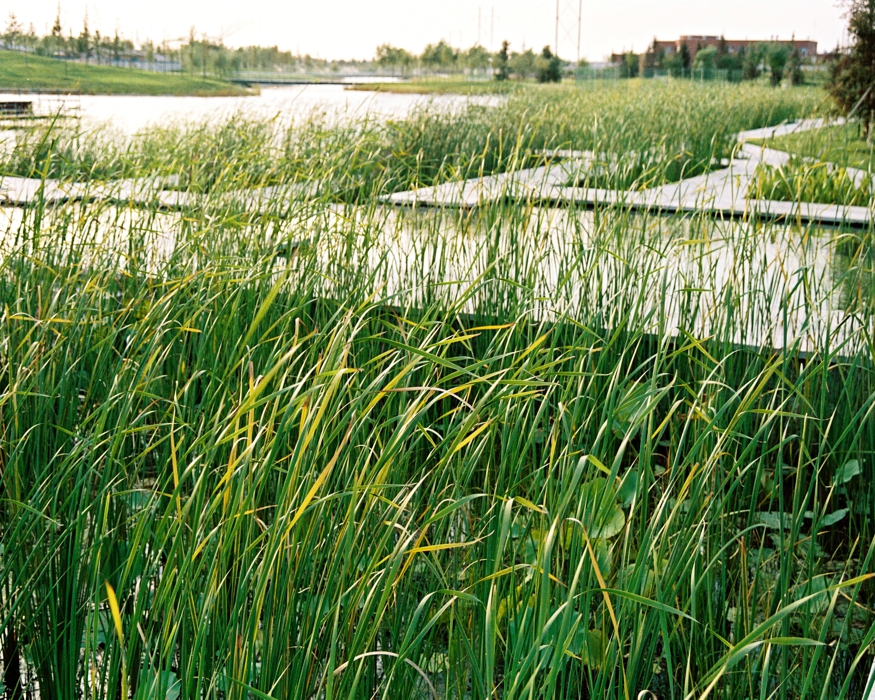
The second challenge is technical: Beijing is a semi-dry region, with 660mm of annual rainfall and the soil for this site is sandy loam. About 80% of the rainfall is concentrated in July and August. The terraced wetland is designed to catch the substantial amount of storm water in the campus area and let water flow slowly terrace by terrace through the wetland, purified and deposited, and then seeps into a stream that flows into the pond.
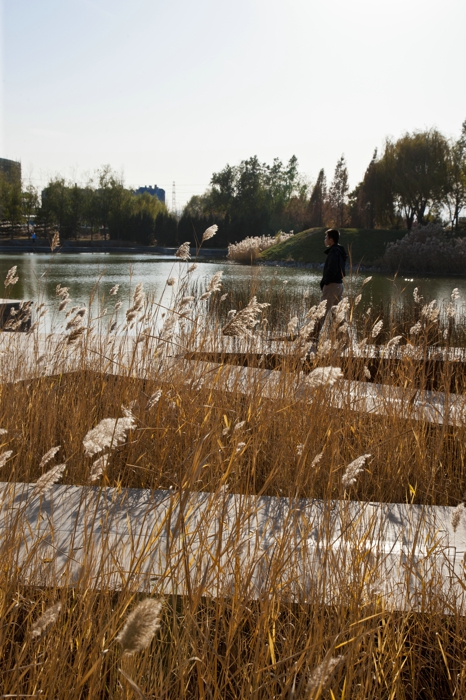
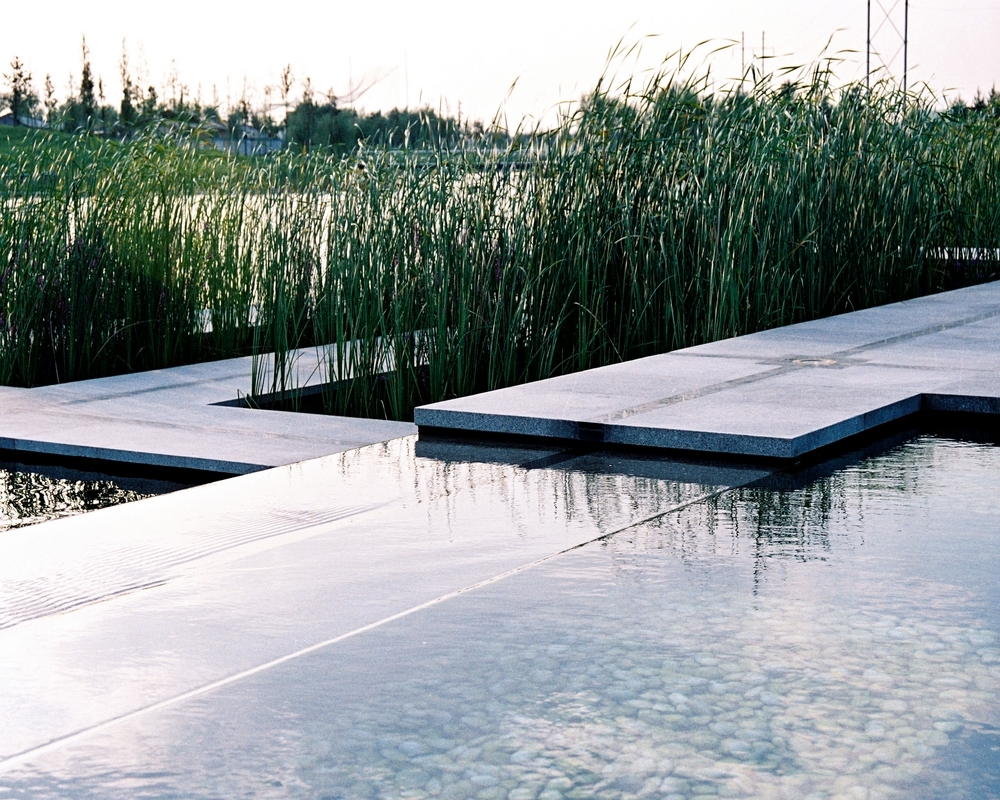
A soft pond edge was designed so that native plants can grow along it.
2.3 The Challenge of Accessibility
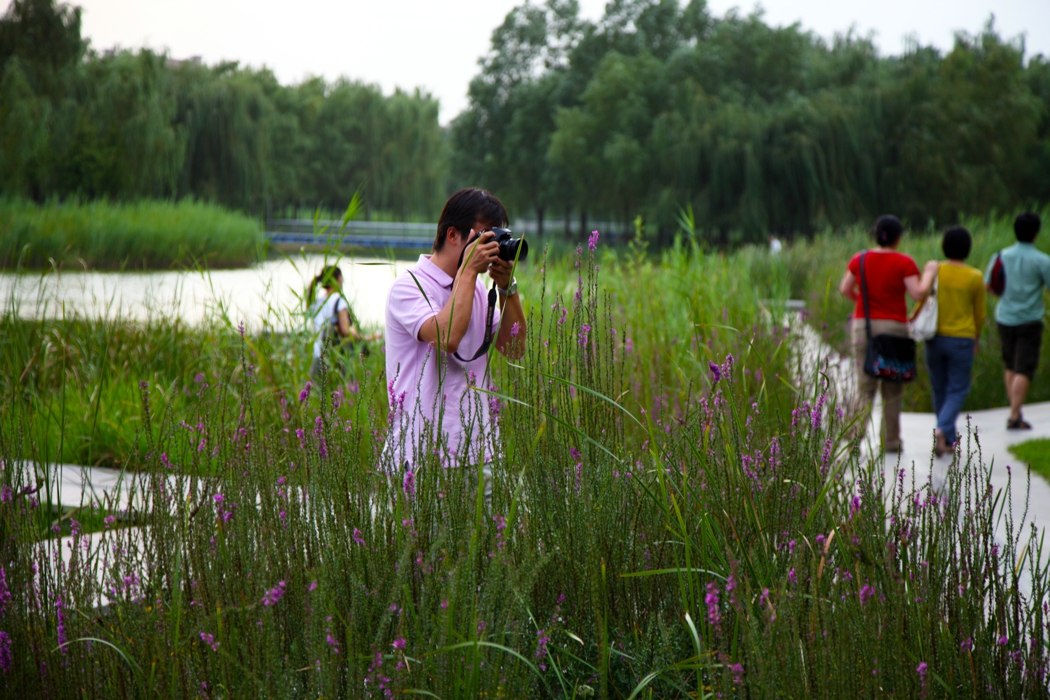
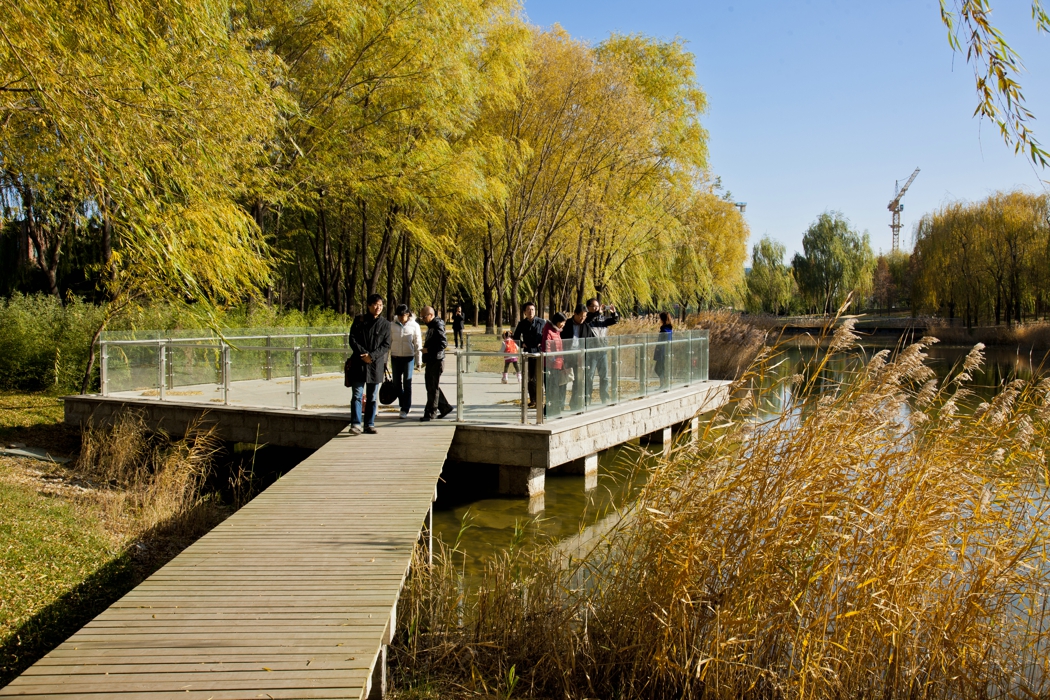
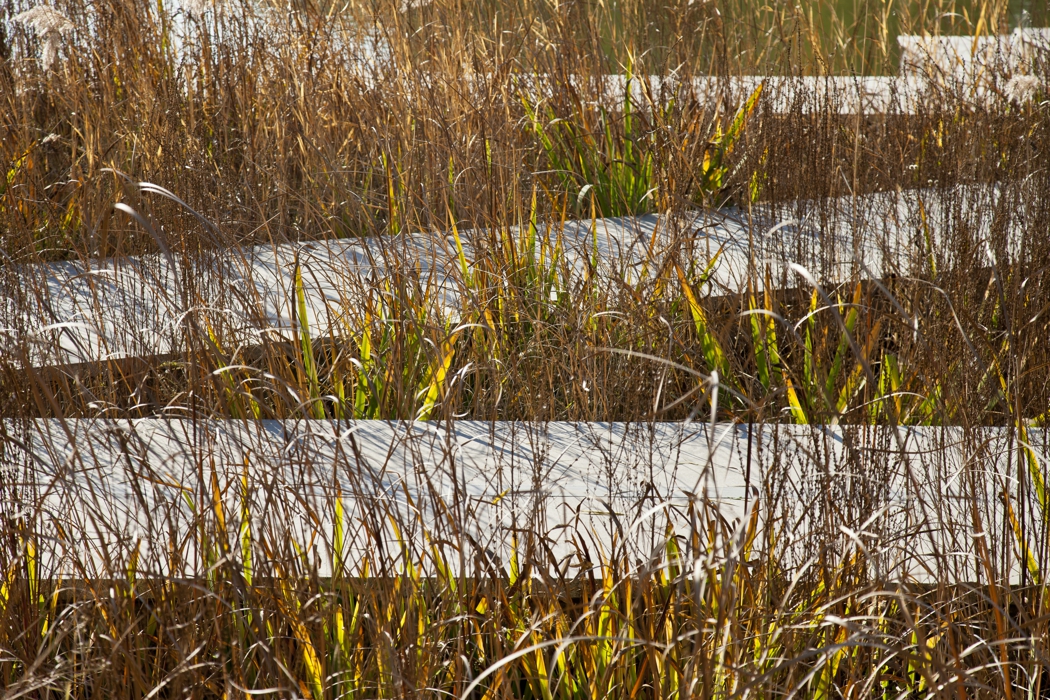
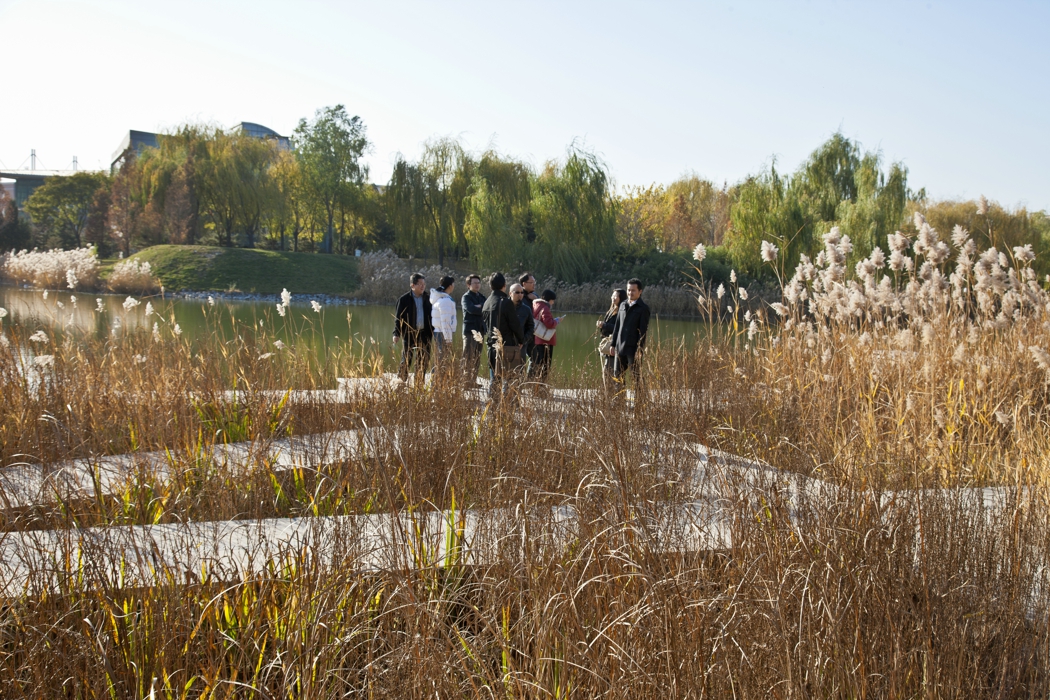
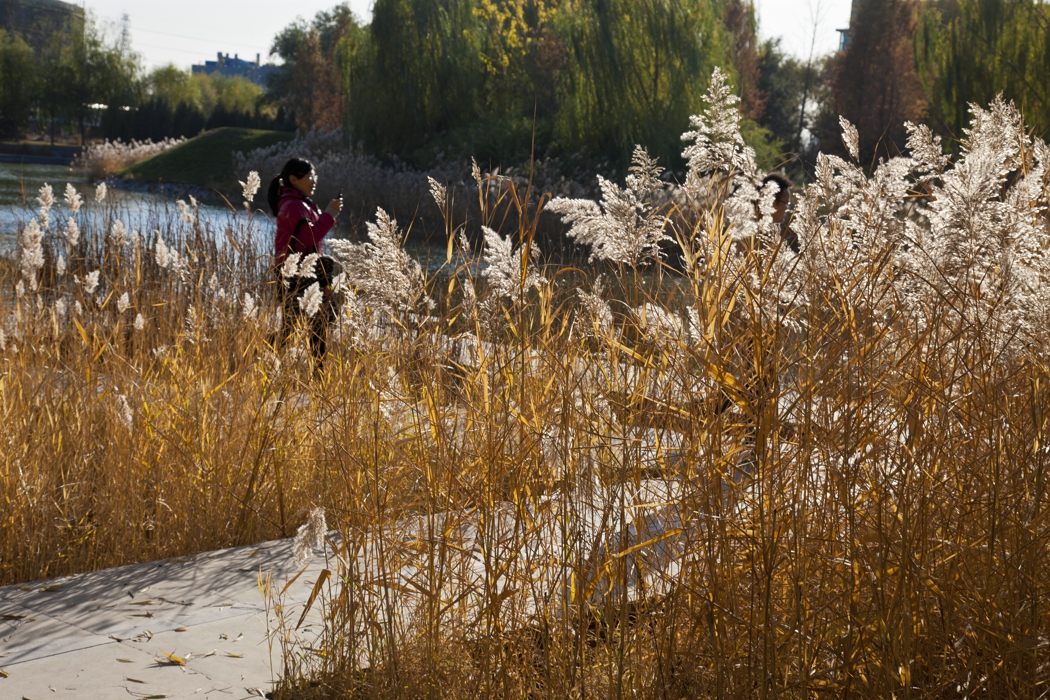
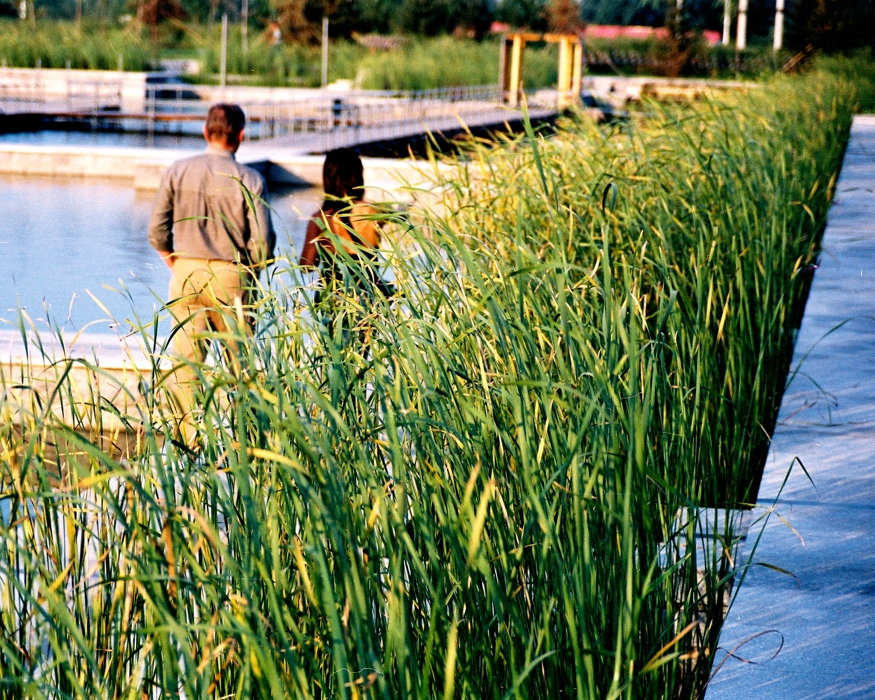
The campus was designed for 20 thousands of researchers and staffs, so the central park is expected to be intensively used in the summer time. It is therefore a great challenge to design a wetland and waterfront which is highly accessible yet allow diverse native plants grow along the water edge and in the wetland. The design solution was to integrate a grid of paths and the terraced wetland.
2.4 The Challenge of Ecology v.s Aesthetics
The park is a public space and it's one of the great challenges to make the ecologically oriented landscape beautiful. Diverse native plants species were selected and designed in community or pure population, so that their aesthetic value are visualized. These native plants include Typha, Scipus, Typha, Nuphar, Nymphoides and Phragnites.
3. Design Strategy
Cell is the basic unit of life, it is a highly effective metabolic system and has the capacity to self-propagate, and it also functions with other cells. Life science park should be the last living cell of the land and Zhongguancun area, which is a sustainable environment that cultivates a system for innovaton.
Four important features in this plan:
1) Environment
a sustainable wetland system. This wetland system is just like a living cell which has the cell fluid and cell materials, which nourished the innovation system in the park to grow.
The water source of the wetland is from 3 parts: 1 the runoff of the whole park; 2 the reclaimed sewage water, 3 if need, in some situation, Shangzhang reservoir will be a supplementary water source of the wetland.
While the wetland system has two components: the outer sewage water treatment wetland and the central landscape and recreational wetland. This wetland system is a self-regenerate , self-sustainable ecological matrix, which is the innovation source and origin of the employees in the park.
2) Functional groups
highly effective innovation unit. The functional building groups is just like the core of the cell and the connection part of the cells, which has a whole and perfect structure, highly effective operating and be rich in innovation capacity.
3) Fluent transportation networks
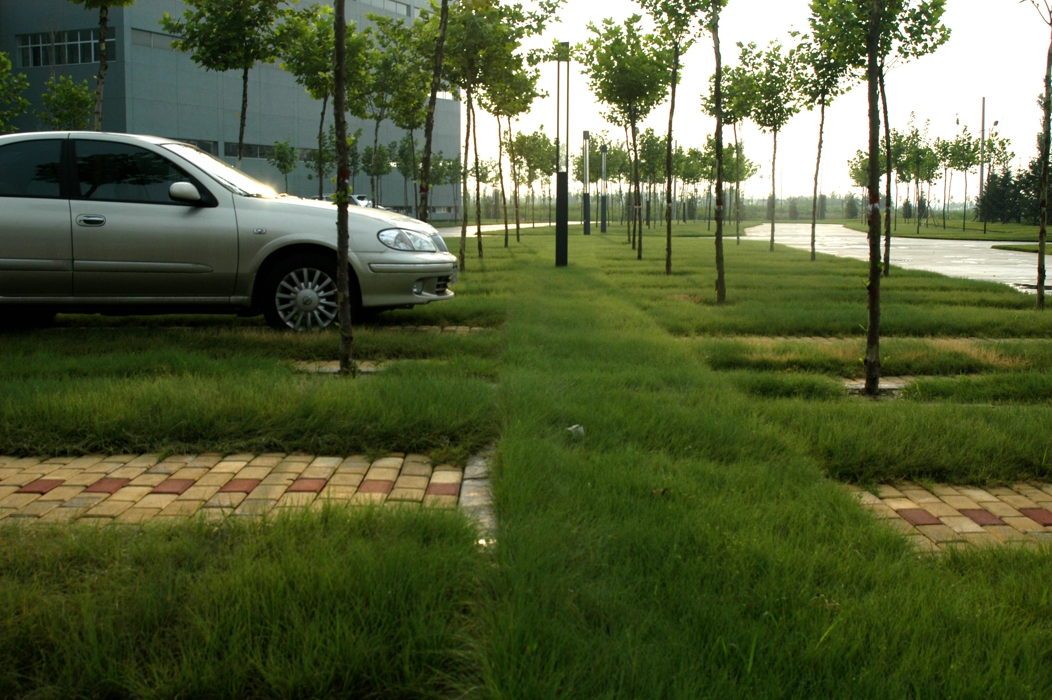
It is like the channel between cells which is used to transform information and materials. The transportation network of the life science park includes the following 5 components: motor vehicles transportation and parking lots, people, cargo transportation, water, and information.
4) Edge, the interface connect the inner part and the outside, which is like the cell membrane
The edge is boundary of the park and the outside, boundary of different functional groups, and boundary along the inner ring road.