Landscape Acupuncture: Transforming a Working Landscape, Qinhuangdao Forest Park-II
2013-04-07
Share
Project Information
- Project Location:
- China Qinhuangdao, Hebei Province, China
- Project Scale:
- 233 Ha
- Design Time:
- 2010-9-
- Build Time:
- 2011-6-
Project Profile
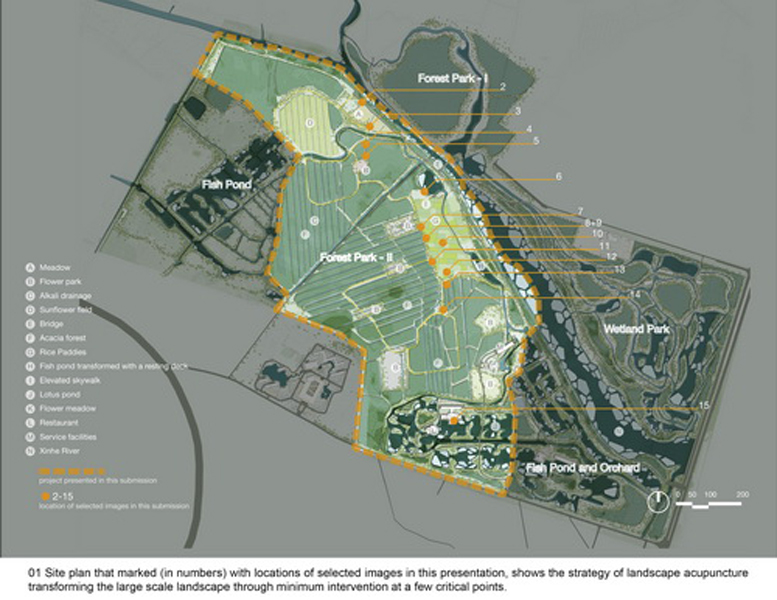
1 Project StatementTaking a minimal intervention and "landscape acupuncture" strategy, some abandoned farm lands and fish ponds with an ordinary tree plantation started in 1950s, serving as a windbreak, have been transformed into a lively urban park, which provide multiple ecosystem services including food production, serving as a habitat for a diverse flora and fauna and providing recreational and aesthetically pleasant experiences for visitors.
2 Project Narratives
2.1 Objectives and Challenges
The Qinhuangdao Forest Park-II, about 100 hectares (247 acres) in size, is part of the larger Beidaihe National Forest Park (1000 hectares, or 2470 acres in size). It is on the west coast of the Bohai Sea, and is located between two densely populated districts of Qinhuangdao, a renowned coastal destination for tourists in northern China. The whole area was afforested in 1950s to form a windbreak, transforming coastal sand dunes into a green wedge for the city that also protected the coastal land and railway from erosion caused by the sea. It was a boring tree plantation dominated by fast growing wood species, mainly poplar (Populus tomentosa and Populus canadensis) and black locust (Robinia pseudoacacia). Dotting the Forest Park are fish ponds and rice paddies, most of which have been abandoned since this area was designated as a national forest park in 1993.
The objective of the project was to transform the over-matured and monotonous windbreak forest into a scenic urban park, providing recreational and aesthetic experiences for the local residents. Further, the fishponds and agricultural land were to be made into functional public spaces. The windbreak plantation was to become accessible and interesting so that it can be approachable and enjoyed by visitors.
The challenges of the site include: (1) How to enrich and rejuvenate the monotonous and over-matured forest plantation so that its scenic value and ecological diversity can be improved; (2) How to transform the agricultural land and fish ponds into functional public spaces; (3) How to make the windbreak accessible and attractive so that it can be approachable by visitors; (4) How to transform a landscape at such a large scale within a limited budget and timeline.
2.2 Design Strategy
The key approach is “Landscape Acupuncture” called by landscape architects: the identification of some critical points and positions and minimal interventions taken to dramatically change the landscape. These interventions comprised four measures as follows:
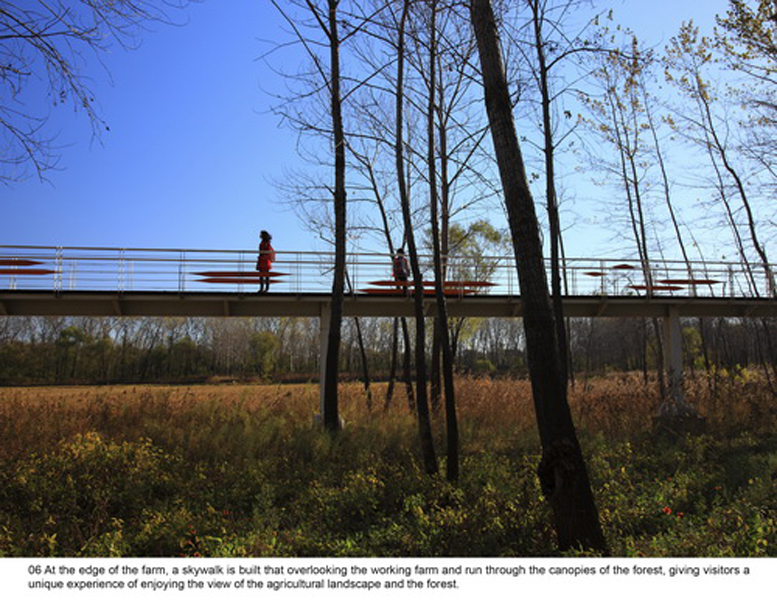
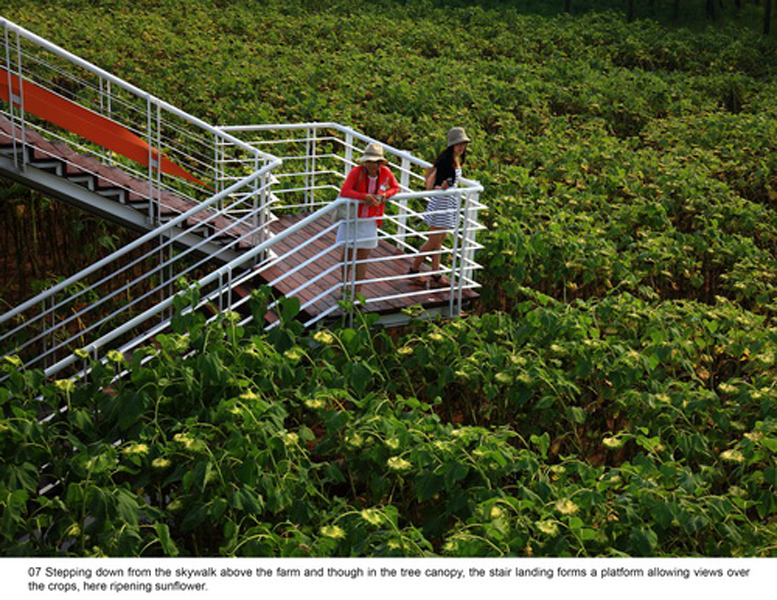
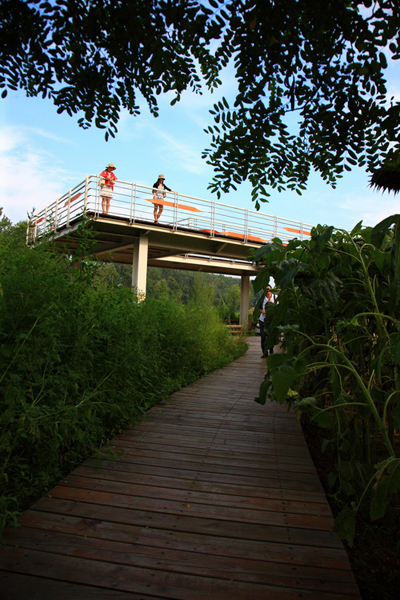
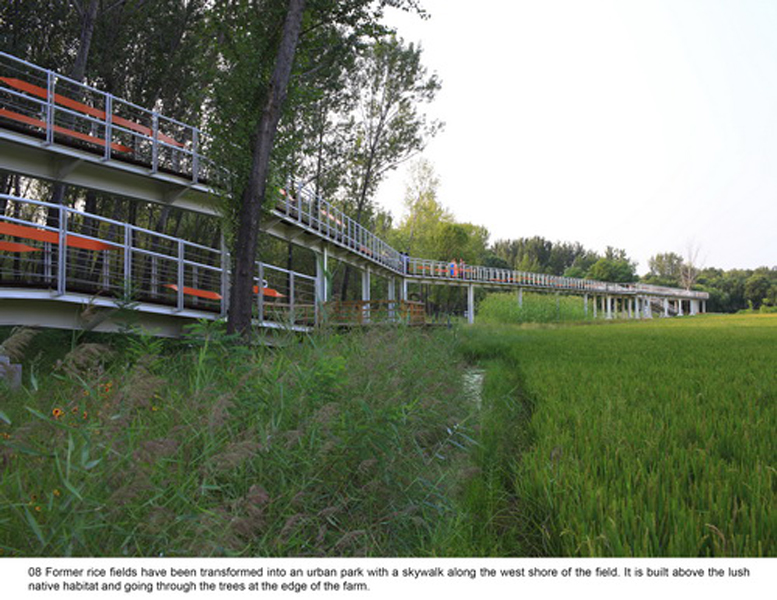
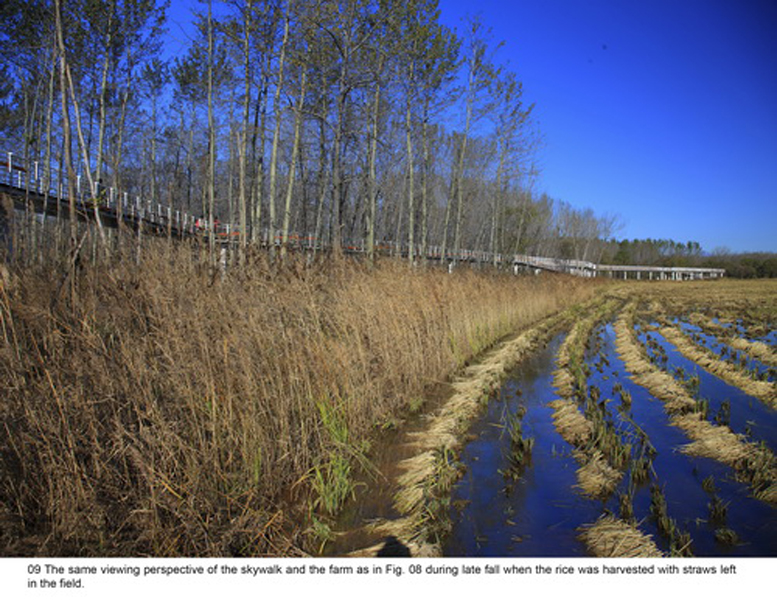
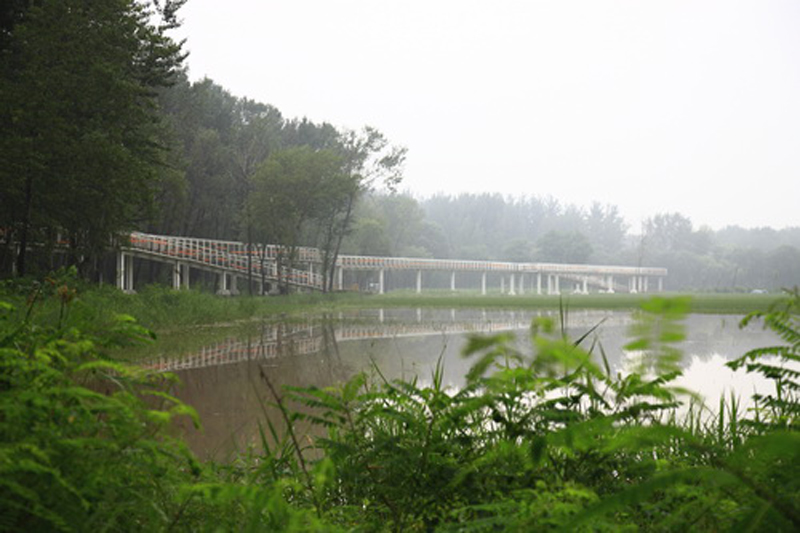
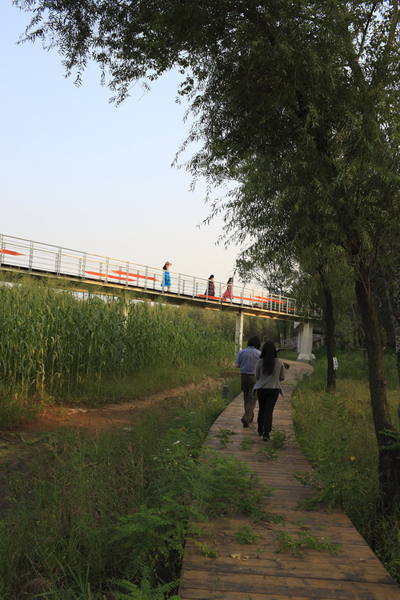
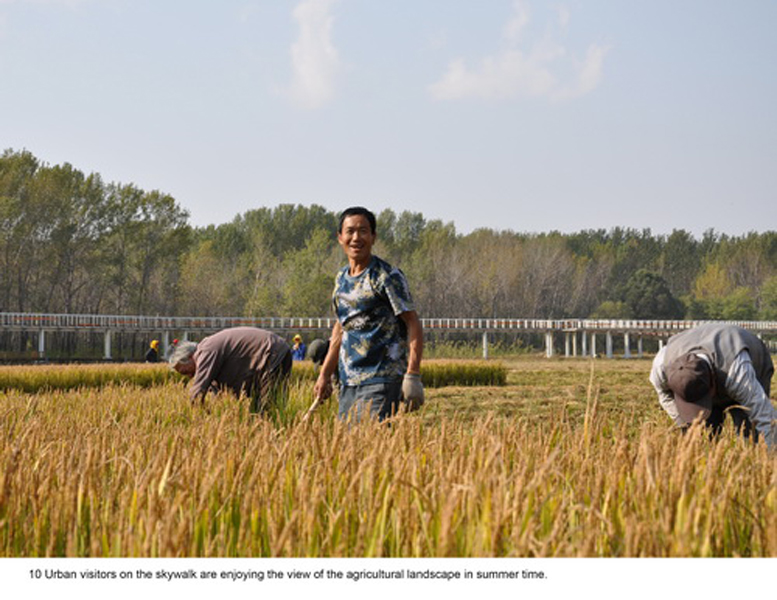
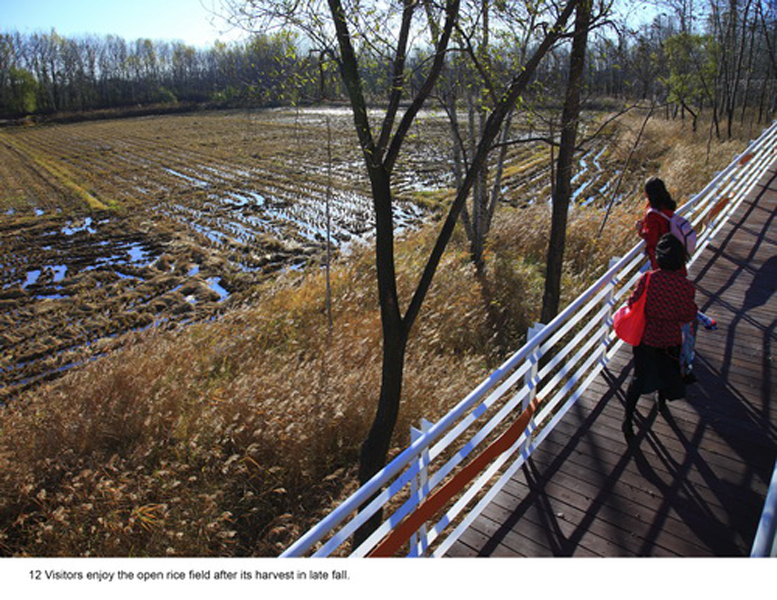
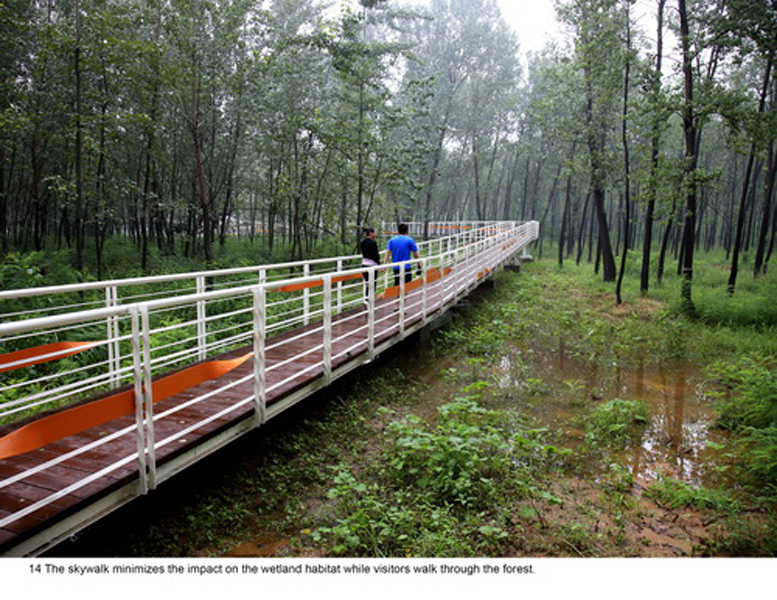
(1) The existing farm (growing rice, wheat and other crops) of 5 hectares was transformed into an urban farm, which would involve local communities in the production process. A skywalk and boardwalk is built on the edge of the farm allowing visitors to enjoy the scenic farmland and observe the working landscape in every season.
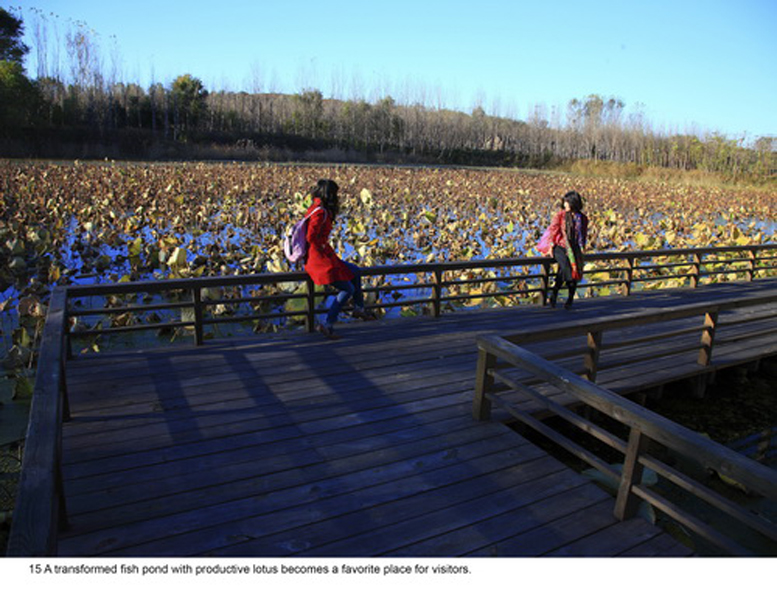
(2) The abandoned fishponds were used for the construction of wetlands, which would catch stormwater and enrich biodiversity in the park. Lotuses and various wetland plants were grown to create a beautiful landscape, as well as productive. Some fishponds were made more accessible by boardwalks and platforms, providing opportunities for sports and fishing in the park.
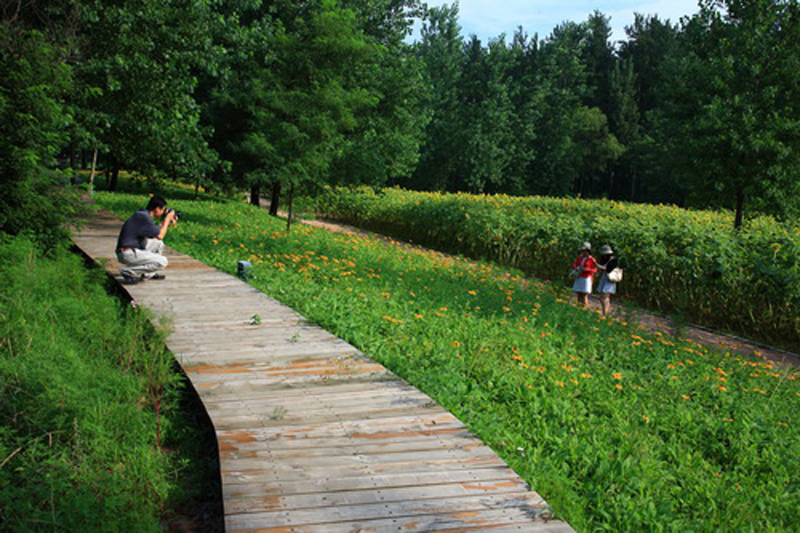
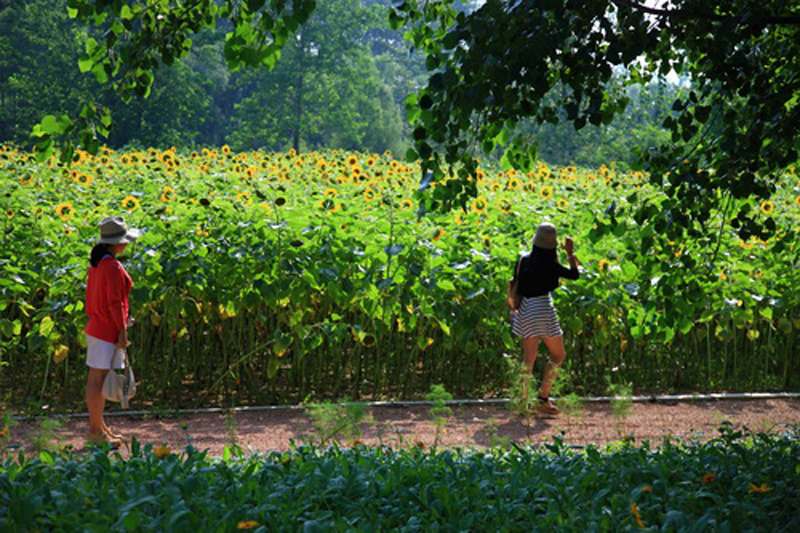
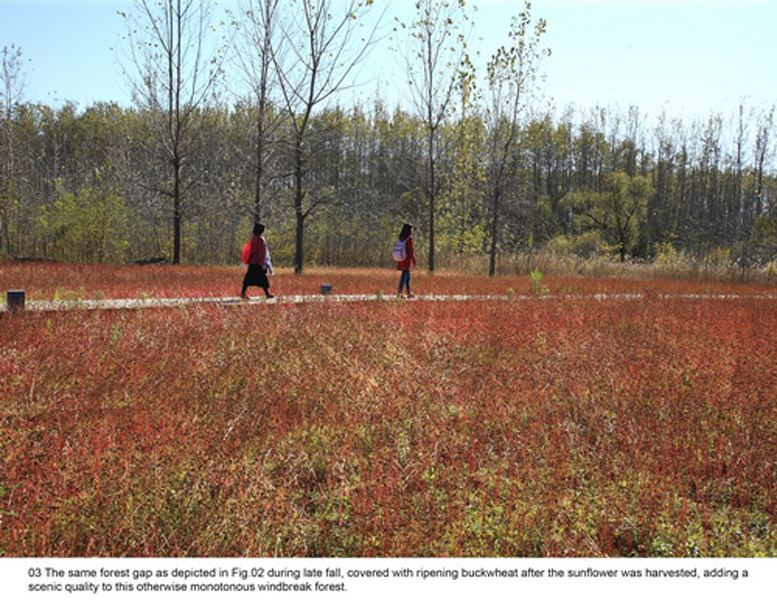
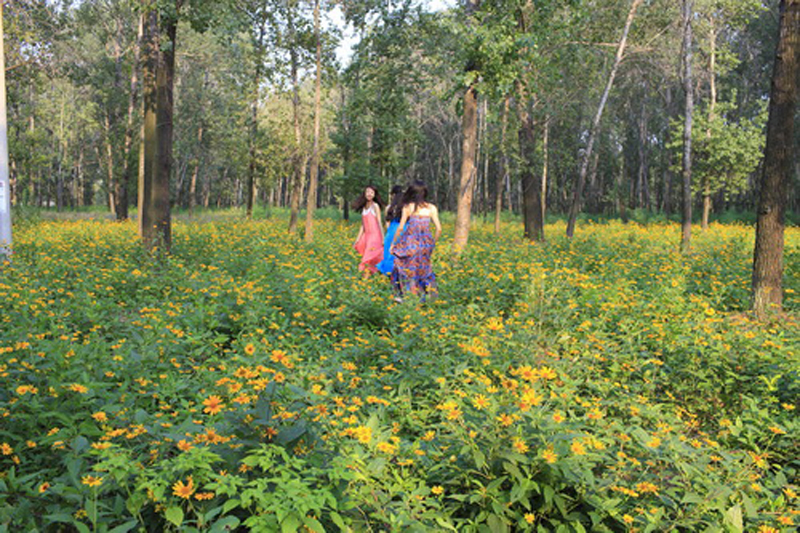
(3) Covering forest gaps with flowers and crops: The forest gaps were coveredby self-reproductive perennial flowers and productive crops grown in seasonal rotation, such as sun flowers in summer and buckwheat in fall and Winter, allow visitors have an enriched experience in the forest.
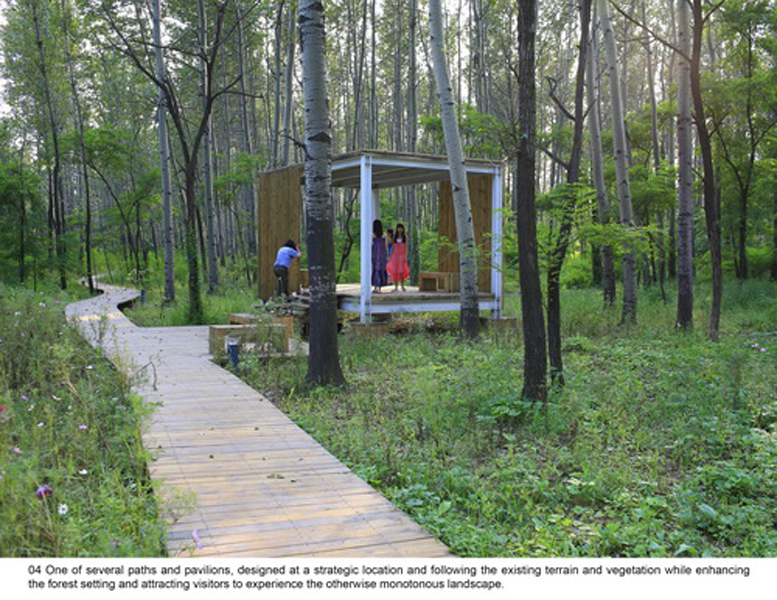
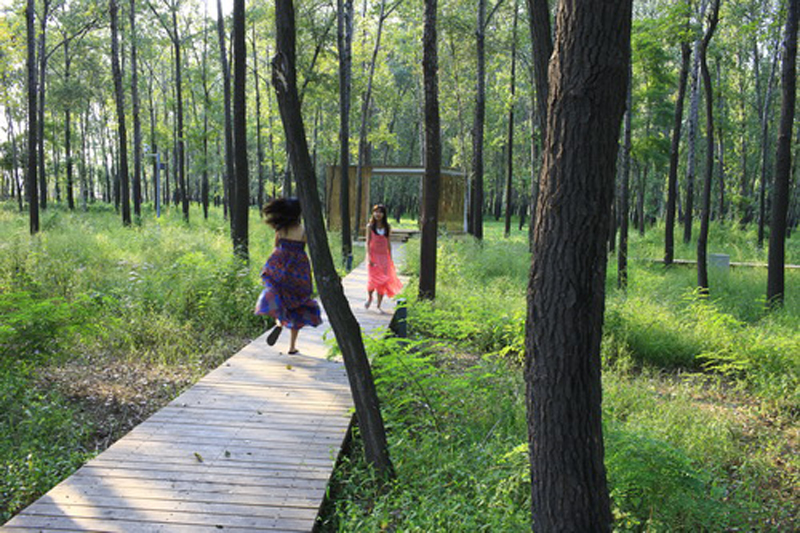
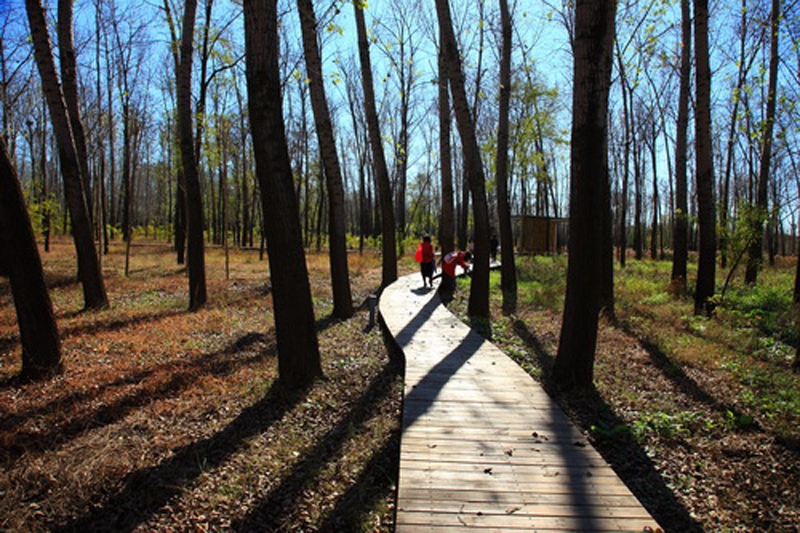
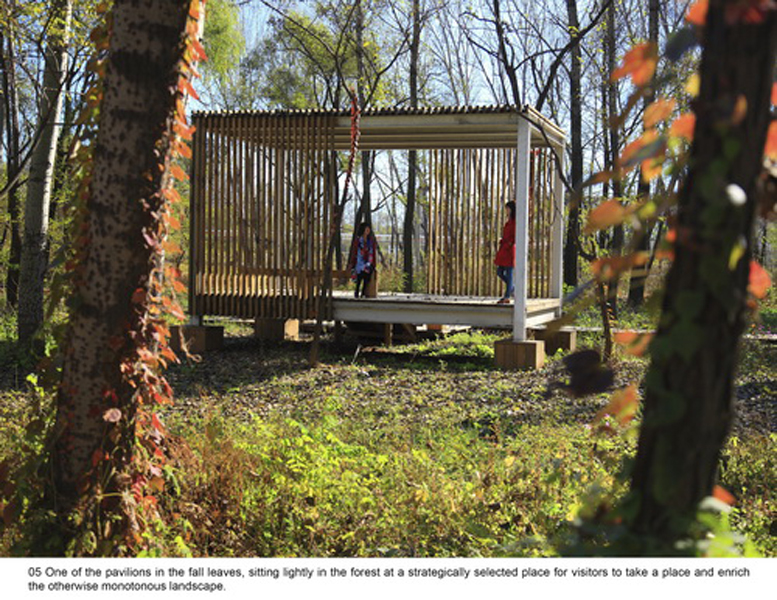
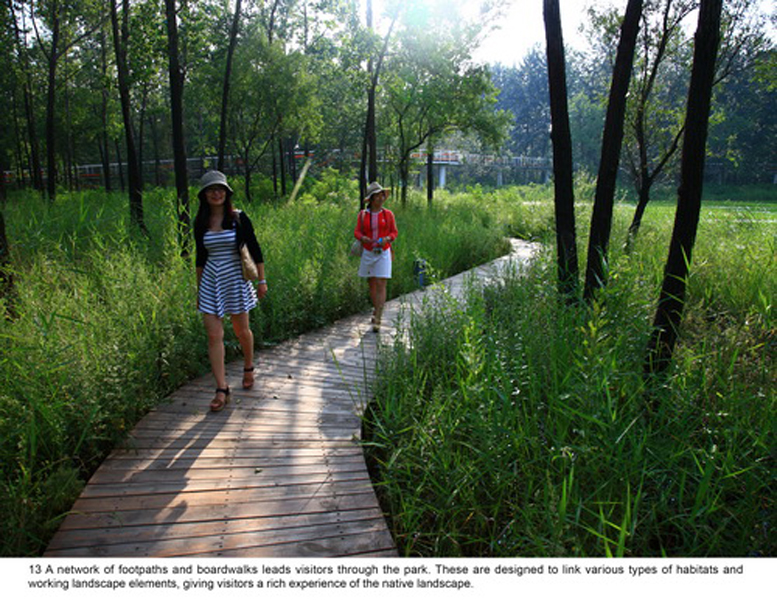
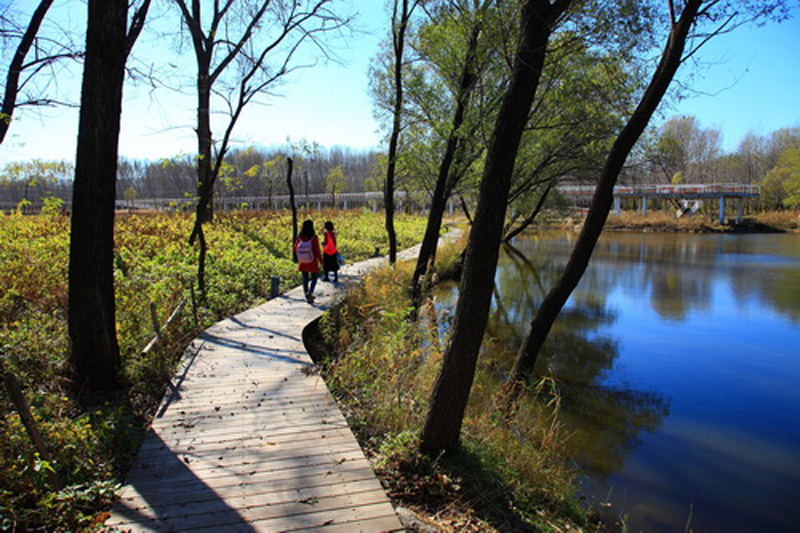
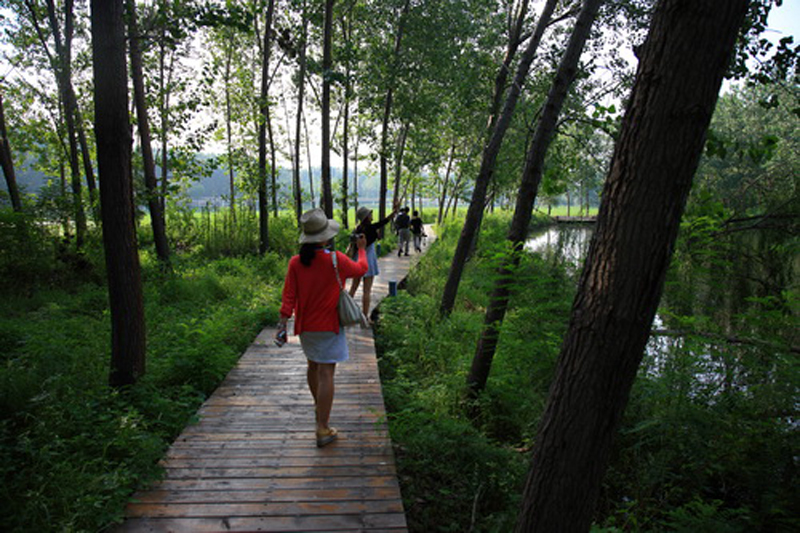
(4) A network of experience route: A network of footpaths and boardwalks leads visitors through the park. These are designed to link various types of habitats, giving visitors a rich experience of the landscape. Pavilions and platforms at strategic locations give the park identity and points of orientation.
By these ‘landscape acupuncture’ elements and minimum intervention, the former monotonous windbreak forest and abandoned farm have been successfully transformed into a productive and low maintenance landscape that functions as an urban park and urban farm, providing multiple ecosystems services, and attract visitors, as well as local residents who can enjoy working in the park as a community gathering place.
Plant list
Rice (Oryza sativa)
Sunflower (Helianthus annuus)
Buckwheat (Fagopyrum esculentum)
Chinese Lotus (Nelumbo nucifera)
Reeds (Phragmites australis)
Black-eyed Susan (Rudbeckia hirta)
Poplar (Populus tomentosa and Populus canadensis)
Black Locust (Robinia pseudoacacia)