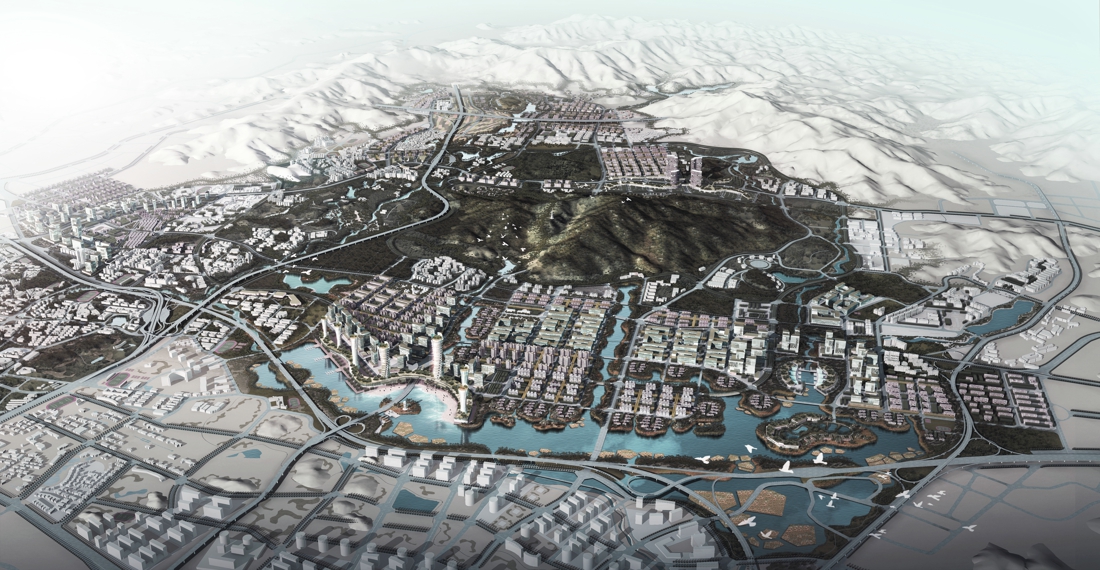
Guangzhou Tianhe Smart City Daguan Wetland
Project Information
- Project Location:
- China Guangzhou, Guangdong
- Project Scale:
- 46.8 Hectares
- Design Time:
- September 2012
- Build Time:
- June 2015
- Client:
- Management Committee of Tianhe Science and Technology Park, Guangzhou High-tech Industrial Development Zone
- Related Papers
Project Profile
1. Project Statement
The project adopts the theory of "sponge city" to restore the damaged ecosystem in the site, especially the wetland system, and applies low-impact development technology to design the site as an urban stormwater wetland corridor. The design effectively alleviates surrounding urban inundation, improves over-ground water quality, restores the stormwater management and ecological self-purification functions of the green space.
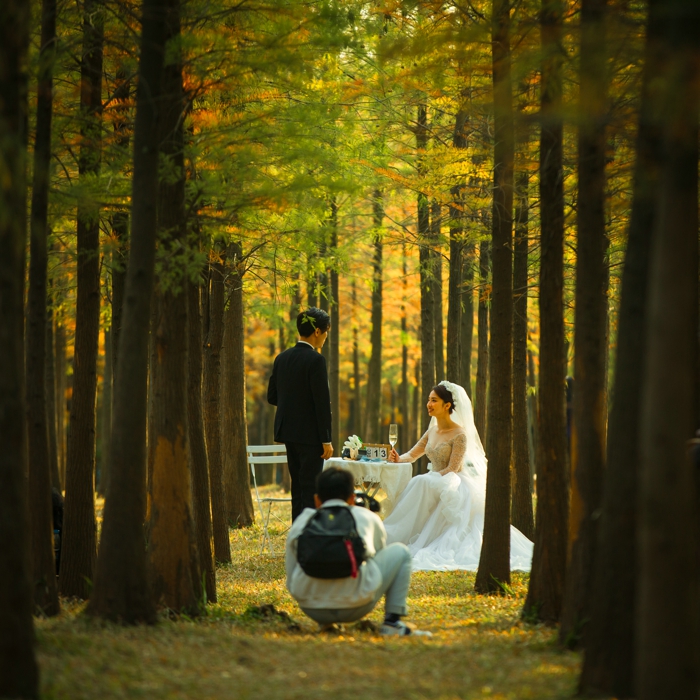
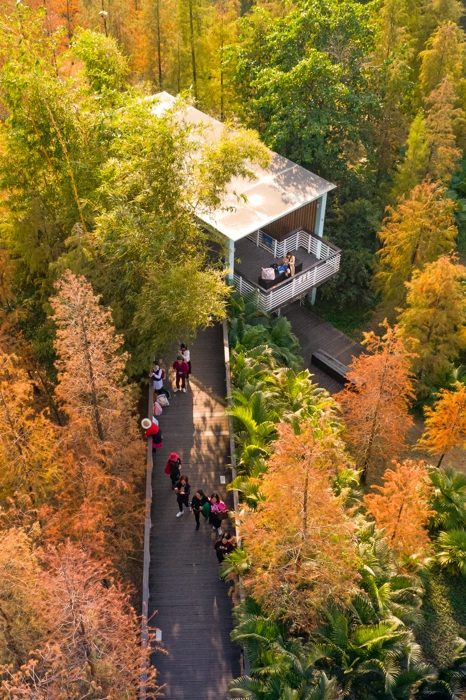
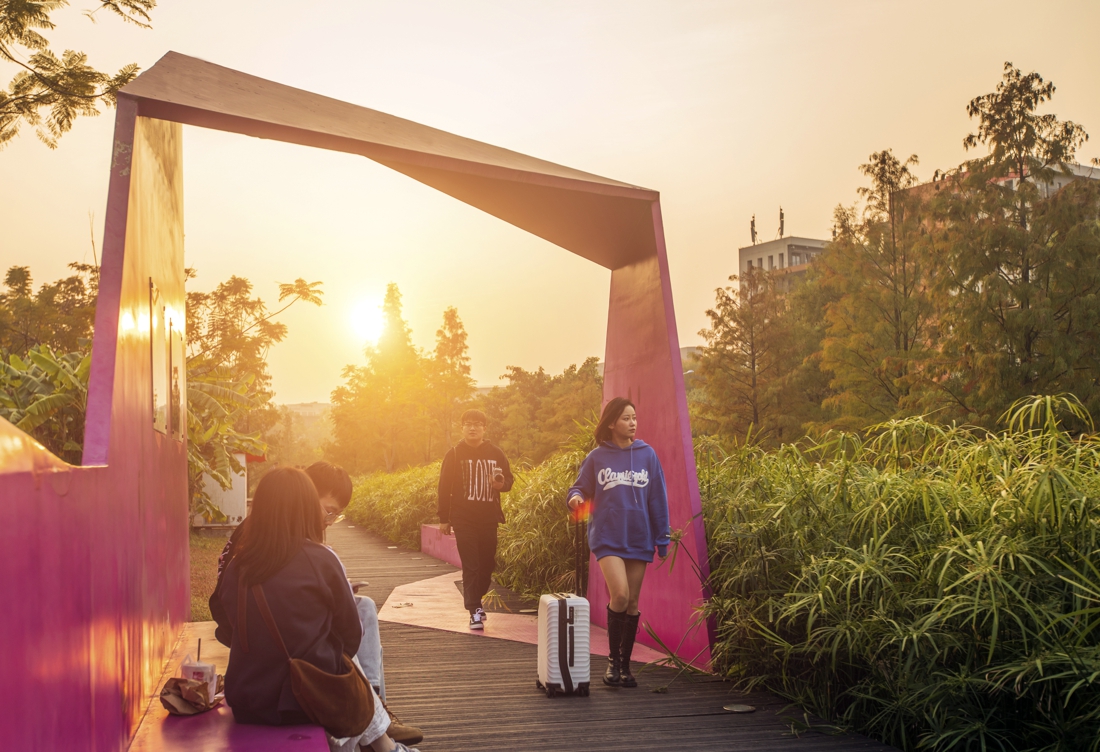
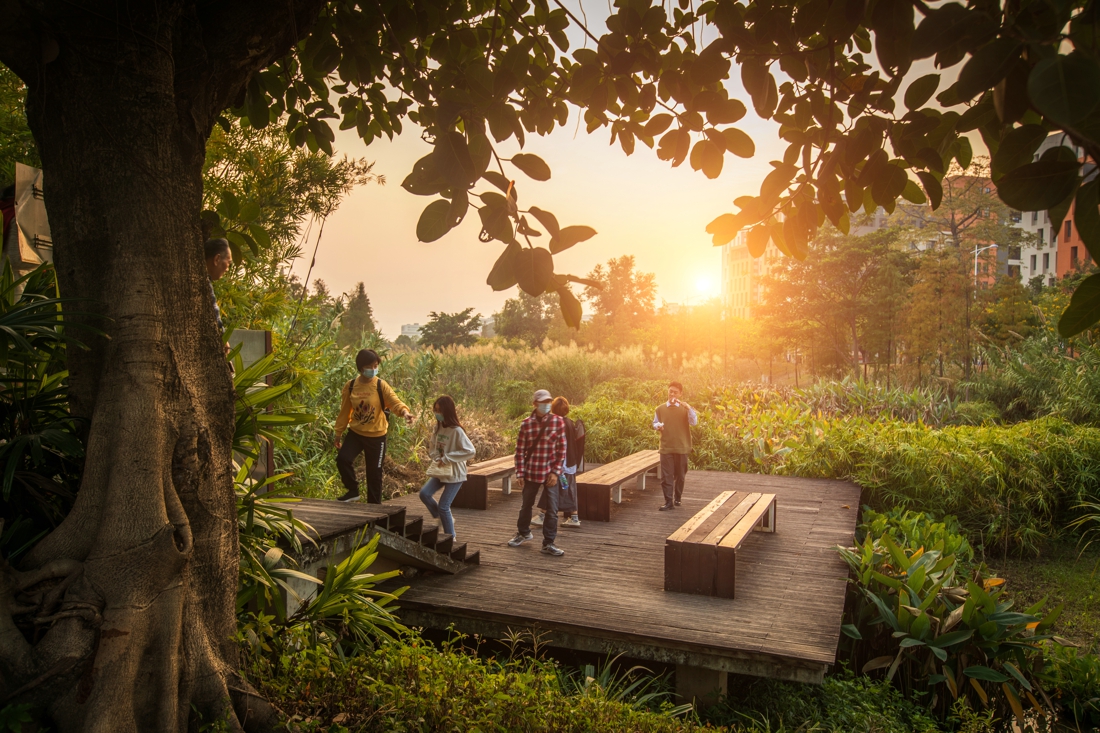
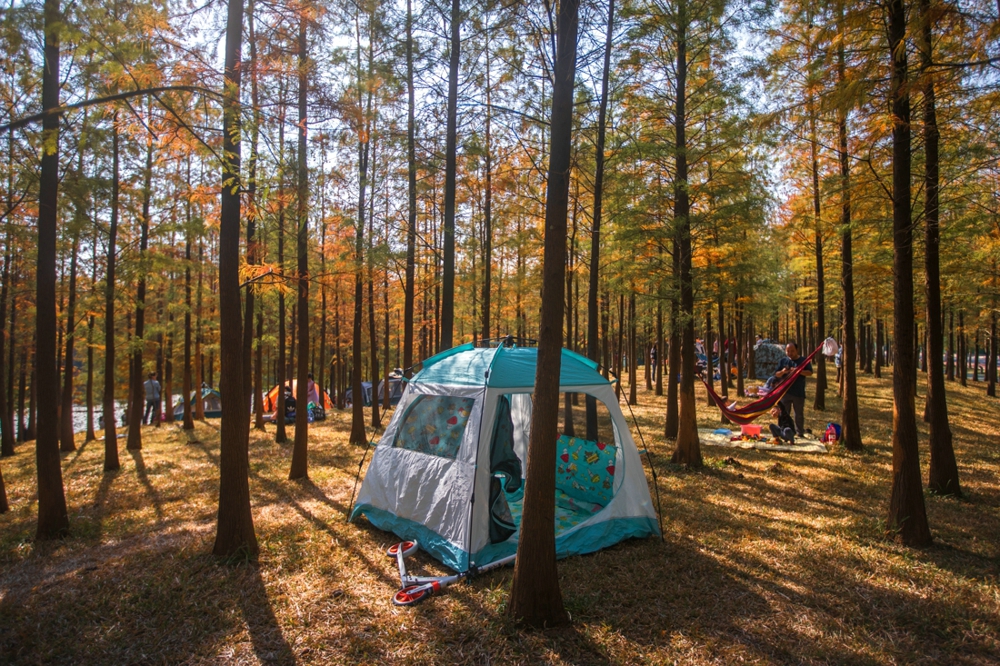
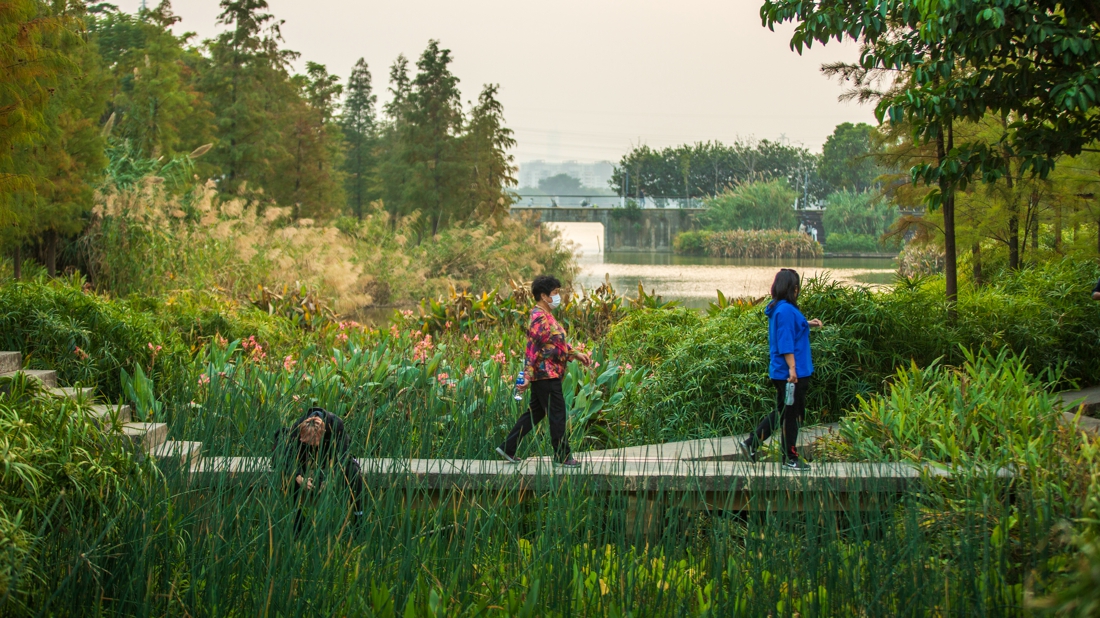
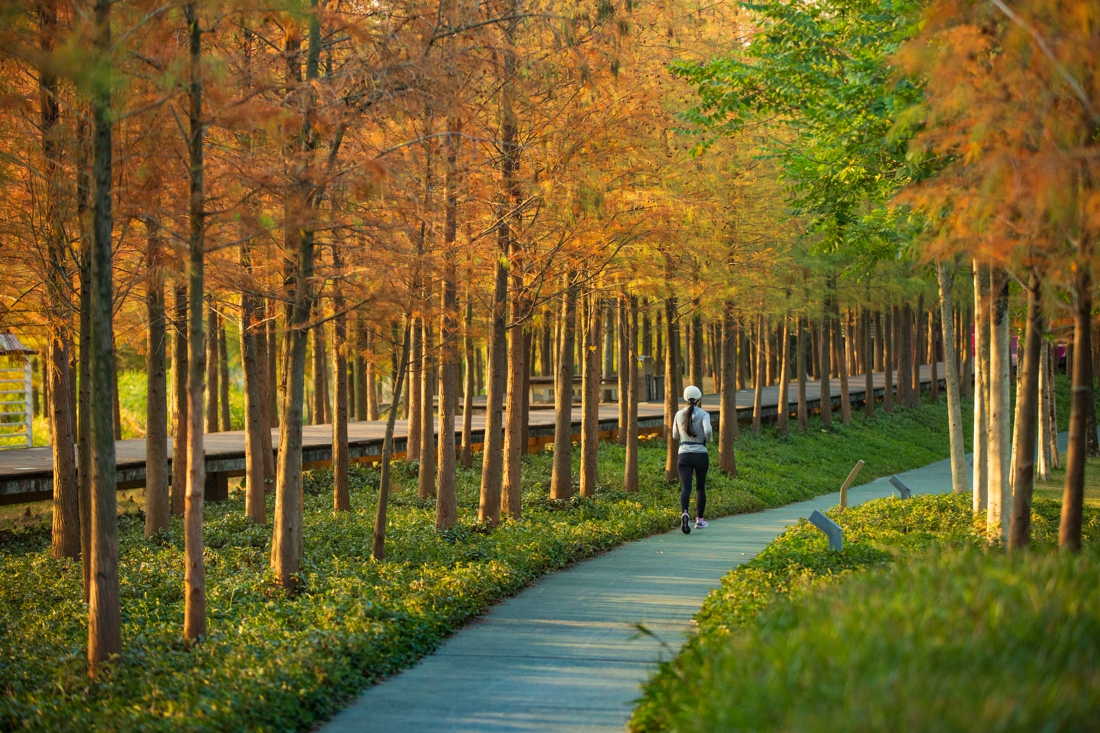
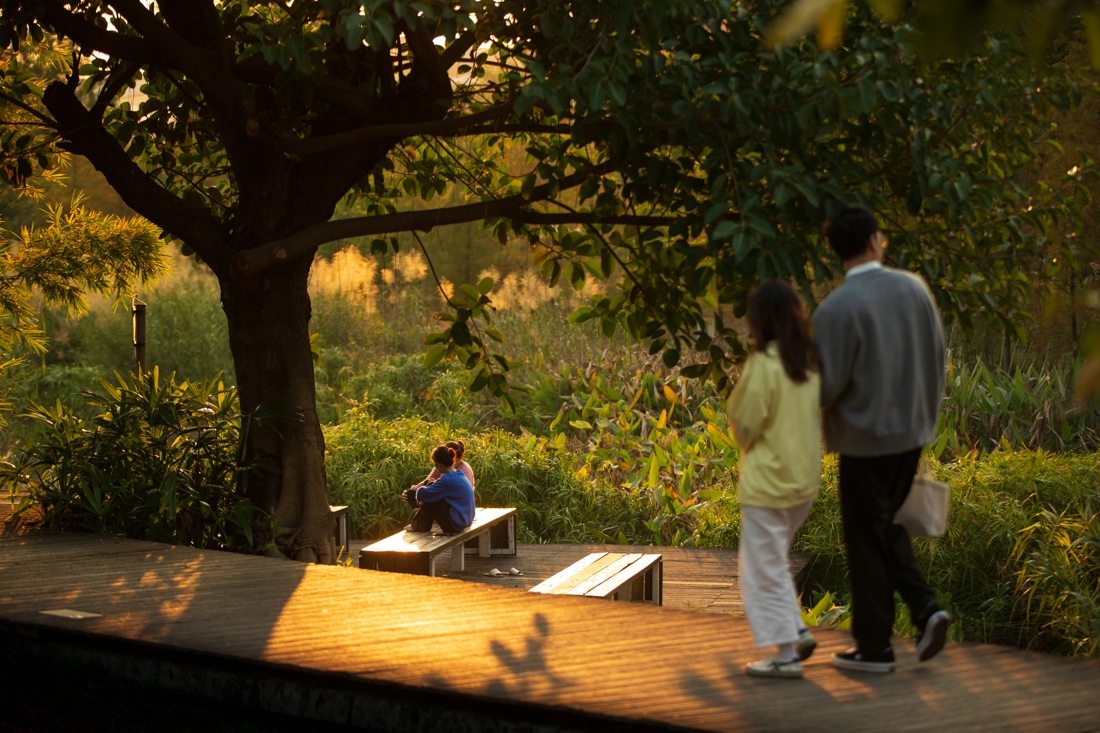
The project also provides an urban public open space that can be used for recreation, study and outdoor exercise, which makes it a piece of valuable urban ecological infrastructure with comprehensive function.
2. Objective and Challenge
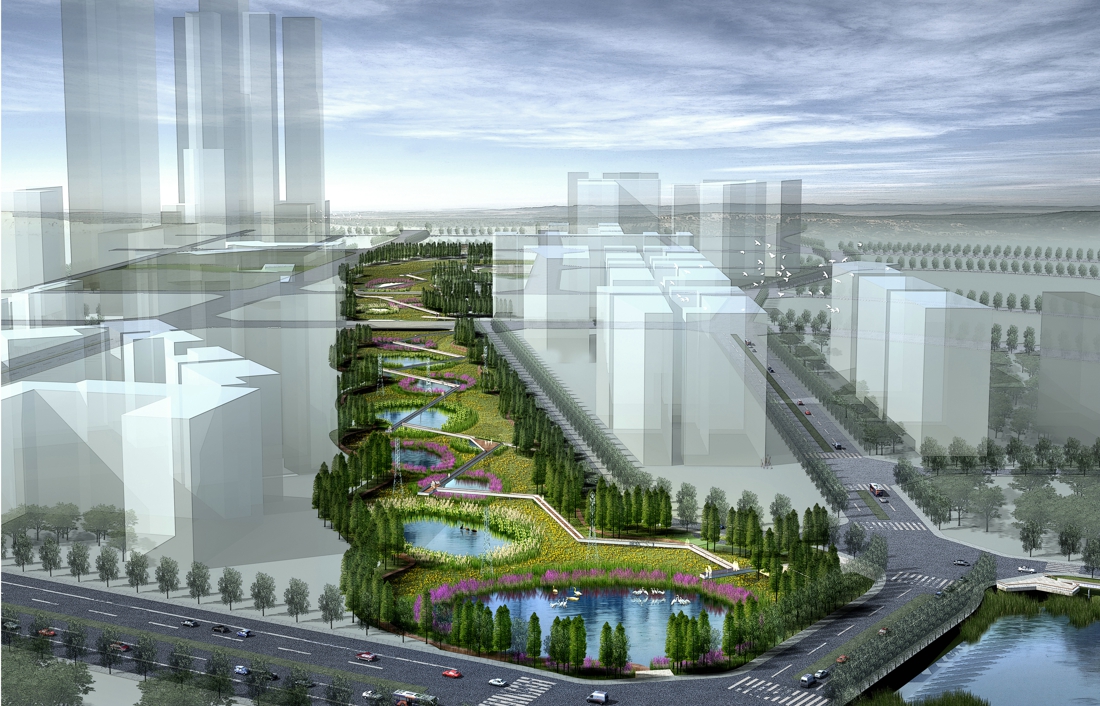
The project is located in the Tianhe Smart City of Guangzhou, a landmark landscape node in the Tianhe Smart Water Corridor, covering an area of approximately 46.8 hectares. It was mainly farmland and fish ponds, except for the Xintang Reservoir,
The first challenge of the project is to deal with the natural climate in Guangzhou. Guangzhou has a high annual rainfall and frequent torrential rains, which can easily cause flooding and inland inundation. The site is identified as an important catchment in the area through GIS runoff analysis, with Xintang Reservoir in the middle and Yangmei River at the end. How to restore the floodplain its natural storage function and ease the flood control pressure of Yangmei River is the key problem that the design must solve.
The second challenge is to improve the local water quality. River pollution in the Tianhe area is relatively serious, and the water quality of many rivers such as the Yangmei River is below Grade IV. As part of the smart water corridor, the project cleans up the pollution from its sources and contributes to the improvement of the overall water environment.
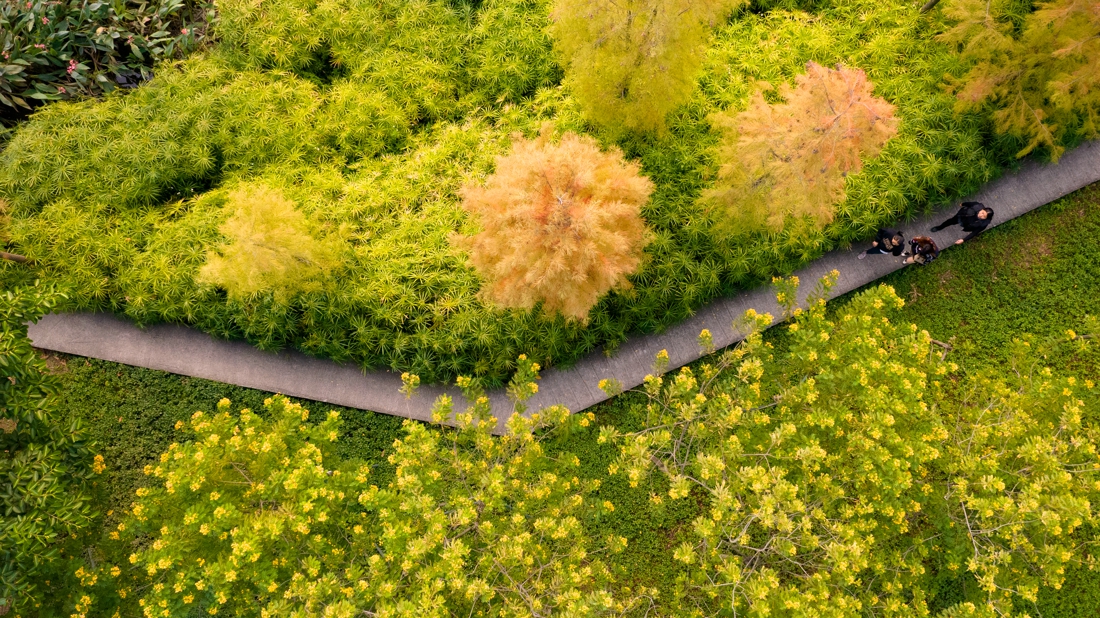
The third challenge is to create a water-adaptable plant community. The selection of plants must first adapt to the alternating drought and flood conditions on the site. The water level fluctuates greatly during the rainy and dry seasons. The plants must be both wet and drought-tolerant.
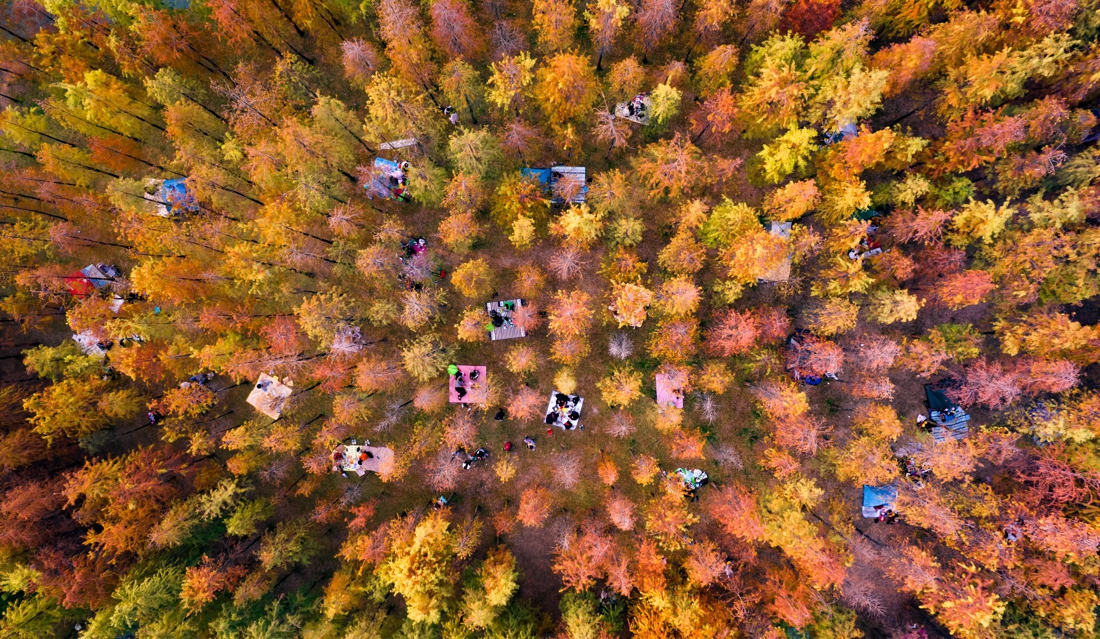
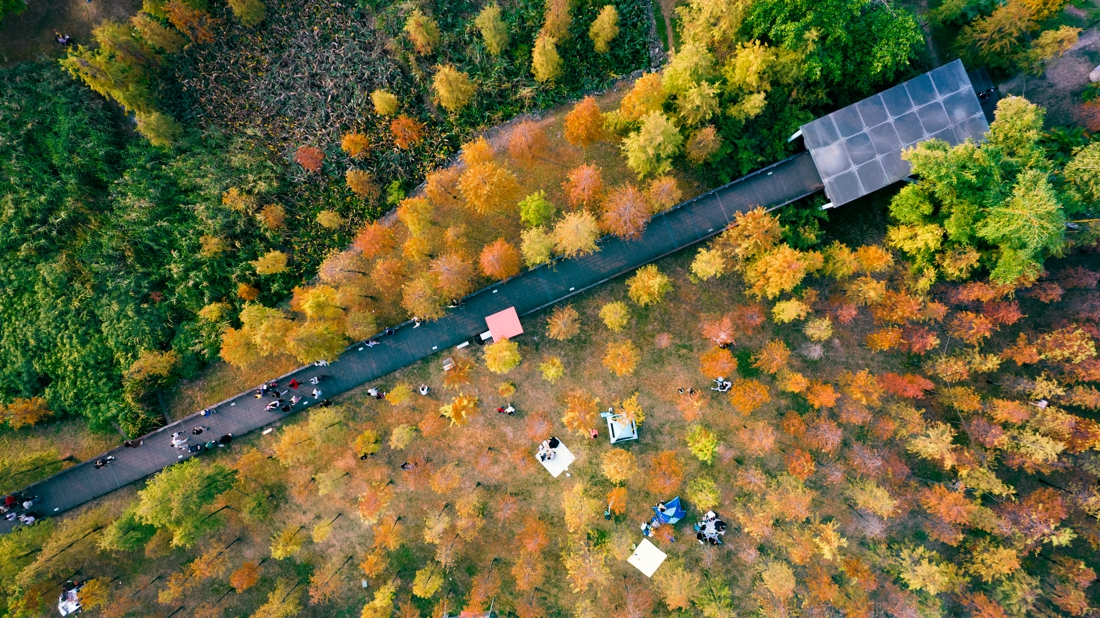
The fourth challenge is to provide an open space that meets the leisure needs of the surrounding residents. While the site exerts its ecological benefits, it should also take into account the needs of people. The surrounding area is mainly offices but a residential area is in plan, which means the demand for open space will gradually increase.
3. Design Strategy
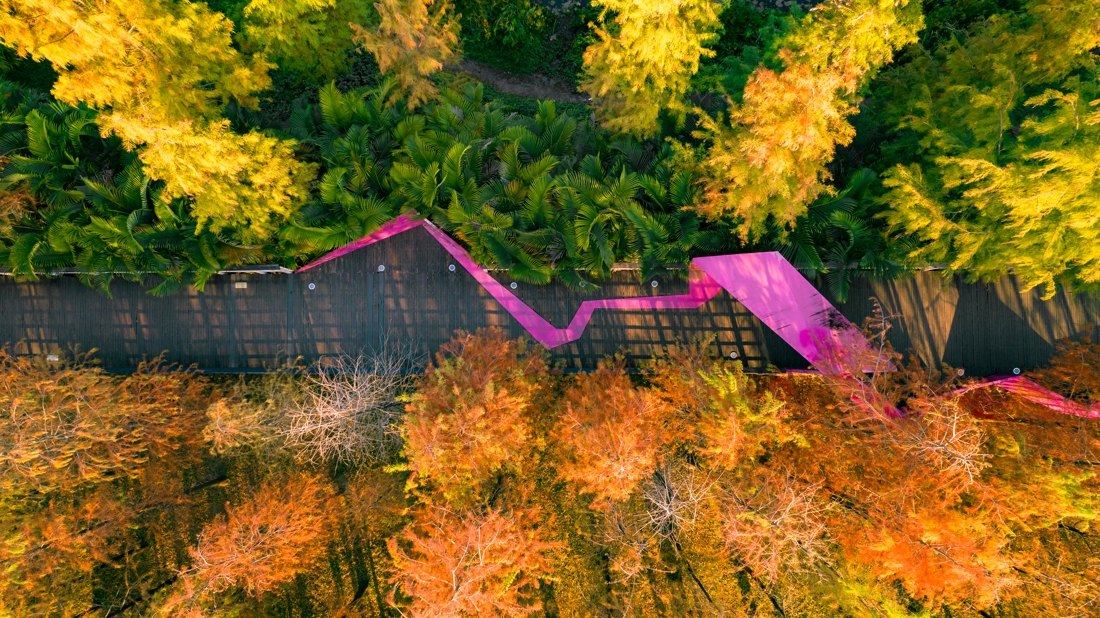
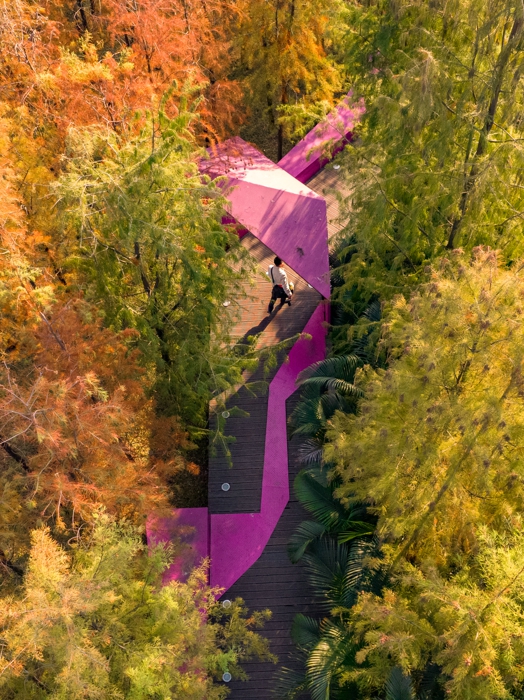
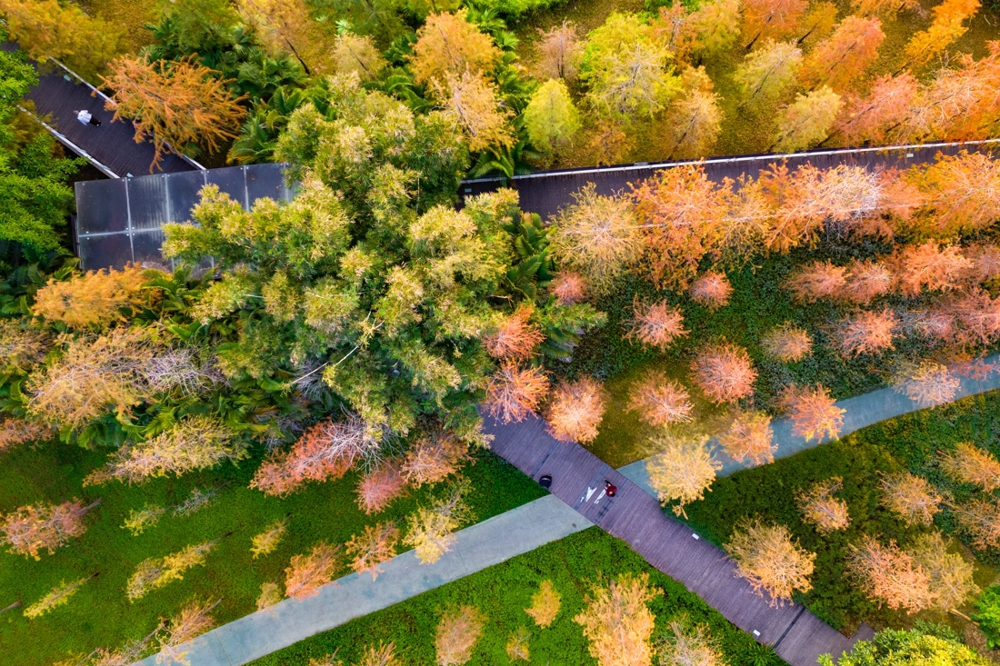
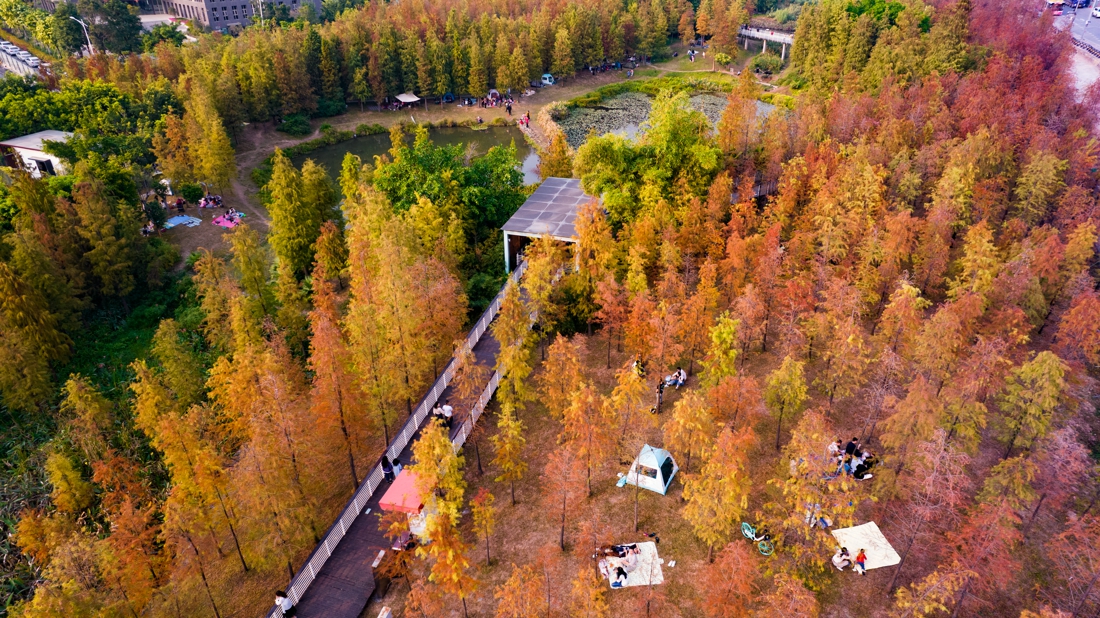
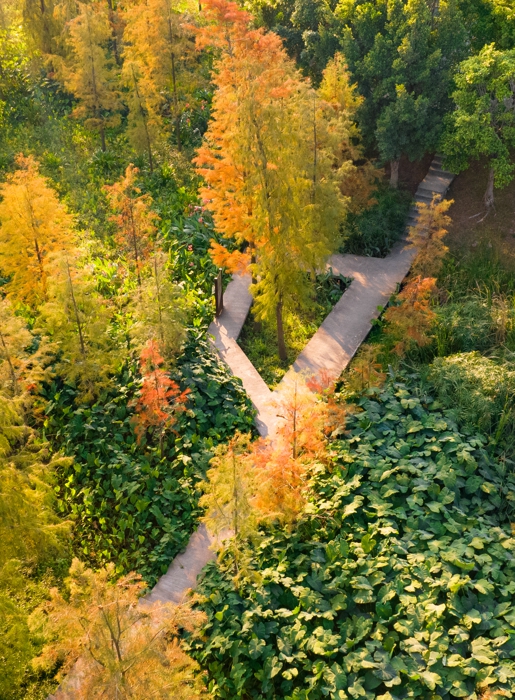
The overall design strategy is to: Continue the texture of the pond and digging in the center of the site to form a “wetland bubble”; the excavated earth is piled on both banks of the river to increase the height difference between the top of the bank and the river to form a valley. The trail along the water bubble is arranged with pavilions and waterfront platforms to form a continuous walking system; squares and playgrounds are arranged at important landscape nodes to improve the function of the venue.
The overall spatial structure of the site can be summarized as "one core and two wings", in which "one core" refers to the Xintang Reservoir, and "two wings" are the two valleys upstream and downstream of the Xintang Reservoir.
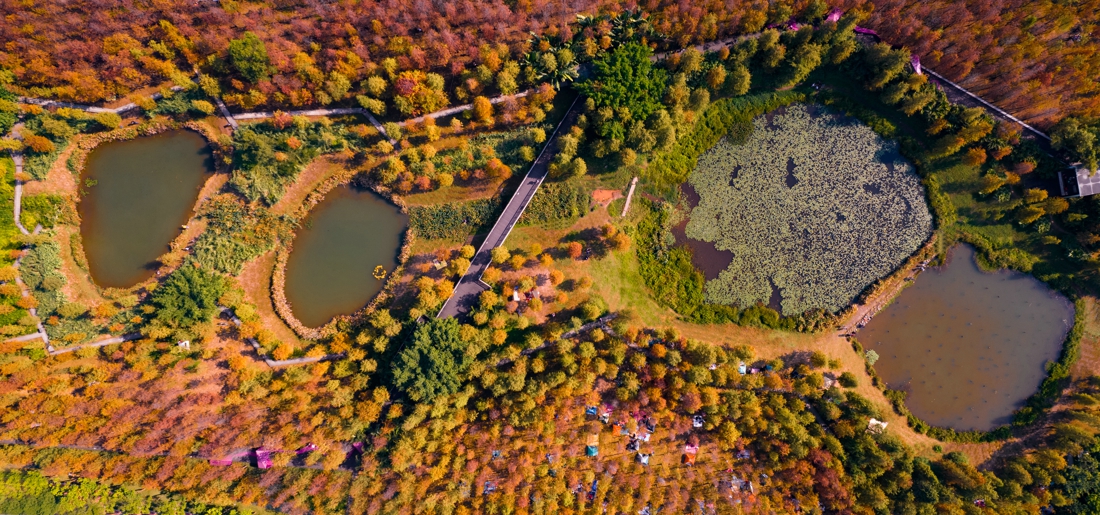
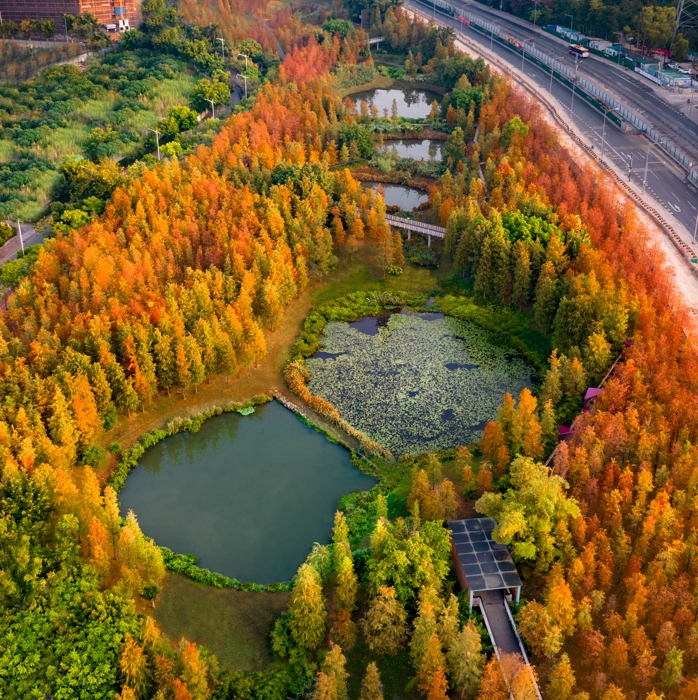
The site is divided into three main areas, the upstream Baihua Valley area, with artificial wetland purification landscape and sports infrastructure as the main features; the middle reaches of the Xintang Reservoir sightseeing area, featuring a wide lake and a bicycle path around the lake; the downstream ecological valley area, which features artificial wetland landscape and wetland flowers.
The sunken green space is formed through topography transformation, which can collect and store the rainfall through the natural topography. Technical interferences such as wet ponds and rainwater wetlands were applied to retain rainwater in the site, significantly reducing the discharge of stormwater. The retained rainwater is reused, not only for re-filling the landscape water pond, but also for the landscape irrigation of the site.
A continuous multi-pond-wetland coupling system with different purification functions is designed at the upstream of the Xintang Reservoir. Stormwater passes through the sedimentation filtration zone, pathogen purification zone, heavy metal purification zone, nutrient purification zone and comprehensive purification zone in a designed sequence. The water gets through quality stabilization area and purification units before finally flowing into the Xintang Reservoir for storage. A sediment filtration area, with gravel and coarse sand, was laid at the bottom of the pool, and reeds (which can provide large biomass, strong sand-fixing power and strong dirt absorption ability) were planted, which effectively slows down the flow of stormwater runoff, and filters large suspended solids, gravels and some natural pollutants.
The pathogen purification area mainly grows cattails and other emergent plants with developed root systems and large biomass. The antibiotics released from the roots were used to remove a series of pathogens such as E. coli. In the heavy metal purification zone, a plant community dominated by floating and submerged plants was constructed to effectively remove heavy metal pollutants from the water. In the nutrient substance purification area, emergent and floating water plants (such as reeds, cattails, water onions, iris, water hyacinth, water lilies, sophora pagoda, etc.) were grown to take out pollutants such as nitrogen and phosphorus.
In the terraced field comprehensive purification area terraces were created surface wetlands and subsurface wetlands to increase the dissolved oxygen of the water body. We chose aquatic plants with taller plants height, well-developed root systems, and strong oxygen transport capabilities (such as calamus, iris, lythrum, Cigu, water chestnut, etc.), together with the microorganisms in the soil to further remove pollutants. In that areas that used for water stabilization, , a variety of aquatic plants with excellent purification functions and excellent viewing effects were planted to create rainwater wetland landscapes with a variety of colors and rich species.
The downstream section of the Xintang Reservoir was divided into a stormwater wetland buffer zone and a wet pond storage area. The stormwater wetland buffer zone was formed by a series of pit ponds with a depth of around 0.5m. The wet and aquatic plants in the pond reduce the flow to allow for a longer purification process. At the same time, the pond bottom was not treated with anti-seepage treatment, and water can be naturally purified by the soil and microbial system, which also allows the collected stormwater to constantly replenish the groundwater.
The wet pond storage area was formed by a series of pit ponds with depth around 1.5m. The permanent volume water depth is about 0.5-1.0m. The storage volume plays an important part to regulate water level when a rainstorm occurs, which can effectively reduce the runoff of the catchment basin, which reduces the risk of severe flooding risk in the surrounding area.
The project advocates the beauty of weeds and low-carbon landscapes, and a large number of low-maintenance native plants were used. It brings back the beautiful memory of ancient mother river to the visitors.
4. Conclusion
Using the theory and technology of the "sponge city", Tianhe Smart City Daguan Wetland restored the ecological function of the site for stormwater and flood regulation, which explored the method of building a sponge city on a micro scale and provided surrounding residents an open space for leisure and recreation. It also became a place to popularize environmental and ecological knowledge. After the completion of the park, it has won the popularity of the general public; for the city managers who have committed to urban ecological governance for a long time, it was even more significant. Tianhe Smart Sponge City is an advanced stage of ecological management in Guangzhou, and it is also a new way of life.