Heze Sponge System Planning
Project Information
- Project Location:
- China Shandong, Heze
- Related Papers
Project Profile
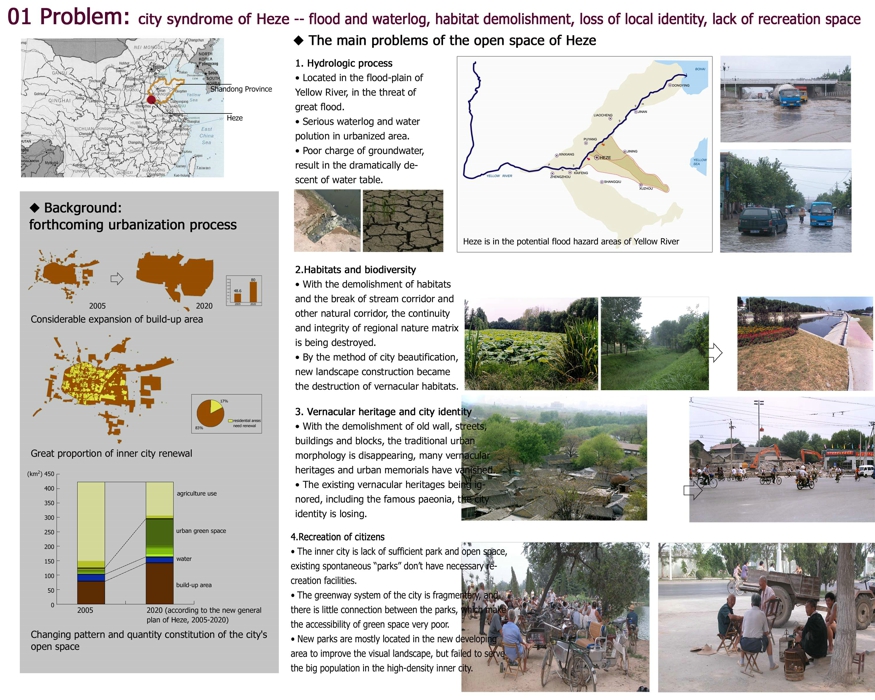
01 Problem: city syndrome of Heze -- flood and waterlog, habitat demolishment, loss of local identity, lack of recreation space
Background:
forthcoming urbanization process
Considerable expansion of build-up area
Great proportion of inner city renewal
2020 (according to the new general plan of Heze, 2005-2020)
Changing pattern and quantity constitution of the city's open space
The main problems of the open space of Heze
1. Hydrologic process
• Located in the flood-plain of Yellow River, in the threat of great flood.
• Serious waterlog and water polution in urbanized area.
• Poor charge of groundwater, result in the dramatically descent of water table.
2.Habitats and biodiversity
• With the demolishment of habitats and the break of stream corridor and other natural corridor, the continuity
and integrity of regional nature matrix is being destroyed.
• By the method of city beautification, new landscape construction became the destruction of vernacular habitats.
3. Vernacular heritage and city identity
• With the demolishment of old wall, streets, buildings and blocks, the traditional urban morphology is disappearing, many vernacular heritages and urban memorials have vanished.
• The existing vernacular heritages being ignored, including the famous paeonia, the city identity is losing.
4.Recreation of citizens
• The inner city is lack of sufficient park and open space, existing spontaneous “parks” don’t have necessary re-
creation facilities.
• The greenway system of the city is fragmentary, and there is little connection between the parks, which make
the accessibility of green space very poor.
• New parks are mostly located in the new developing area to improve the visual landscape, but failed to serve
the big population in the high-density inner city.
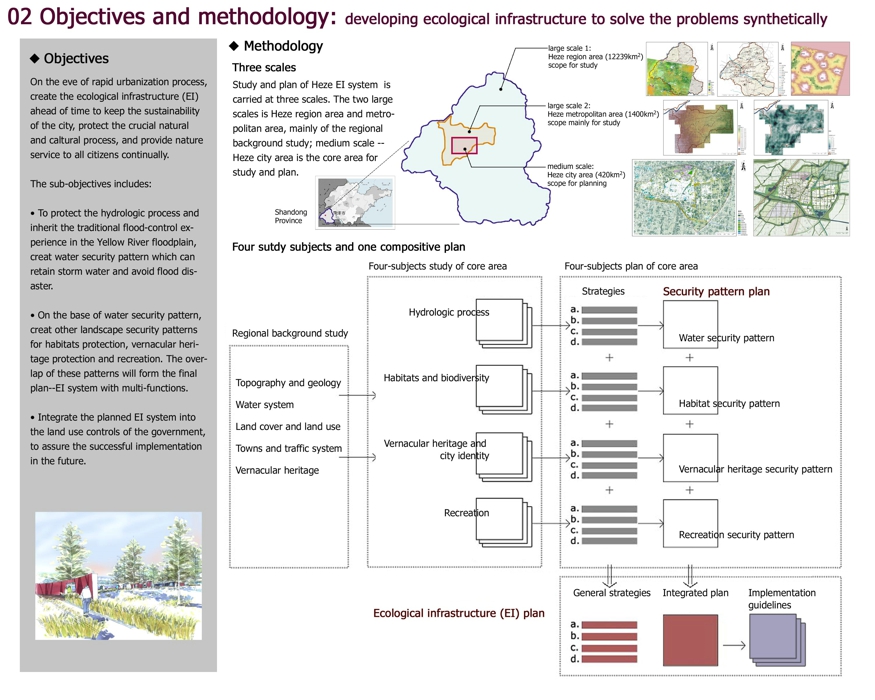
02 Objectives and methodology: developing ecological infrastructure to solve the problems synthetically
Objectives
On the eve of rapid urbanization process, create the ecological infrastructure (EI) ahead of time to keep the sustainability of the city, protect the crucial natural and caltural process, and provide nature service to all citizens continually.
The sub-objectives includes:
• To protect the hydrologic process and inherit the traditional flood-control experience in the Yellow River floodplain,
creat water security pattern which can retain storm water and avoid flood disaster.
• On the base of water security pattern, creat other landscape security patterns for habitats protection, vernacular heri-
tage protection and recreation. The overlap of these patterns will form the final plan--EI system with multi-functions.
• Integrate the planned EI system into the land use controls of the government, to assure the successful implementation in the future.
Methodology
Three scales
Study and plan of Heze EI system is carried at three scales. The two large scales is Heze region area and metro-
politan area, mainly of the regional background study; medium scale -- Heze city area is the core area for study and plan.
Shandong Province
large scale 1:
Heze region area (12239km2)
scope for study
large scale 2:
Heze metropolitan area (1400km2)
scope mainly for study
medium scale:
Heze city area (420km2)
scope for planning
Four sutdy subjects and one compositive plan
Regional background study
Topography and geology
Water system
Land cover and land use
Towns and traffic system
Vernacular heritage
Four-subjects study of core area
Hydrologic process
Habitats and biodiversity
Vernacular heritage and
city identity
Recreation
Four-subjects plan of core area
Strategies
Security pattern plan
Water security pattern
Habitat security pattern
Vernacular heritage security pattern
Recreation security pattern
Ecological infrastructure (EI) plan
General strategies
Integrated plan
Implementation
guidelines
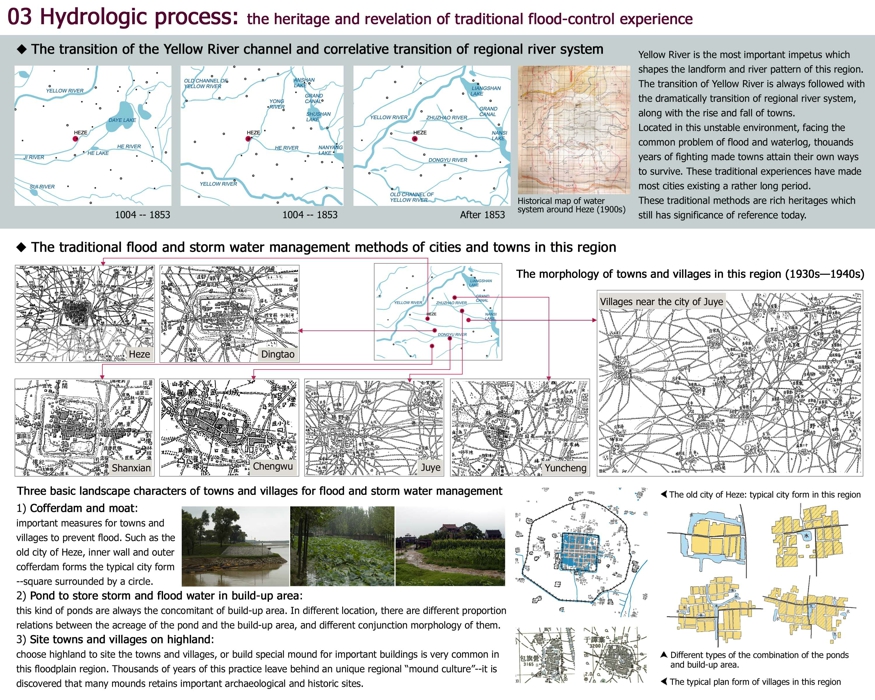
03 Hydrologic process: the heritage and revelation of traditional flood-control experience
◆ The transition of the Yellow River channel and correlative transition of regional river system
Historical map of water system around Heze (1900s)
Yellow River is the most important impetus which shapes the landform and river pattern of this region. The transition of Yellow River is always followed with the dramatically transition of regional river system, along with the rise and fall of towns.
Located in this unstable environment, facing the common problem of flood and waterlog, thouands years of fighting made towns attain their own ways to survive. These traditional experiences have made most cities existing a rather long period. These traditional methods are rich heritages which still has significance of reference today.
◆ The traditional flood and storm water management methods of cities and towns in this region
The morphology of towns and villages in this region (1930s—1940s)
Three basic landscape characters of towns and villages for flood and storm water management
1) Cofferdam and moat:
important measures for towns and villages to prevent flood. Such as the old city of Heze, inner wall and outer
cofferdam forms the typical city form--square surrounded by a circle.
2) Pond to store storm and flood water in build-up area:
this kind of ponds are always the concomitant of build-up area. In different location, there are different proportion
relations between the acreage of the pond and the build-up area, and different conjunction morphology of them.
3) Site towns and villages on highland:
choose highland to site the towns and villages, or build special mound for important buildings is very common in
this floodplain region. Thousands of years of this practice leave behind an unique regional “mound culture”--it is
discovered that many mounds retains important archaeological and historic sites.
The old city of Heze: typical city form in this region
Different types of the combination of the ponds and build-up area
The typical plan form of villages in this region
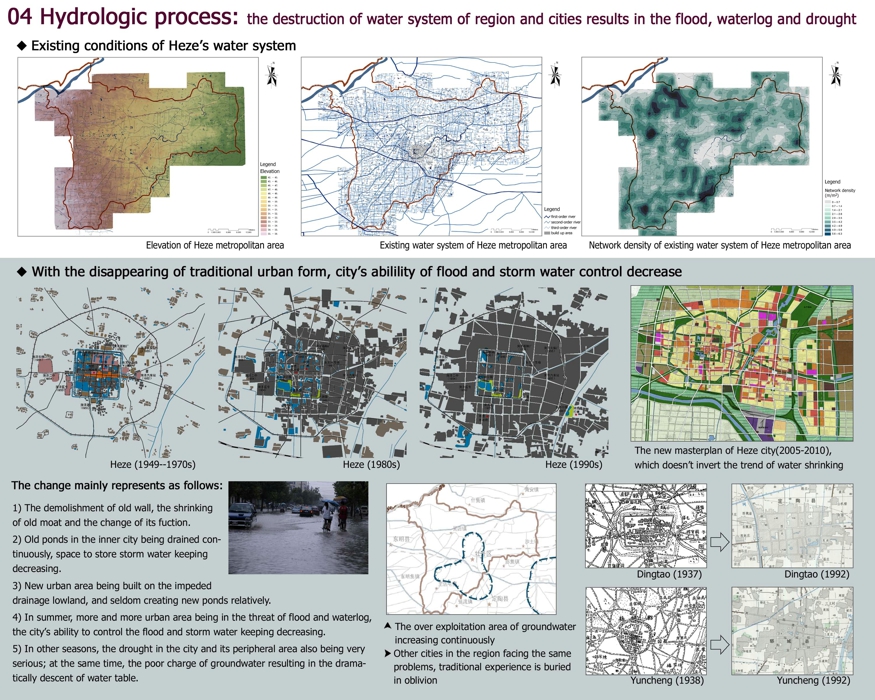
04 Hydrologic process: the destruction of water system of region and cities results in the flood, waterlog and drought
◆ Existing conditions of Heze’s water system
Elevation
Elevation of Heze metropolitan area
first-order river
second-order river
third-order river
build up area
Existing water system of Heze metropolitan area
Network density
(m/m2)
Network density of existing water system of Heze metropolitan area
◆ With the disappearing of traditional urban form, city’s abilility of flood and storm water control decrease
The new masterplan of Heze city(2005-2010), which doesn’t invert the trend of water shrinking
The change mainly represents as follows:
1) The demolishment of old wall, the shrinking of old moat and the change of its fuction.
2) Old ponds in the inner city being drained continuously, space to store storm water keeping decreasing.
3) New urban area being built on the impeded drainage lowland, and seldom creating new ponds relatively.
4) In summer, more and more urban area being in the threat of flood and waterlog, the city’s ability to control the flood and storm water keeping decreasing.
5) In other seasons, the drought in the city and its peripheral area also being very serious; at the same time, the poor charge of groundwater resulting in the dramatically descent of water table.
The over exploitation area of groundwater increasing continuously
Other cities in the region facing the same problems, traditional experience is buried in oblivion
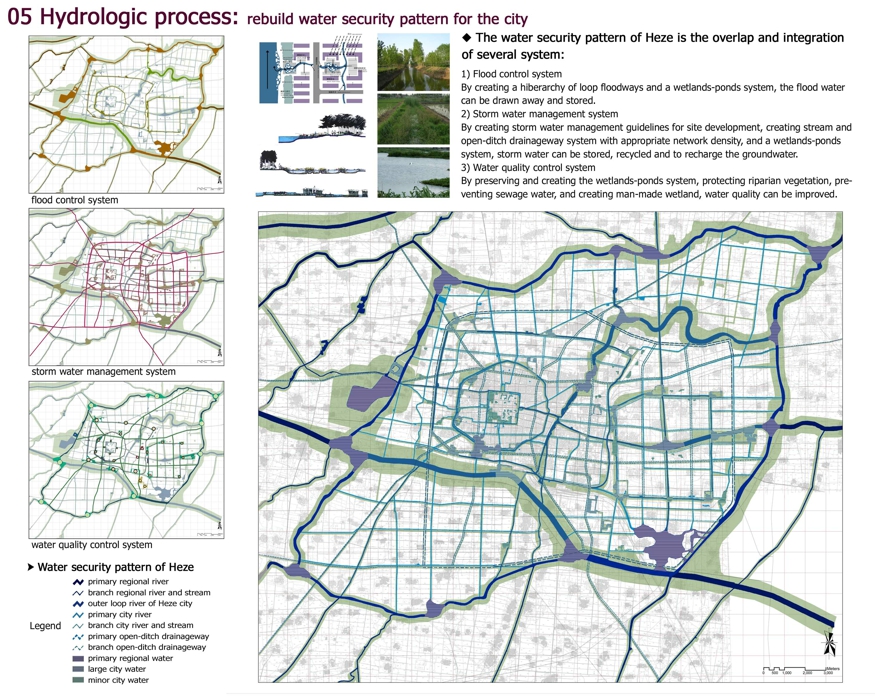
05 Hydrologic process: rebuild water security pattern for the city
flood control system
storm water management system
water quality control system
Water security pattern of Heze
primary regional river
branch regional river and stream
outer loop river of Heze city
primary city river
branch city river and stream
primary open-ditch drainageway
branch open-ditch drainageway
primary regional water
large city water
minor city water
The water security pattern of Heze is the overlap and integration
of several system:
1) Flood control system
By creating a hiberarchy of loop floodways and a wetlands-ponds system, the flood water can be drawn away and stored.
2) Storm water management system
By creating storm water management guidelines for site development, creating stream and open-ditch drainageway system with appropriate network density, and a wetlands-ponds system, storm water can be stored, recycled and to recharge the groundwater.
3) Water quality control system
By preserving and creating the wetlands-ponds system, protecting riparian vegetation, preventing sewage water, and creating man-made wetland, water quality can be improved.
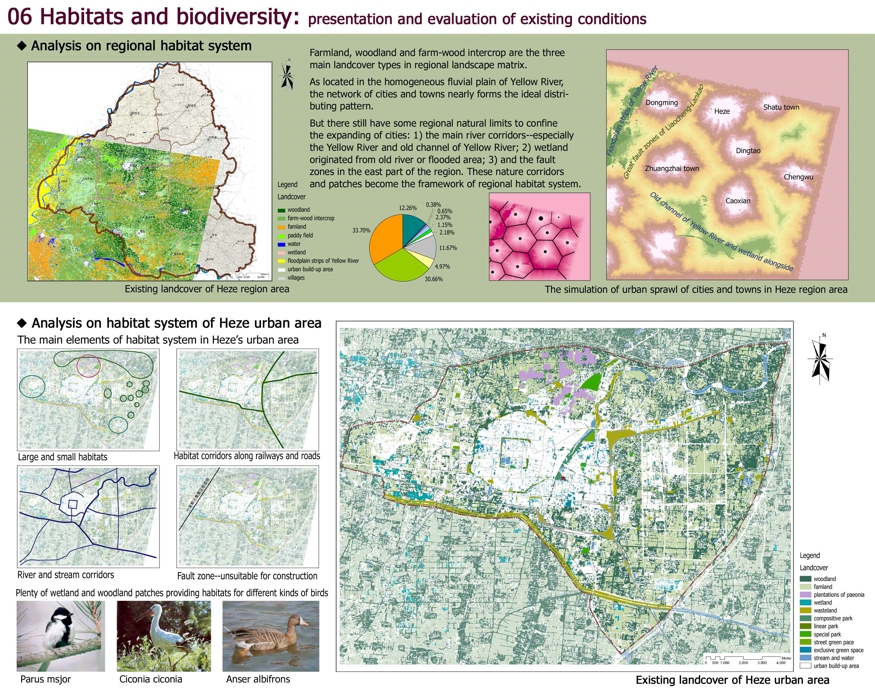
06 Habitats and biodiversity: presentation and evaluation of existing conditions
◆ Analysis on regional habitat system
Existing landcover of Heze region area
woodland
farm-wood intercrop
famland
paddy field
water
wetland
floodplain strips of Yellow River
urban build-up area
villages
Farmland, woodland and farm-wood intercrop are the three main landcover types in regional landscape matrix.
As located in the homogeneous fluvial plain of Yellow River, the network of cities and towns nearly forms the ideal distributing pattern.
But there still have some regional natural limits to confine the expanding of cities: 1) the main river corridors--especially the Yellow River and old channel of Yellow River; 2) wetland originated from old river or flooded area; 3) and the fault zones in the east part of the region. These nature corridors and patches become the framework of regional habitat system
The simulation of urban sprawl of cities and towns in Heze region area
Floodplain strips of Yellow River
Great fault zones of Liaocheng-Lankao
Old channel of Yellow River and wetland alongside
◆Analysis on habitat system of Heze urban area
The main elements of habitat system in Heze’s urban area
Large and small habitats
Habitat corridors along railways and roads
River and stream corridors
Fault zone--unsuitable for construction
Plenty of wetland and woodland patches providing habitats for different kinds of birds
大山雀Parus msjor
白鹳 Ciconia ciconia
白额雁 Anser albifrons
Existing landcover of Heze urban area
woodland
famland
plantations of paeonia
wetland
wasteland
compositive park
linear park
special park
street green pace
exclusive green space
stream and water
urban build-up area
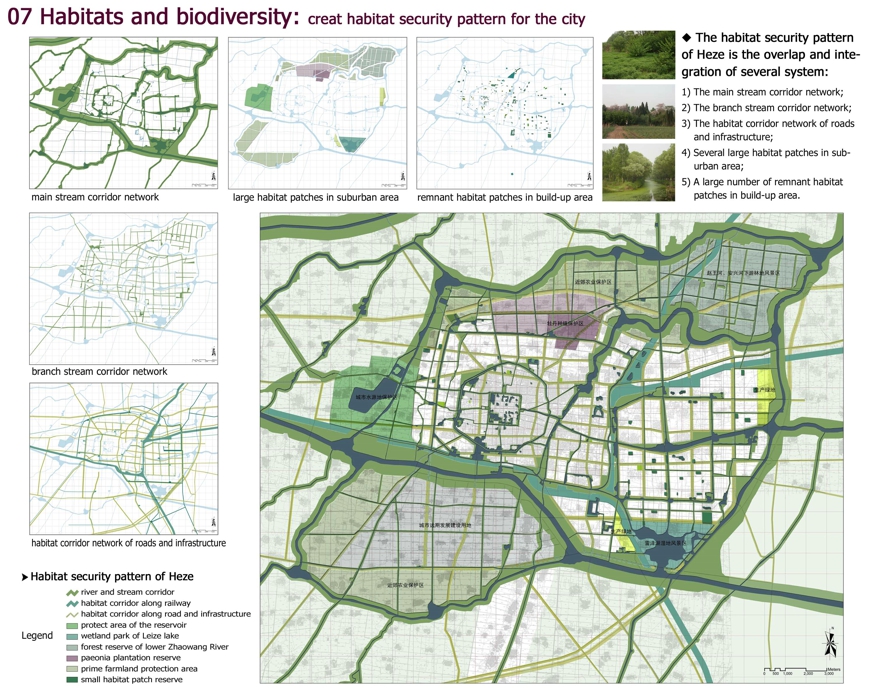
07 Habitats and biodiversity: creat habitat security pattern for the city
The habitat security pattern of Heze is the overlap and integration of several system:
1) The main stream corridor network;
2) The branch stream corridor network;
3) The habitat corridor network of roads and infrastructure;
4) Several large habitat patches in suburban area;
5) A large number of remnant habitat patches in build-up area.
main stream corridor network
large habitat patches in suburban area
remnant habitat patches in build-up area
branch stream corridor network
habitat corridor network of roads and infrastructure
Habitat security pattern of Heze
river and stream corridor
habitat corridor along railway
habitat corridor along road and infrastructure
protect area of the reservoir
wetland park of Leize lake
forest reserve of lower Zhaowang River
paeonia plantation reserve
prime farmland protection area
small habitat patch reserve
08 Vernacular heritage and city identity: presentation and evaluation of existing conditions
Heritage sites in Heze region area
Heritage sites in Heze metropolitan area
Legend
archaeological site
historic tomb
stone inscription
historic building
historic site of revolution war
historic garden
museum and cultural facility
historic route
cities and towns
build-up area
road and highway
Heritage sites in Heze urban area
vernacular heritage site
vernacular heritage route
vernacular heritage zone
build-up area
road
stream and pond
A great deal of vernacular heritage sites distribute in the Heze region, among which the most characteristic heritages are: the mounds with archaeological and historic sites; the plantation and gardens of paeonia.
In the Heze city, because of the effective traditional flood and storm water management, the old city of Heze avoided serious destruction by flood for many times and then retained many historic sites, including its old wall and moat.
But in recent fifty years, these historic sites mostly were demolished by new urban development, including some historic paeonia gardens.
Historical map of Heze (1756), showing all the important buildings in the city
Demolished historic buildings and landscape
famous eight sceneries of old Heze
historic building
city gate
turret
bridge
wall, moat and
outer cofferdam
Demolished historic gardens of paeonia
demolished historic garden of paeonia
existing paeonia plantation
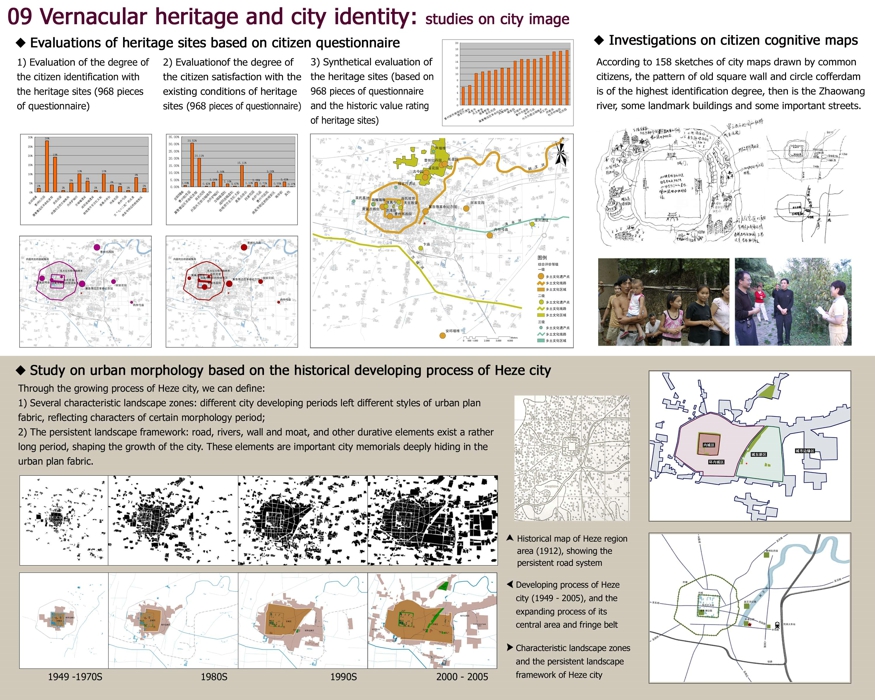
09 Vernacular heritage and city identity: studies on city image
◆ Evaluations of heritage sites based on citizen questionnaire
1) Evaluation of the degree of the citizen identification with the heritage sites (968 pieces of questionnaire)
2) Evaluationof the degree of the citizen satisfaction with the existing conditions of heritage sites (968 pieces of questionnaire)
3) Synthetical evaluation of the heritage sites (based on 968 pieces of questionnaire and the historic value rating
of heritage sites)
◆ Investigations on citizen cognitive maps
According to 158 sketches of city maps drawn by common citizens, the pattern of old square wall and circle offerdam
is of the highest identification degree, then is the Zhaowang river, some landmark buildings and some important streets.
◆ Study on urban morphology based on the historical developing process of Heze city
Through the growing process of Heze city, we can define:
1) Several characteristic landscape zones: different city developing periods left different styles of urban plan
fabric, reflecting characters of certain morphology period;
2) The persistent landscape framework: road, rivers, wall and moat, and other durative elements exist a rather
long period, shaping the growth of the city. These elements are important city memorials deeply hiding in the
urban plan fabric.
Historical map of Heze region area (1912), showing the persistent road system
Developing process of Heze city (1949 - 2005), and the expanding process of its central area and fringe belt
Characteristic landscape zones and the persistent landscape framework of Heze city
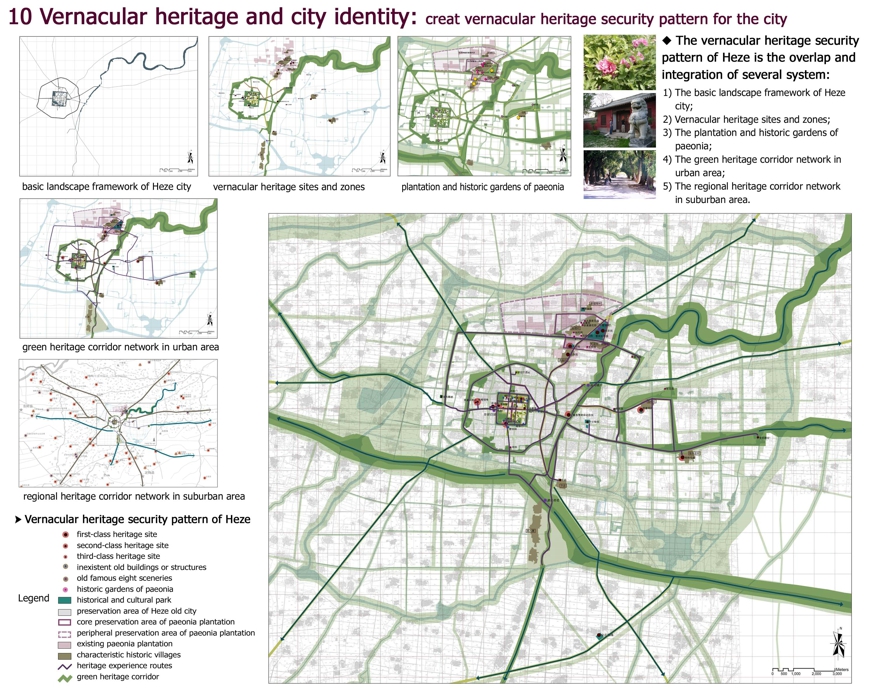
10 Vernacular heritage and city identity: creat vernacular heritage security pattern for the city
The vernacular heritage security pattern of Heze is the overlap and integration of several system:
1) The basic landscape framework of Heze city;
2) Vernacular heritage sites and zones;
3) The plantation and historic gardens of paeonia;
4) The green heritage corridor network in urban area;
5) The regional heritage corridor network in suburban area.
basic landscape framework of Heze city
vernacular heritage sites and zones
plantation and historic gardens of paeonia
green heritage corridor network in urban area
regional heritage corridor network in suburban area
Vernacular heritage security pattern of Heze
Legend
first-class heritage site
second-class heritage site
third-class heritage site
inexistent old buildings or structures
old famous eight sceneries
historic gardens of paeonia
historical and cultural park
preservation area of Heze old city
core preservation area of paeonia plantation
peripheral preservation area of paeonia plantation
existing paeonia plantation
characteristic historic villages
heritage experience routes
green heritage corridor
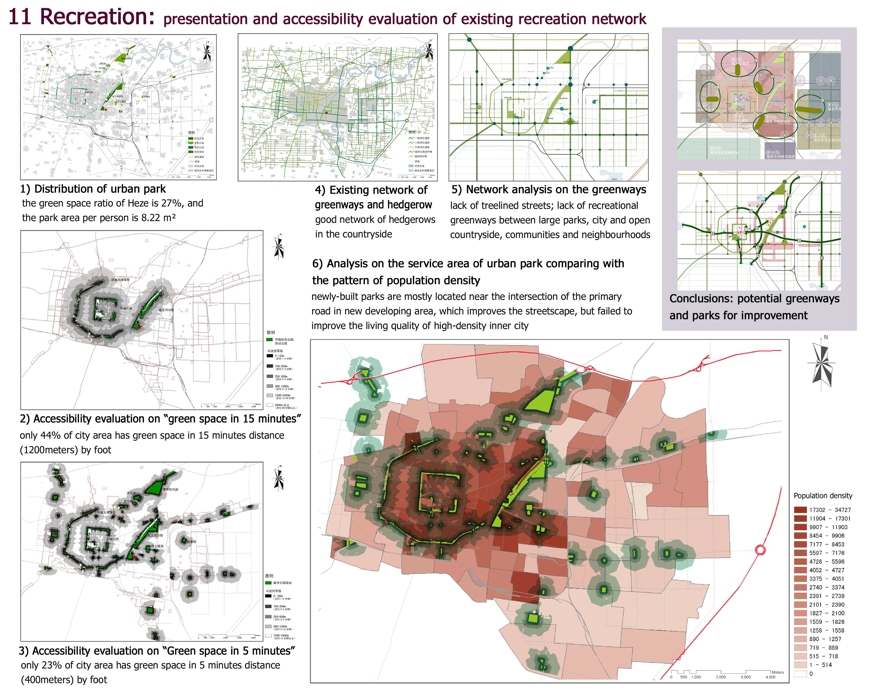
11 Recreation: presentation and accessibility evaluation of existing recreation network
1) Distribution of urban park
the green space ratio of Heze is 27%, and the park area per person is 8.22 m²
2) Accessibility evaluation on “green space in 15 minutes”
only 44% of city area has green space in 15 minutes distance (1200meters) by foot
3) Accessibility evaluation on “Green space in 5 minutes”
only 23% of city area has green space in 5 minutes distance (400meters) by foot
4) Existing network of greenways and hedgerow
good network of hedgerows in the countryside
5) Network analysis on the greenways
lack of treelined streets; lack of recreational greenways between large parks, city and open countryside, communities and neighbourhoods
6) Analysis on the service area of urban park comparing with the pattern of population density
newly-built parks are mostly located near the intersection of the primary
road in new developing area, which improves the streetscape, but failed to improve the living quality of high-density inner city
Conclusions: potential greenways and parks for improvement
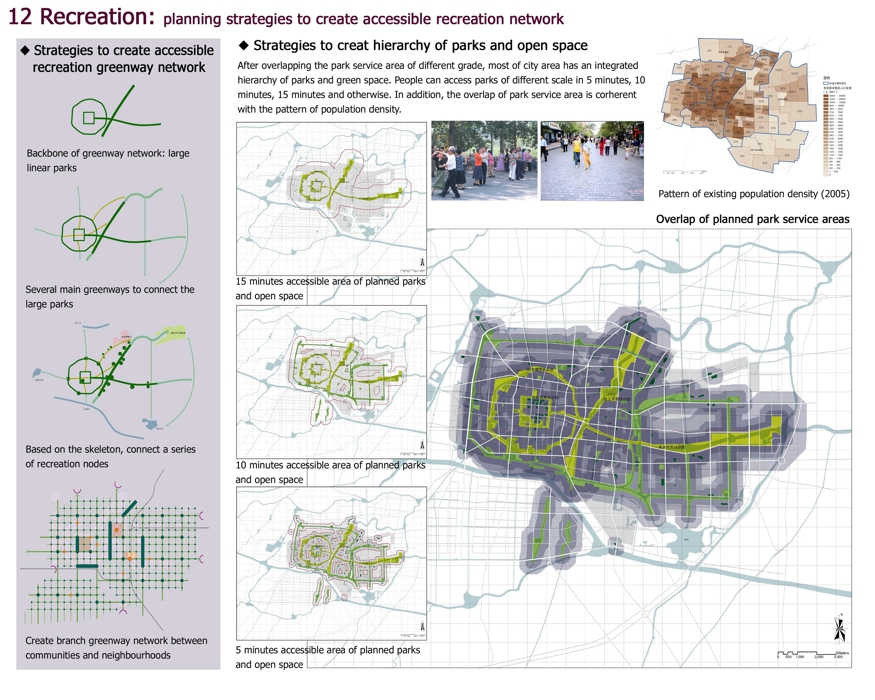
12 Recreation: planning strategies to create accessible recreation network
Strategies to create accessible recreation greenway network
Backbone of greenway network: large linear parks
Several main greenways to connect the large parks
Based on the skeleton, connect a series of recreation nodes
Create branch greenway network between communities and neighbourhoods
Strategies to creat hierarchy of parks and open space
After overlapping the park service area of different grade, most of city area has an integrated hierarchy of parks and green space. People can access parks of different scale in 5 minutes, 10 minutes, 15 minutes and otherwise. In addition, the overlap of park service area is corherent with the pattern of population density.
15 minutes accessible area of planned parks and open space
10 minutes accessible area of planned parks and open space
5 minutes accessible area of planned parks and open space
Overlap of planned park service areas
Pattern of existing population density (2005)
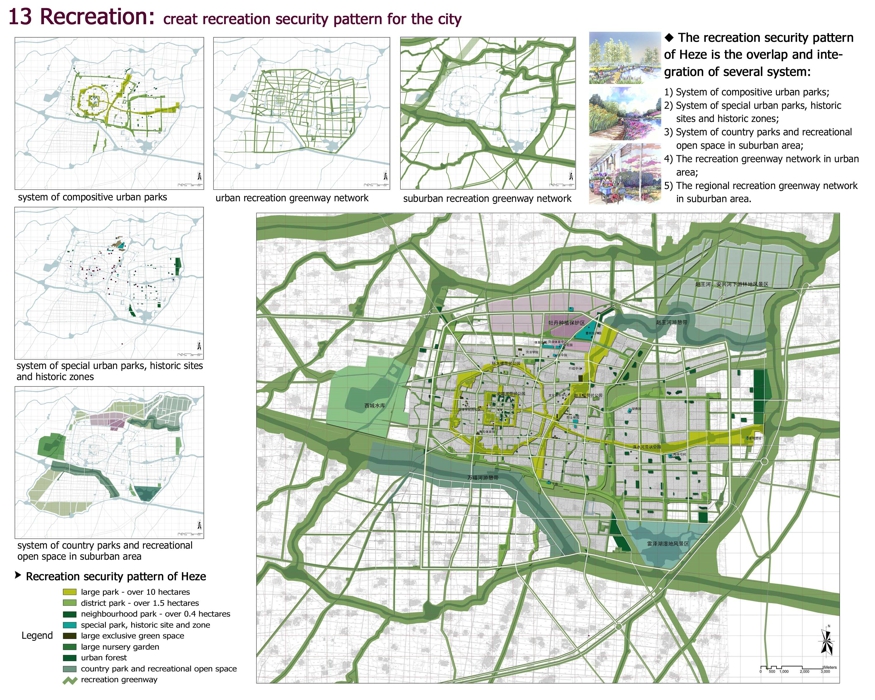
13 Recreation: creat recreation security pattern for the city
The recreation security pattern of Heze is the overlap and integration of several system:
1) System of compositive urban parks;
2) System of special urban parks, historic sites and historic zones;
3) System of country parks and recreational open space in suburban area;
4) The recreation greenway network in urban area;
5) The regional recreation greenway network in suburban area.
system of compositive urban parks
urban recreation greenway network
suburban recreation greenway network
system of special urban parks, historic sites and historic zones
system of country parks and recreational open space in suburban area
Recreation security pattern of Heze
Legend
large park - over 10 hectares
district park - over 1.5 hectares
neighbourhood park - over 0.4 hectares
special park, historic site and zone
large exclusive green space
large nursery garden
urban forest
country park and recreational open space
recreation greenway
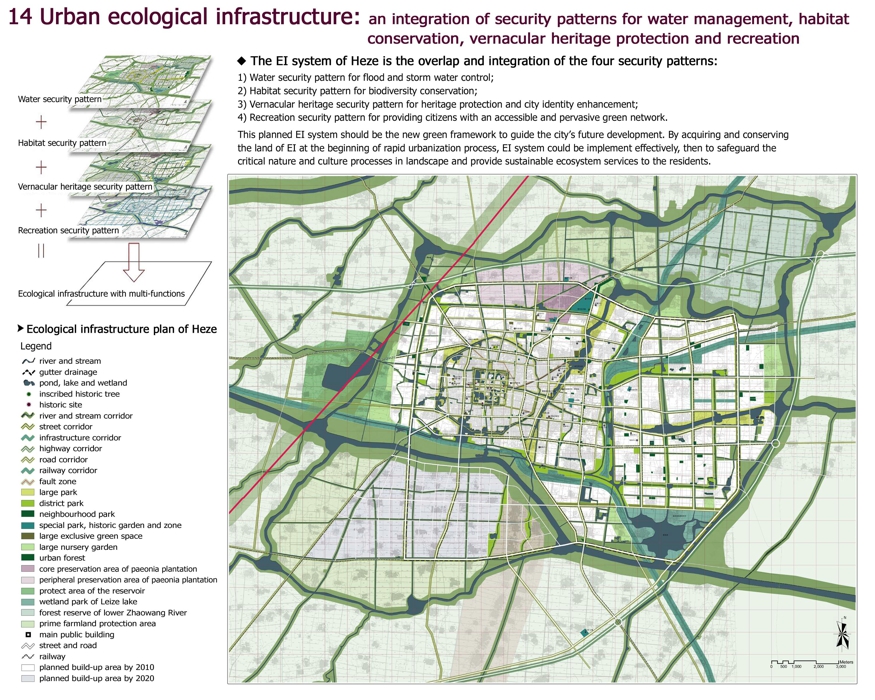
14 Urban ecological infrastructure: an integration of security patterns for water management, habitat conservation, vernacular heritage protection and recreation
The EI system of Heze is the overlap and integration of the four security patterns:
1) Water security pattern for flood and storm water control;
2) Habitat security pattern for biodiversity conservation;
3) Vernacular heritage security pattern for heritage protection and city identity enhancement;
4) Recreation security pattern for providing citizens with an accessible and pervasive green network.
This planned EI system should be the new green framework to guide the city’s future development. By acquiring and conserving the land of EI at the beginning of rapid urbanization process, EI system could be implement effectively, then to safeguard the critical nature and culture processes in landscape and provide sustainable ecosystem services to the residents.
Water security pattern
Habitat security pattern
Vernacular heritage security pattern
Recreation security pattern
Ecological infrastructure with multi-functions
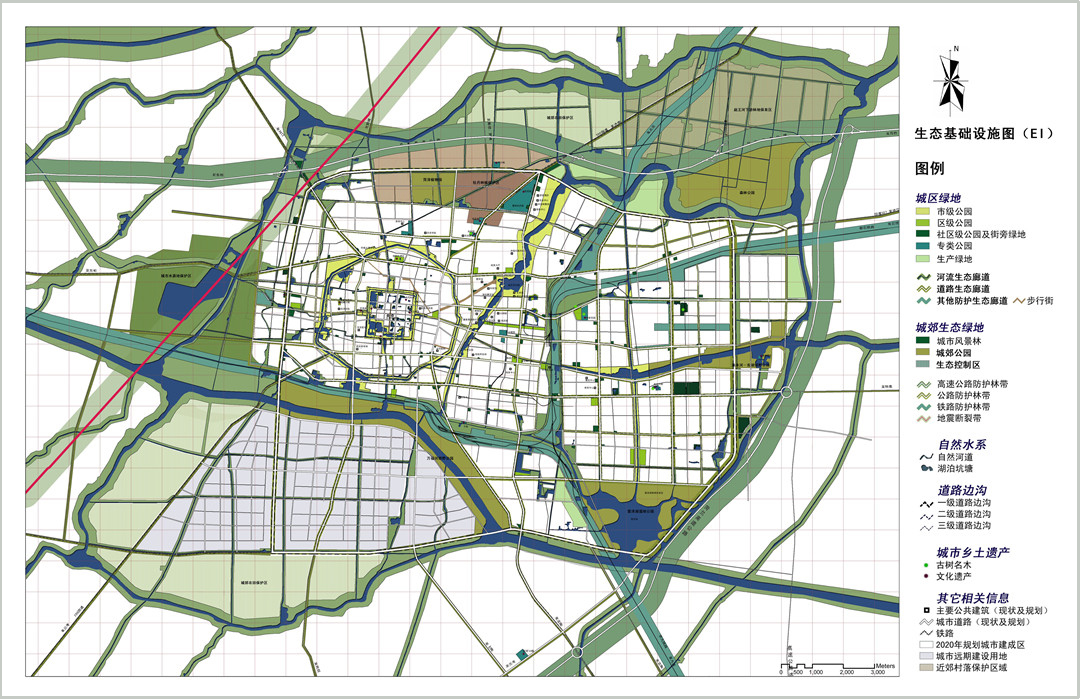
Ecological infrastructure plan of Heze
Legend
river and stream
gutter drainage
pond, lake and wetland
inscribed historic tree
historic site
river and stream corridor
street corridor
infrastructure corridor
highway corridor
road corridor
railway corridor
fault zone
large park
district park
neighbourhood park
special park, historic garden and zone
large exclusive green space
large nursery garden
urban forest
core preservation area of paeonia plantation
peripheral preservation area of paeonia plantation
protect area of the reservoir
wetland park of Leize lake
forest reserve of lower Zhaowang River
prime farmland protection area
main public building
street and road
railway
planned build-up area by 2010
planned build-up area by 2020
15 The control and implementation of urban ecological infrastructure
The structural classification and essential function definition of ecological infrastructure of Heze:
The planned EI system were classified into a series of structure elements, and the two basic sorts were corridors and patches. Then the essential functions of each element were defined, which presented the functions it serves in different security patterns.
security pattern water security pattern habitat security pattern vernacular heritage security pattern recreation security pattern
structure function Water quality control flood control habitat agriculture heritage scenery recreation
regional ecological infrastructure regional EI corridor regional river corridor ● ◎ ● ○ ◎ ● ●
regional road and highway corridor ○ ○ ◎ ○ ◎ ● ●
fault zone belt ○ ○ ◎ ◎ ○ ○ ○
regional EI patch preservation area of paeonia plantation ○ ○ ◎ ● ● ● ●
preservation area of the reservoir ● ◎ ● ◎ ○ ◎ ◎
wetland park of Leize lake ● ● ● ○ ◎ ● ●
forest reserve of lower Zhaowang River ● ● ● ◎ ◎ ● ●
prime farmland protection area ◎ ◎ ● ● ◎ ◎ ◎
urban ecological infrastructure urban EI corridor urban river and stream corridor ● ◎ ● ○ ◎ ● ●
street corridor and pedestrian greenway ○ ○ ◎ ○ ◎ ● ●
infrastructure corridor ○ ○ ◎ ○ ○ ○ ○
urban EI patch large park ◎ ◎ ◎ ○ ● ● ●
district park ◎ ◎ ◎ ○ ● ● ●
neighbourhood park ◎ ◎ ◎ ○ ◎ ● ●
special park and historic garden ○ ○ ◎ ◎ ● ◎ ●
large exclusive green space ◎ ◎ ◎ ○ ◎ ◎ ●
large nursery garden ◎ ○ ◎ ● ◎ ◎ ◎
urban forest ◎ ○ ● ◎ ◎ ● ◎
Based on the definition of EI system structurally and functionally, guidlines were developed for each inscribed corridors and patches, and becoming the two basic control system: the control of corridors and the control of patches.
If the EI system of Heze being built, it can achieve such goals by the year of 2020:
park area per person(m2/person) green space ratio(%) green space per person(m2/person) water area ratio(%)
2005 8.22 27.0 36 4.1
2010 10 35 42 7
2020 13.1 42.8 50.4 11.4
The control of corridors:
1) Regional river corridors;
2) Urban river and stream corridors;
3) Large linear park and open space;
4) Road corridors with gutter drainage and greenways for pedestrian and bicycle.
The control of patches:
1) large habitat patches in suburban area;
2) Small remnant habitat patches in build-up area;
3) Urban park and open space;
4) Historic gardens, sites and historic zones.