Datong Jinhua Palace National Mining Park
Project Information
- Project Location:
- China Datong, Shanxi
- Project Scale:
- 18 Hectares
- Design Time:
- July 2009
- Build Time:
- September 2012
Project Profile
1. Project Statement
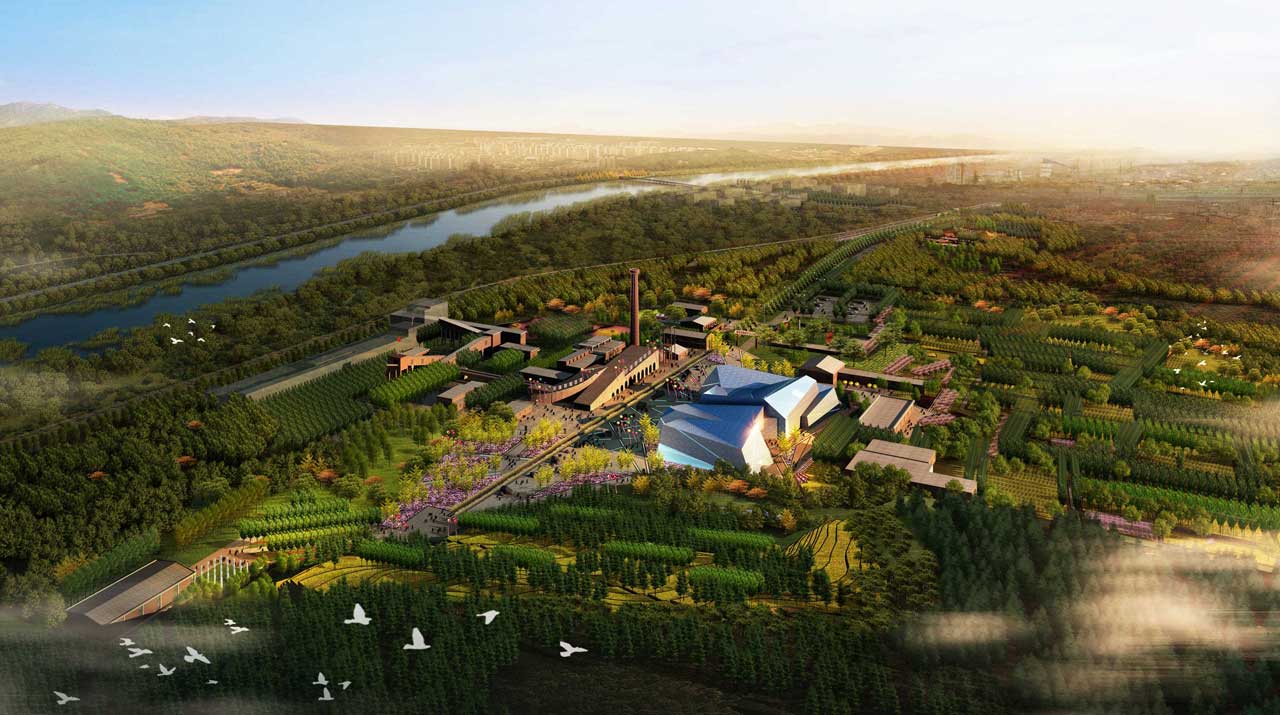
The Datong Jinhua Palace National Mining Park is located 12.5 kilometers west of Datong city center, on the southern side of National Highway 109. It is positioned opposite the renowned Yungang Grottoes across the Shili River. The site preserves the entirety of the production area's factory buildings and equipment. The long history of coal mining at Jinhua Palace adds a rich cultural background to the land, forming the fundamental environmental characteristics of the site.
The design aims to accurately capture both the tangible and intangible memories of the site through thorough preliminary investigation, exploration, and extraction, creating a park environment that is well-suited to the site conditions and distinguished by its unique characteristics.
2. Objective and Challenge
Design Goals
1) Protecting Non-renewable Resources:
The design of Jinhua Palace National Mining Park focuses on preserving the irreplaceable mining heritage resources.
2) Restoring the Ecological Environment:
The project aims to restore the mining ecology, promoting harmony between humans and nature.
3) Highlighting Mining Heritage:
Emphasize the technological, educational, and tourism value of mining relics.
4) Promoting Georesource Utilization:
Advance new methods for utilizing geological resources and contribute to the economic transformation of Shanxi and the construction of a tourism economic belt.
5) Building a World-class National Mining Park:
Establish Jinhua Palace National Mining Park as an international learning base for coal mining systems, a domestic and international tourism destination, and a demonstration site for the ecological restoration of Shanxi's industrial heritage, ultimately becoming a world-class national mining park and a "calling card" for Datong City.
Design Challenges
1) Respecting Site Memory:
The site retains all factory buildings and production equipment from the production area, along with a rich cultural background from Jinhua Palace's long history of coal mining. The design extracts existing elements to accurately capture both tangible and intangible site memories, creating a park environment that aligns with site conditions and is characterized by distinctiveness.
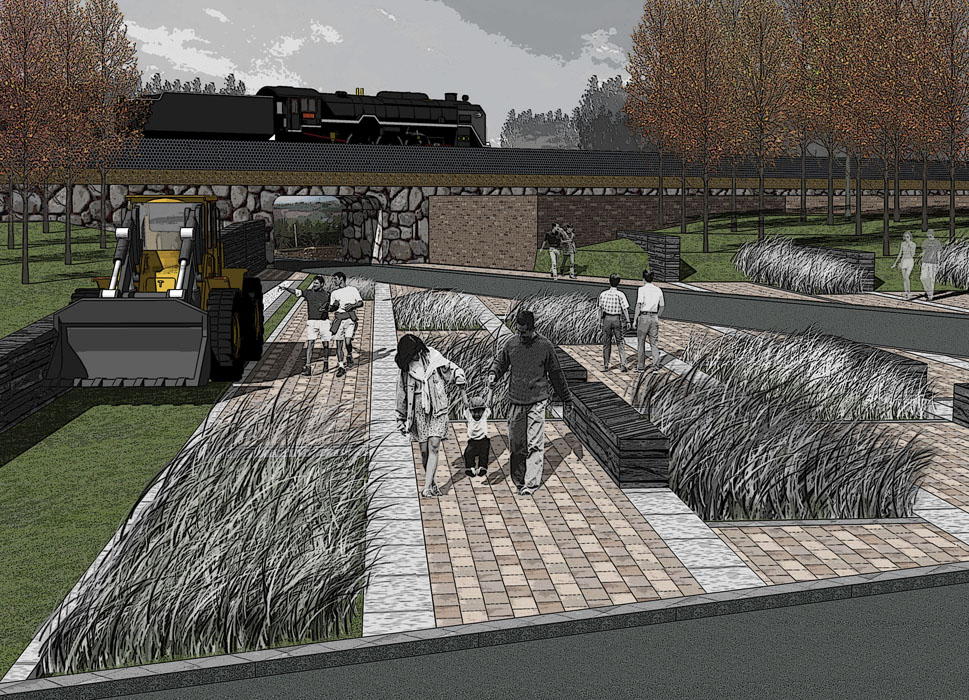
2) Enhancing Functional Image:
The site is currently an active coal mining production area with facilities primarily serving industrial production and a subpar landscape environment. The design proposes specific measures for functional integration, transportation reorganization, landscape enhancement, ecological restoration, architectural renovation, and special project planning, all while preserving the site's characteristics, to improve landscape quality and comprehensively elevate the park's image.
3) Strengthening Regional Interaction:
Located one kilometer south of Yungang Grottoes and north of the significant ecological corridor Shili River in Datong City, the site’s unique location necessitates careful consideration of Yungang Grottoes' overall environmental requirements and Shili River's ecological restoration needs. The design strategically develops tourism projects, distributes service facilities, and designs project themes to secure broader development opportunities.
4) Deepening Cultural Theme:
As a key mining park project approved by the state, the design further explores the themes of coal mining and miner life while delving into geology, culture, history, and society to enrich and enhance the coal culture theme related to the site.
3. Design Strategy
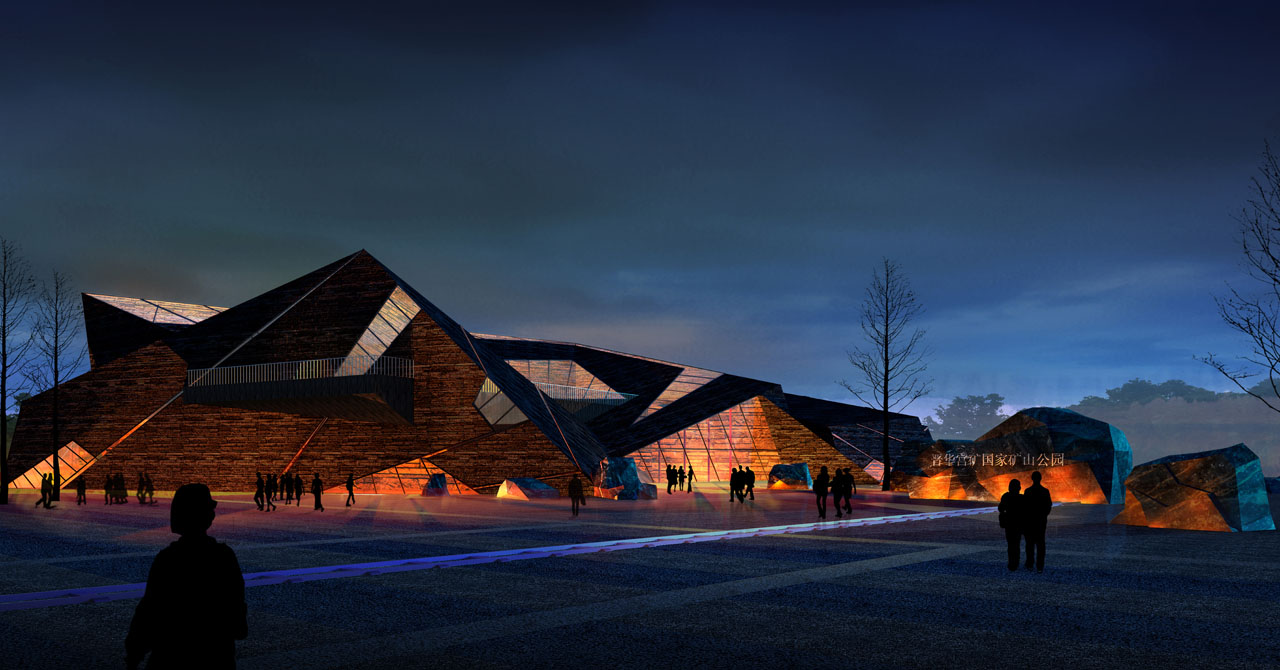
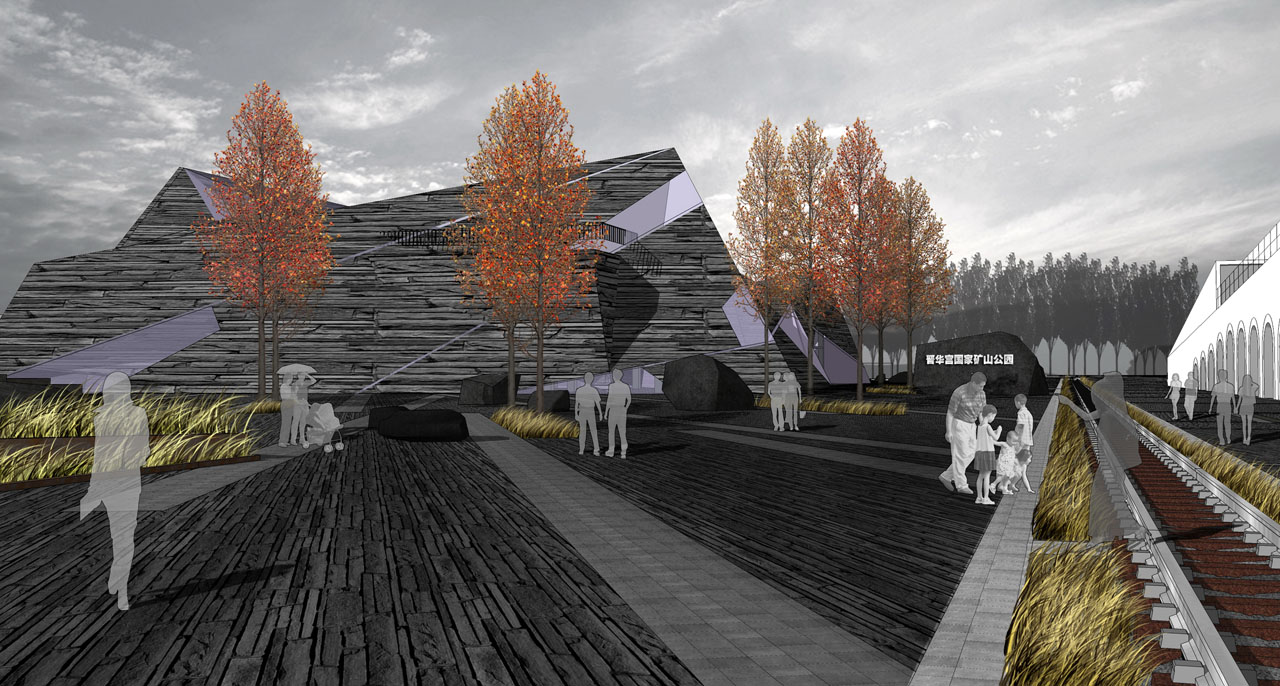
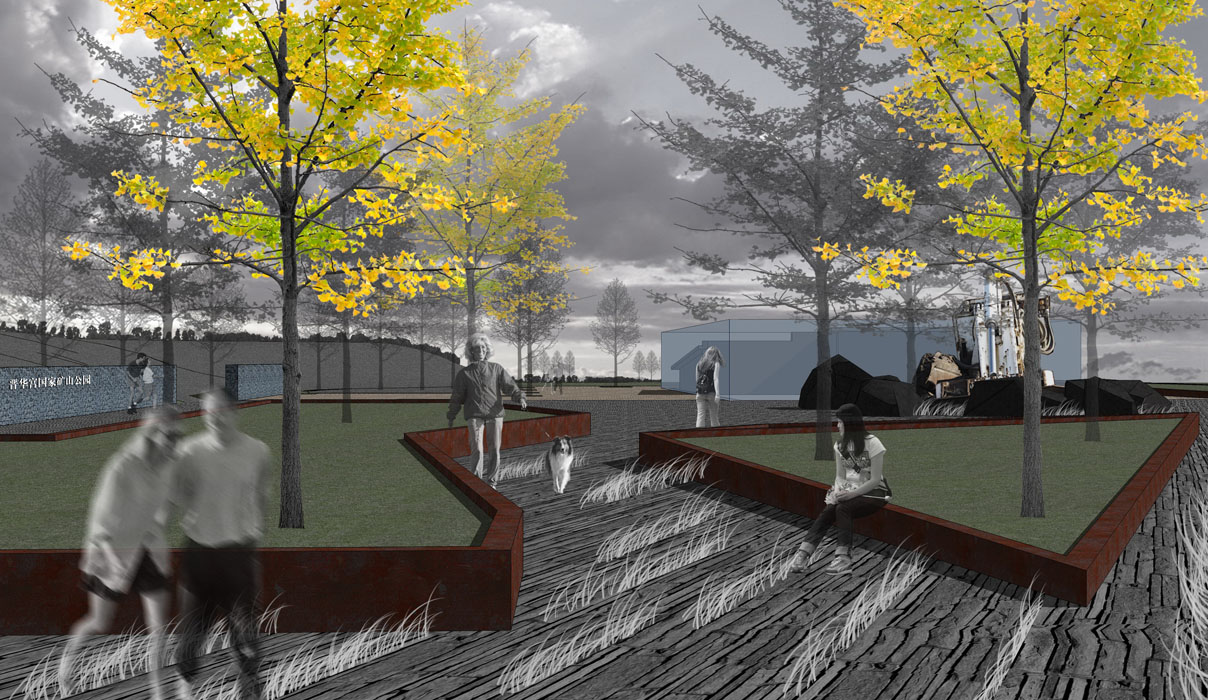
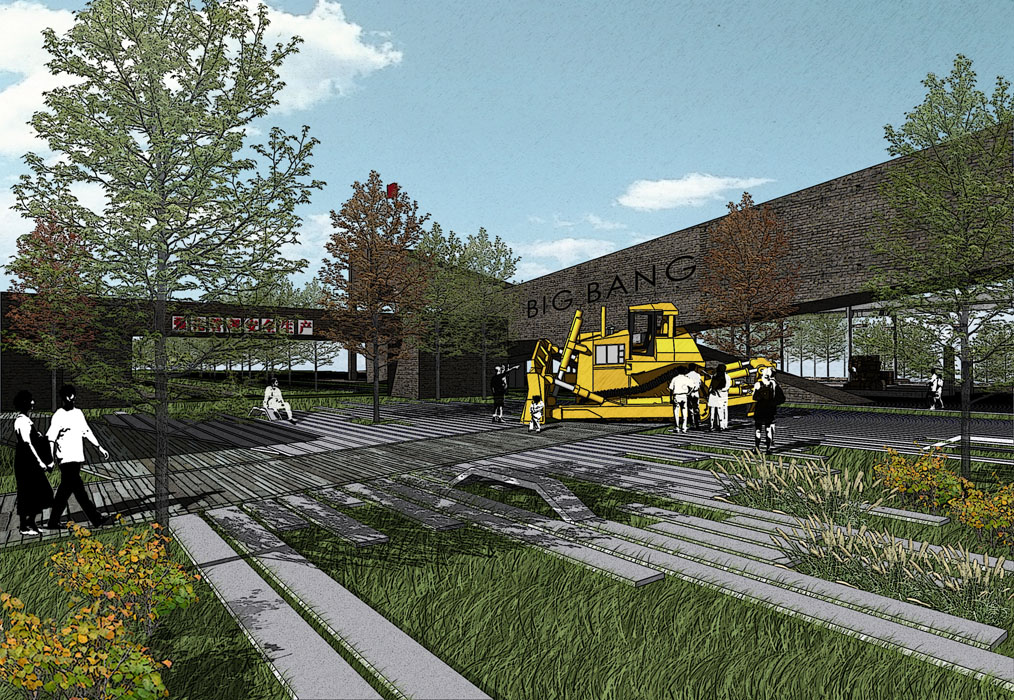
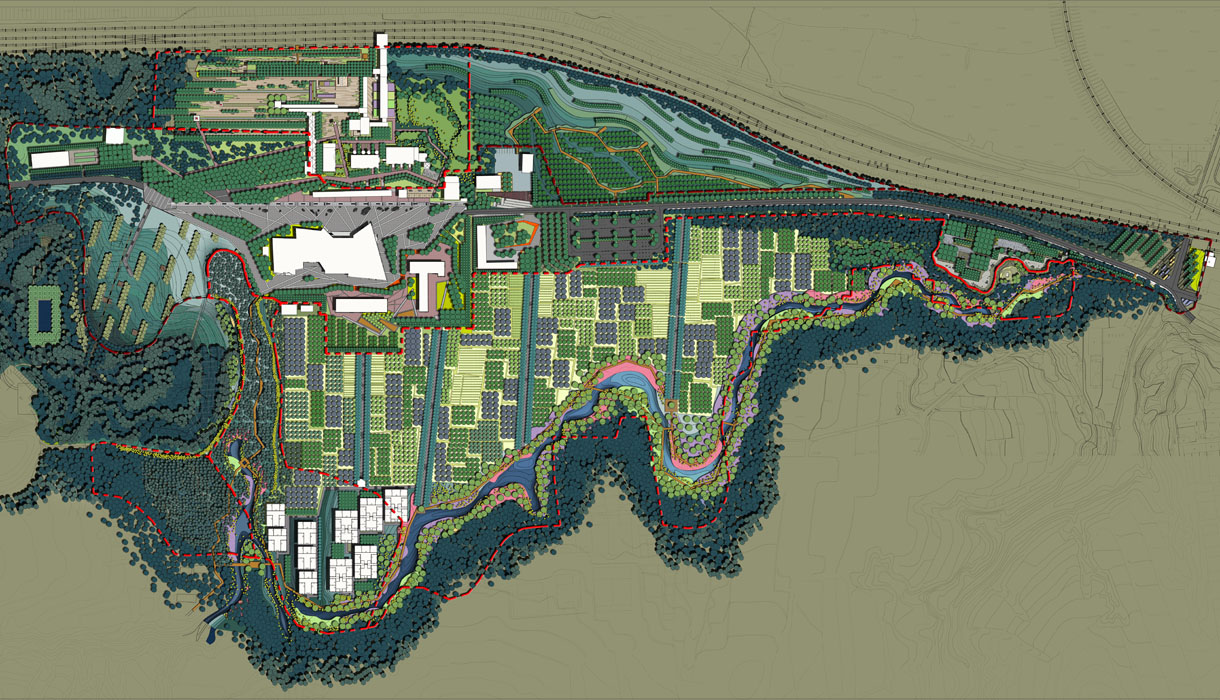
1) Industrial Heritage Zone:
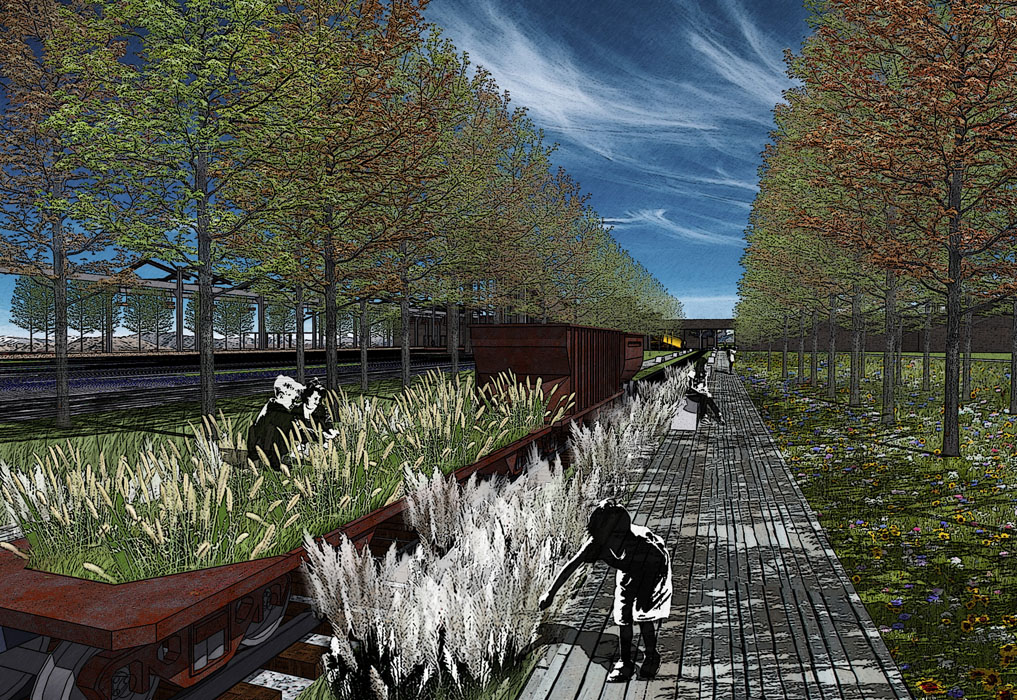
The entrance to the Industrial Heritage Zone features significant elevation changes, designed with terraced greenery planted with ornamental grasses and Xinjiang poplars. The theme square is surrounded by tall trees like Chinese locusts, creating a semi-enclosed space. The square’s small green areas are planted with low-growing ornamental grasses, wildflowers, and flowering shrubs, complemented by paving that evokes a simple and bold modern industrial landscape.
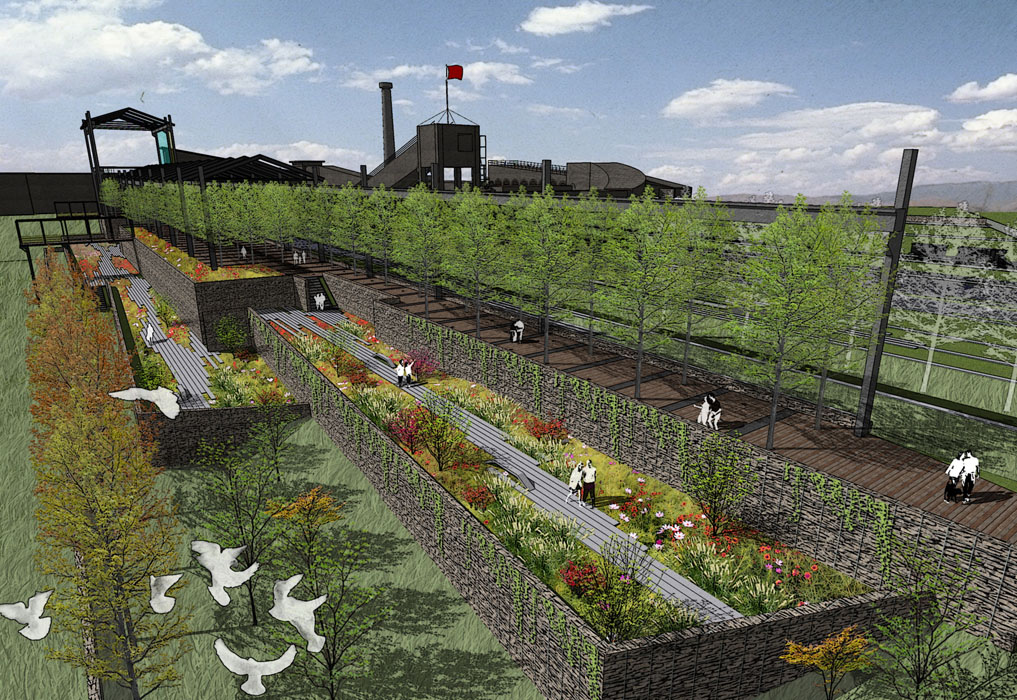
2) Specialty Plant Area:
The Specialty Plant Area is located on a slope with a significant elevation change, with the south side featuring a wetland plant viewing area. This area is planted with willows, purple loosestrife, reeds, and yellow irises, combining with wooden platforms and boardwalks to create a beautiful wetland landscape. Surrounding trees and shrubs, such as torch trees, poplars, lilacs, and honeysuckle, form a “green valley” characteristic of the mining park.
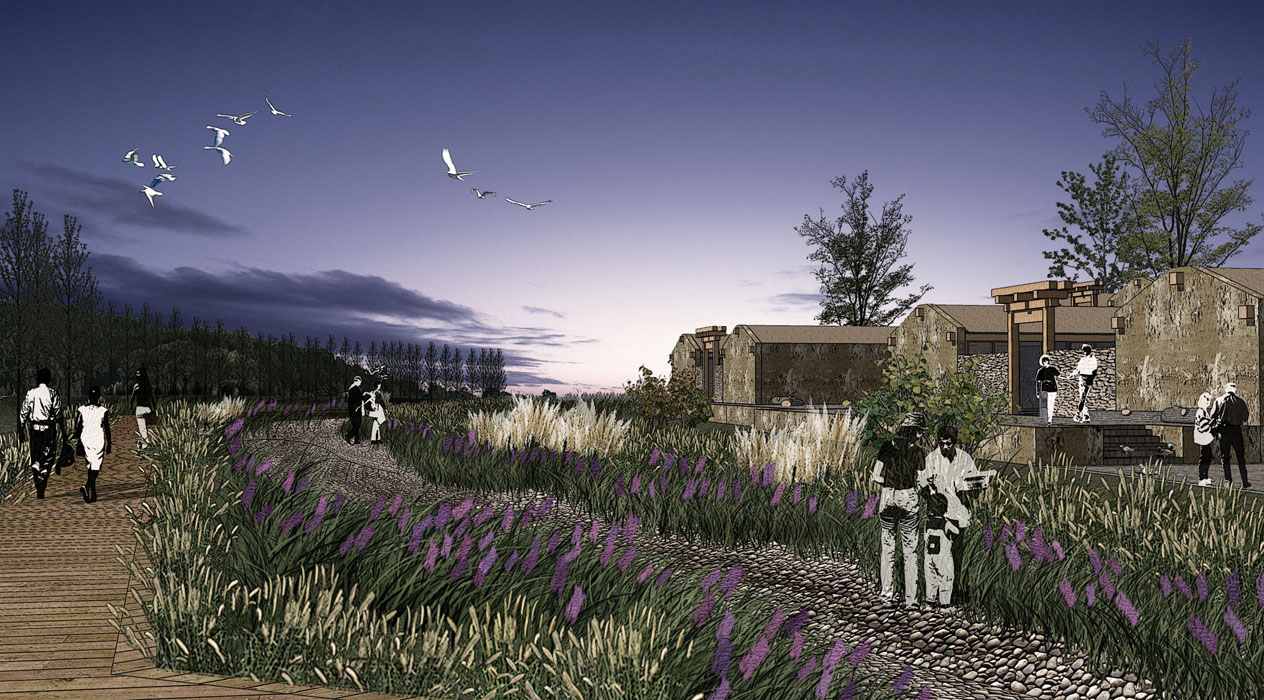
3) Miner Lifestyle Experience Zone:
This area features buildings with dry stone walls and rammed earth walls, modern in style. The plantings mirror the architectural style, featuring tall trees with straight trunks and high branching points. Rural tools, like stone mills, are placed beneath the trees to enhance the area’s appeal.
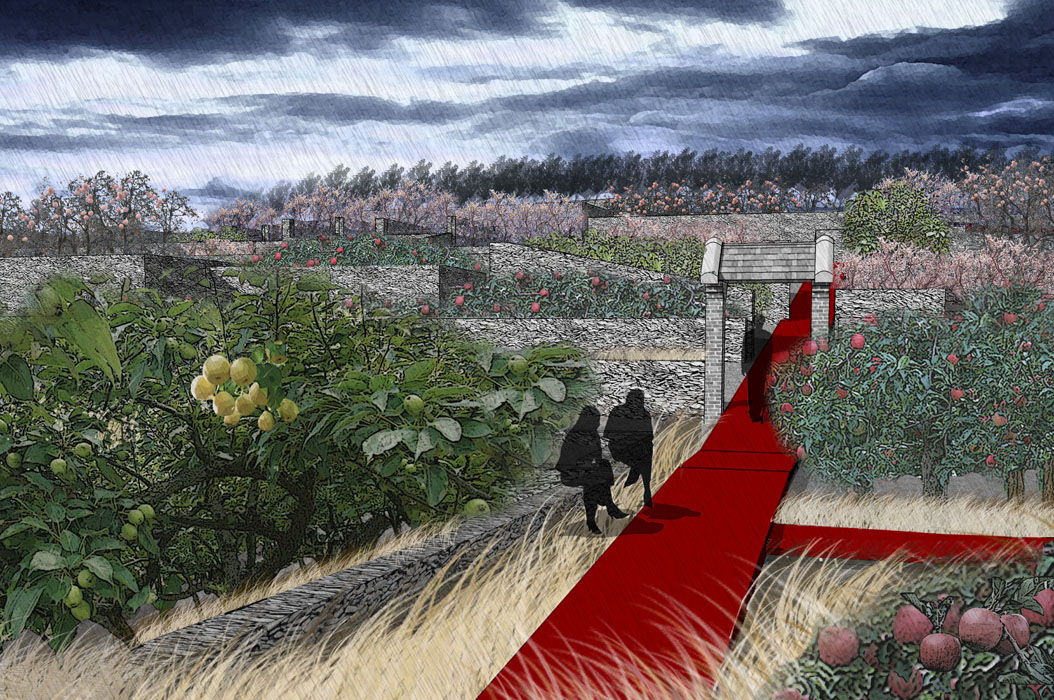
4) Agricultural and Orchard Zone:
The Agricultural and Orchard Zone is planted with fruit trees suitable for Datong's climate, such as apricots, grapes, and jujubes. These trees are arranged in staggered patterns to showcase a variety of seasonal landscapes, from green buds in spring to abundant fruit in autumn, adding economic value to the park.
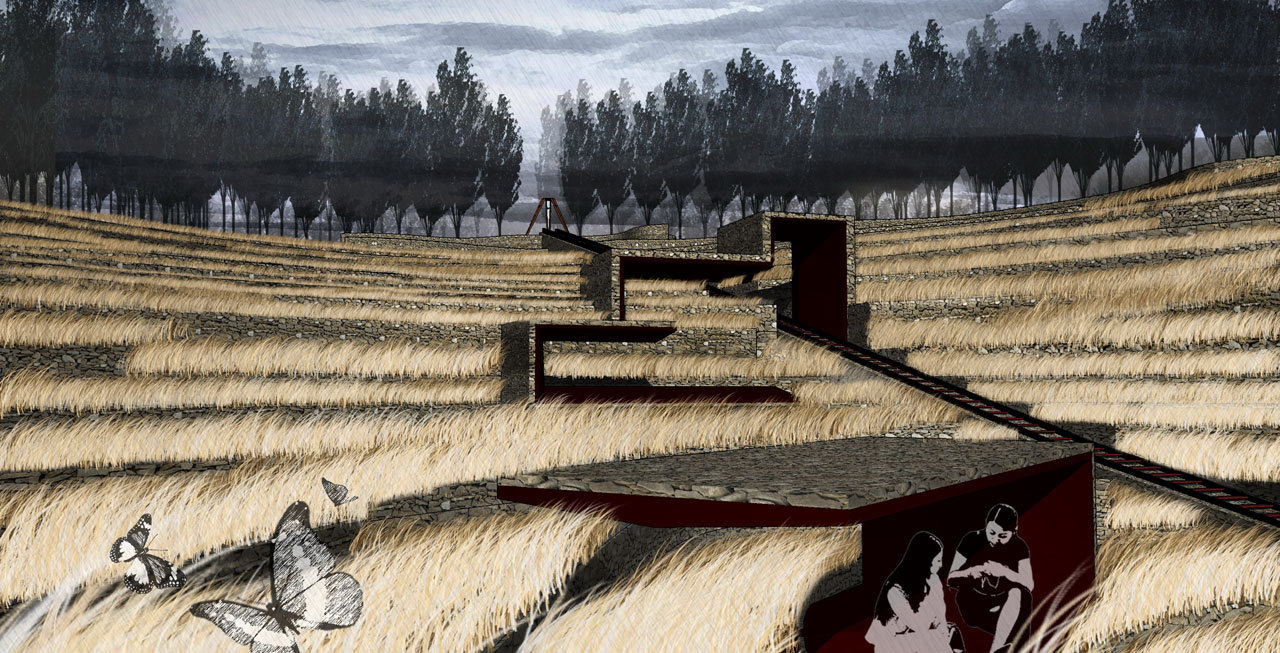
5) Water Collection Ditch Landscape Zone:
The site’s natural drainage channels are retained as water collection ditches, with wildflowers, ornamental trees, and flowering shrubs planted along the banks, complemented by wooden walkways and platforms. Visitors can enjoy a stroll through the floral landscapes.
6) Shelterbelt Zone:
Due to strong northwest winds in Datong during winter, the southwest perimeter of the project site is planted with deep-rooted, fast-growing, cold-resistant, and drought-tolerant trees like Xinjiang poplar and white poplar to protect against wind and sand.
4. Conclusion
The design of Jinhua Palace National Mining Park was completed in September 2012 and is a key supporting project for the Yungang area tourism attractions, receiving support from national and provincial governments. Leveraging its geographic proximity to Yungang Grottoes and its long coal mining history and unique Jurassic coal layer geological wonders, Jinhua Palace has gained national mining park status and was included in the first "National Mining Park Directory."
The park has become an important window into China's coal industry development and a hub for exploring coal culture. It has been recognized as an "International Leisure and Ecotourism Demonstration Zone" by the International Leisure Industry Association, awarded a AAAA-level tourist attraction by the National Tourism Administration, and named "China's Most Distinctive Ecotourism Destination" by the International Cultural Tourism Promotion Conference, China Tourism Brand Association, and China Ecotourism Development Association. The underground exploration tour has also been designated a "National Science Popularization Education Base" by the China Association for Science and Technology.