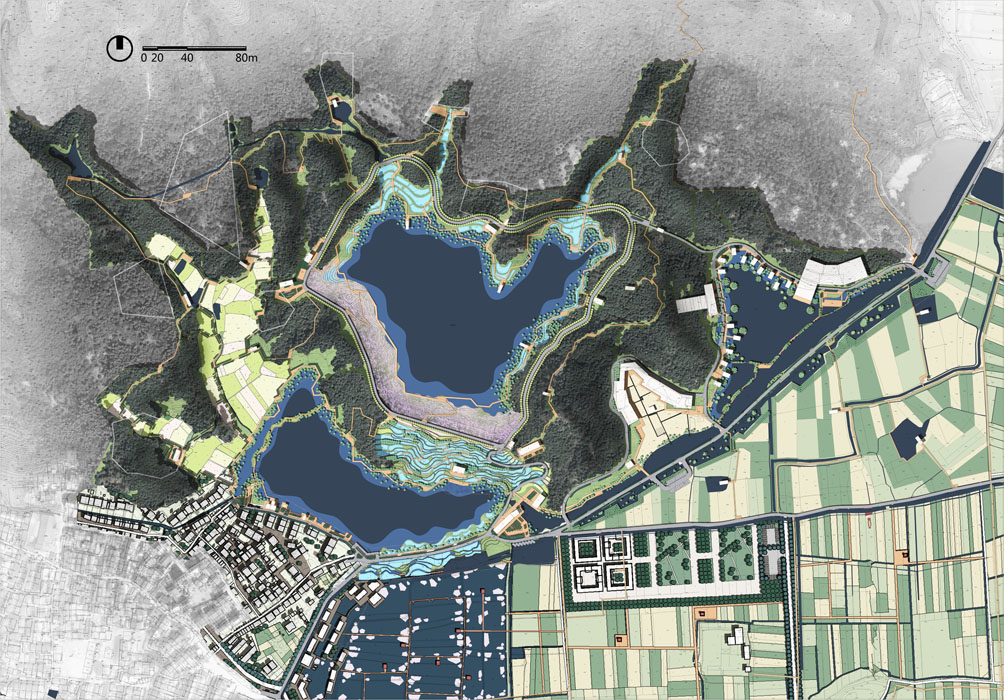
Shaoxing Shangyu Phoenix Mountain Archaeological Park
Project Information
- Project Location:
- China Shaoxing, Zhejiang
- Design Time:
- January 2017
- Client:
- Shaoxing City Shangyu District Bureau of Culture, Radio, Television, and Press
Project Profile
1. Project Statement
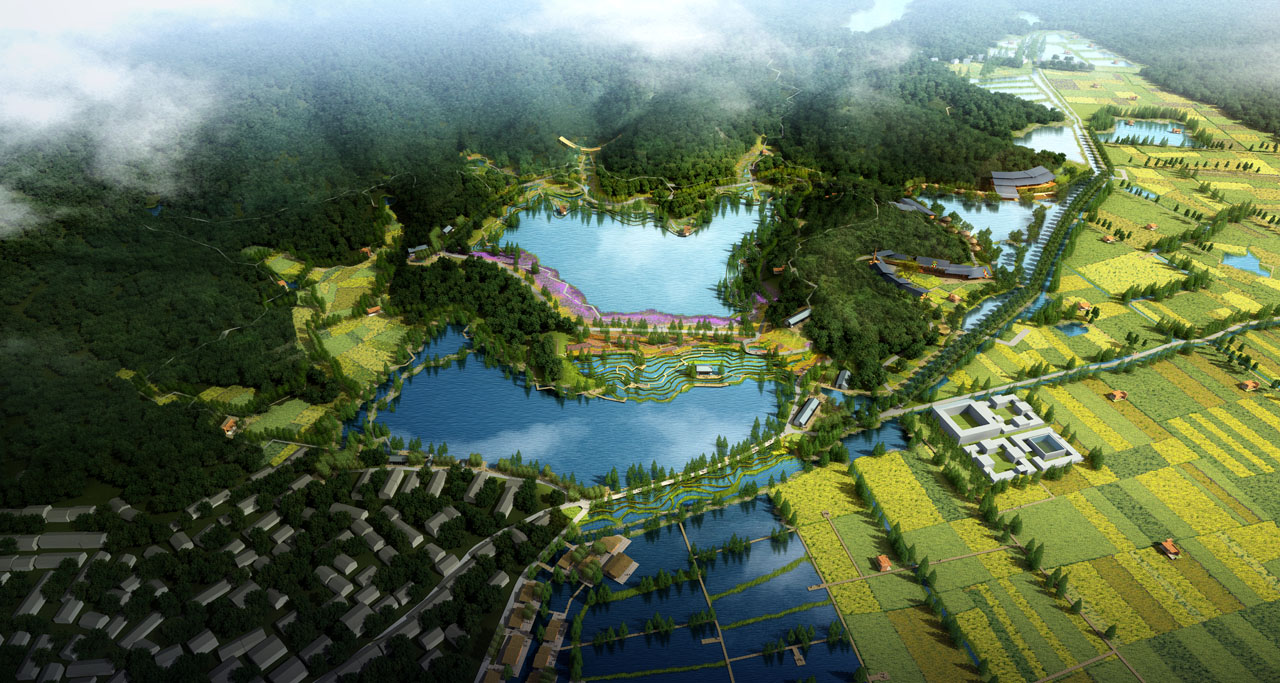
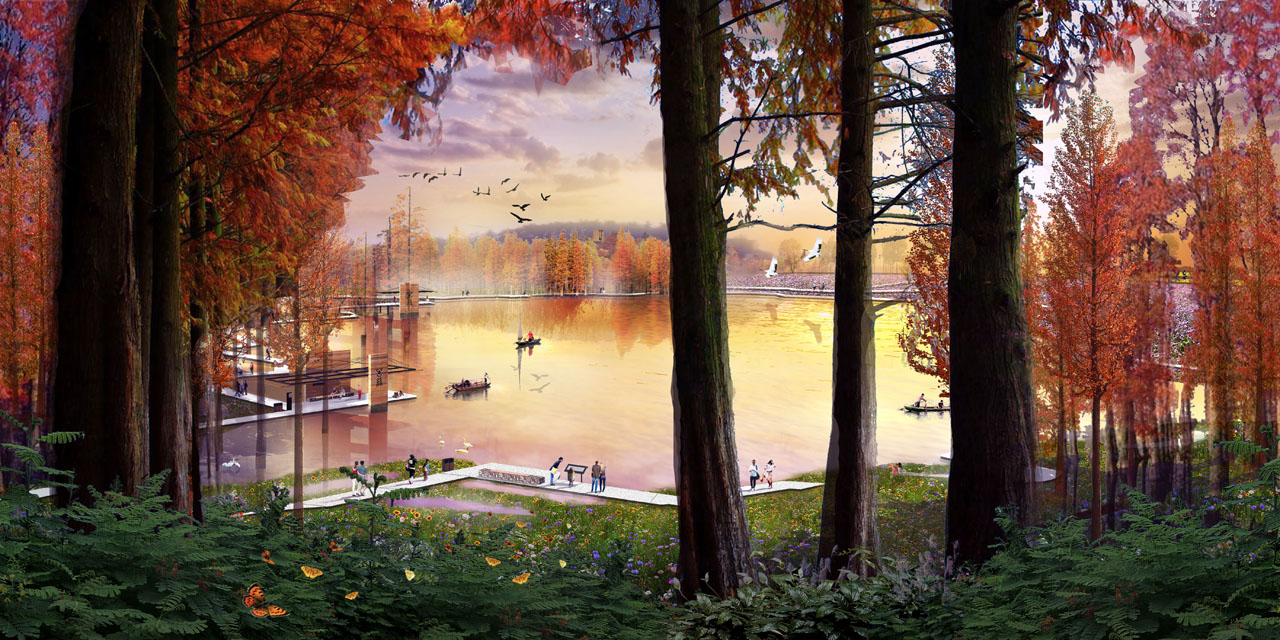
The site is located 11 kilometers from the center of Shangyu District and has convenient transportation access. The core area of the project is centered around the Youyi Reservoir, covering approximately 44 hectares. It features rich Yue kiln culture, beautiful lake and beach landscapes, dense mountain forests, and natural countryside views. However, the water infrastructure has damaged the natural environment, and the overall infrastructure is disorganized.
Based on the current site conditions, the goal is to create a cultural heritage park that combines archaeological education, leisure tourism, and the continuation of natural landscapes.
2. Objective and Challenge
The low hills along the Cao'e River in Shangyu were the center of the Yue kiln during the Han and Six Dynasties. The Three Kingdoms and Western Jin periods (later known as Wu and Jin) were the peak times for early Yue kiln production. There are numerous kiln sites from this period, with at least 57 locations, known for their exquisite porcelain quality and rich variety of types and decorations, reaching the peak of the Han and Six Dynasties. The site currently has eight national treasure-level kiln sites, which are the origin of celadon, mainly from the Eastern Han, Three Kingdoms, and Western Jin periods. The Nigu Poshan Kiln Site is a typical kiln from this period.
The designers propose transforming this cultural heritage site into an educational cultural park, improving the original wetland habitat and serving as a city park to meet the growing outdoor recreation needs of citizens. The biggest challenge is how to improve water infrastructure that has damaged the natural environment, coordinate the disorganized infrastructure, and adhere to the principles of "protection first, rescue priority, reasonable use, and strengthened management" in cultural relics work.
The design aims to create a heritage park based on deep cultural roots, integrating the site, environment, and activities, stimulating tourism, and revitalizing the area with ecological restoration and Yue kiln culture as the foundation.
3. Design Strategy
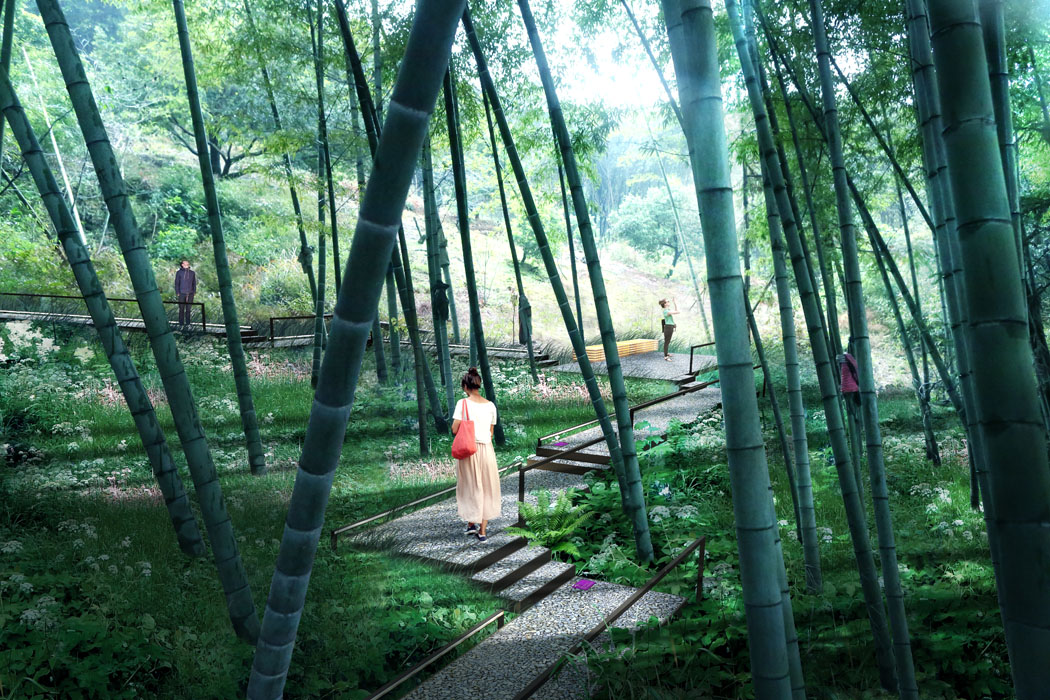
Strategy 1: Minimal Intervention. Protect existing forests and fields, reducing damage.
Strategy 2: Ecological Restoration. Clean up and organize, strengthening the original ecological appearance.
Strategy 3: Integrated Design. Combine site, integrate environment, and embed functional facilities.
Strategy 4: Sustainable Development. Promote scientific education, enhance and develop village flower fields, introduce business activities, and stimulate tourism.
The overall layout includes two lakes, one loop, and multiple points, maximizing the preservation of existing reservoirs, forests, and heritage sites. Existing roads will serve as the main routes for electric vehicles in the park, connecting with Ciyuan Town to ensure the completeness of visitor experiences. Walking paths will guide visitors to various nodes within the site. The main components of the plan include:
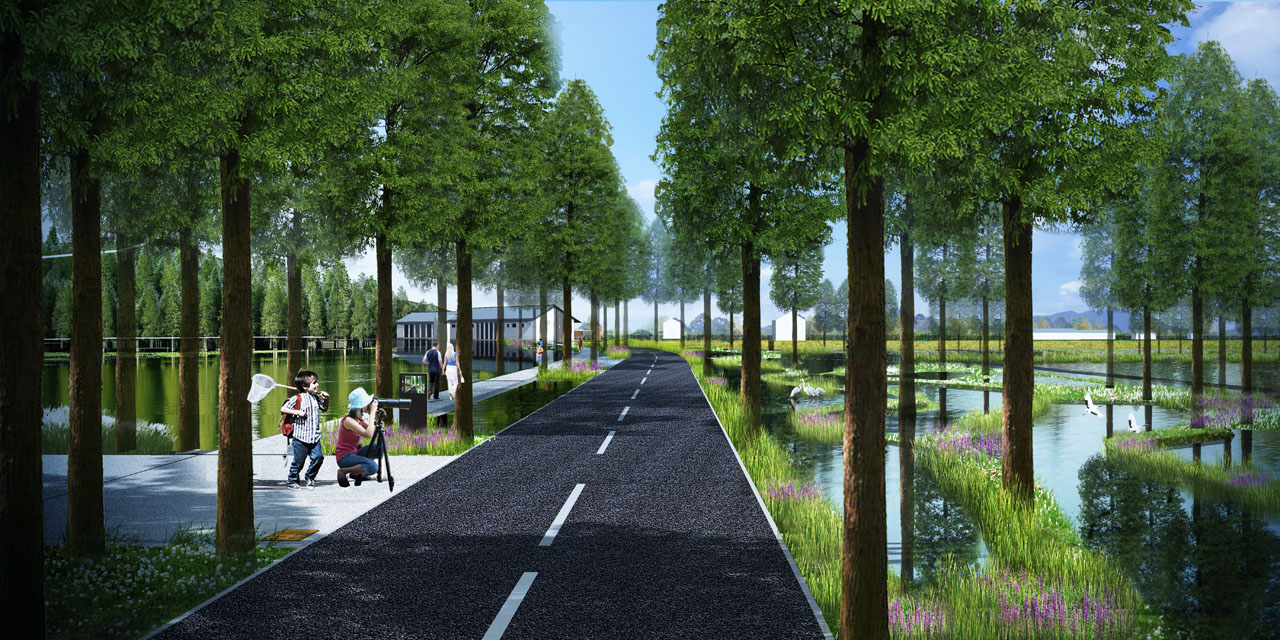
(1) Transportation
The transportation system is organized around vehicle and electric vehicle routes, combined with waterfront leisure walkways, mountain trails, and existing field roads. This forms a multi-route system around the reservoir, linking cultural kiln sites and connecting functional areas, mountain experiences, and agricultural tourism, with clear primary and secondary functions.
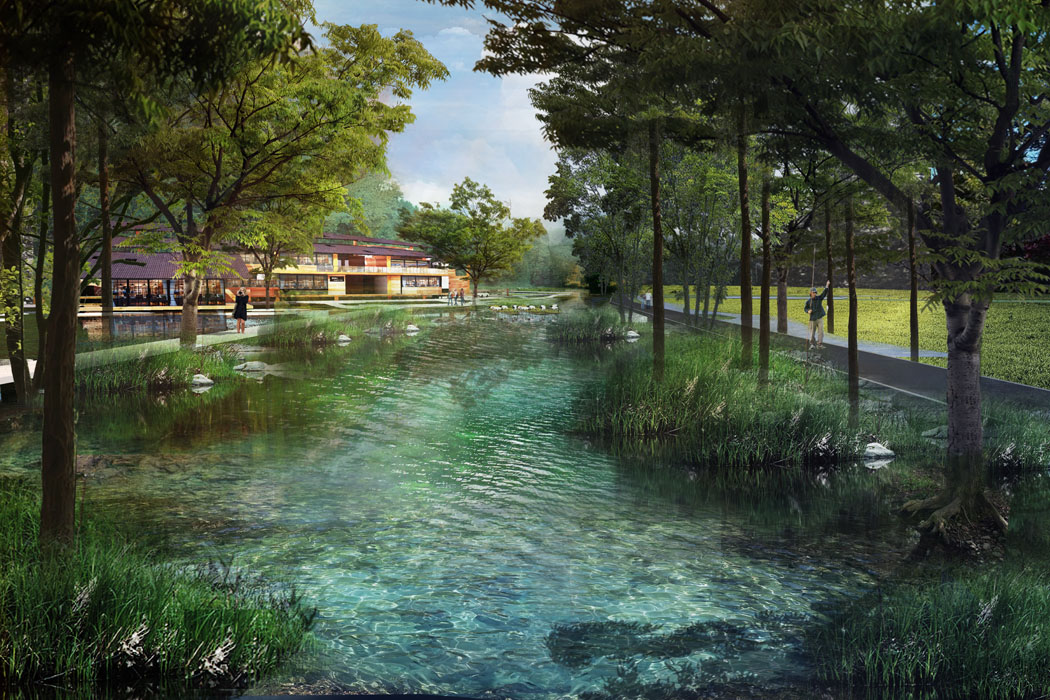
(2) Water System
The water system design focuses on organizing the existing irrigation system. Terraces are designed at the reservoir's rainwater entry points to slow rainwater inflow, collect, and purify water, creating terrace landscapes. The downstream reservoir embankments are removed and redesigned to create terraced fields and wetland landscapes while collecting water.
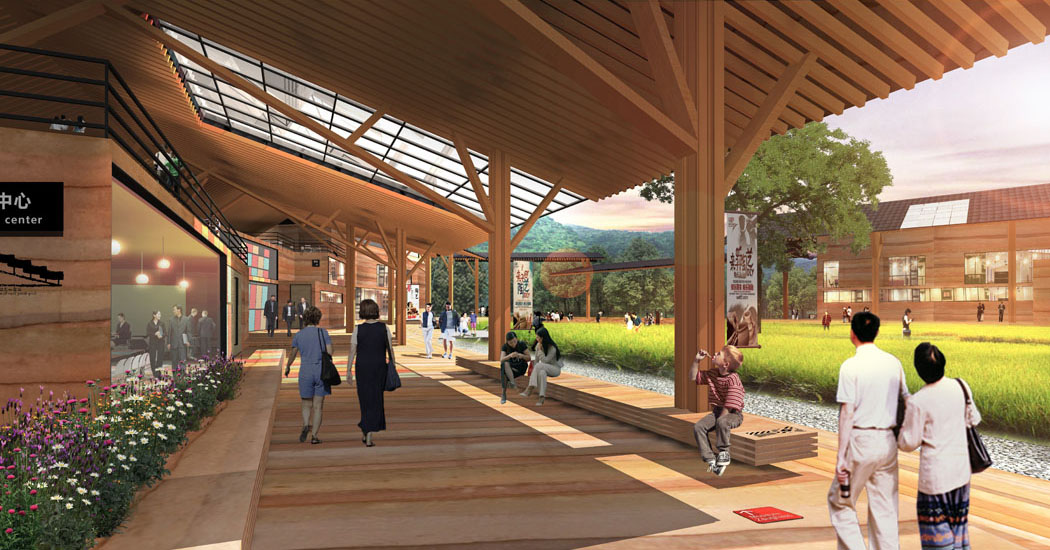
(3) Buildings
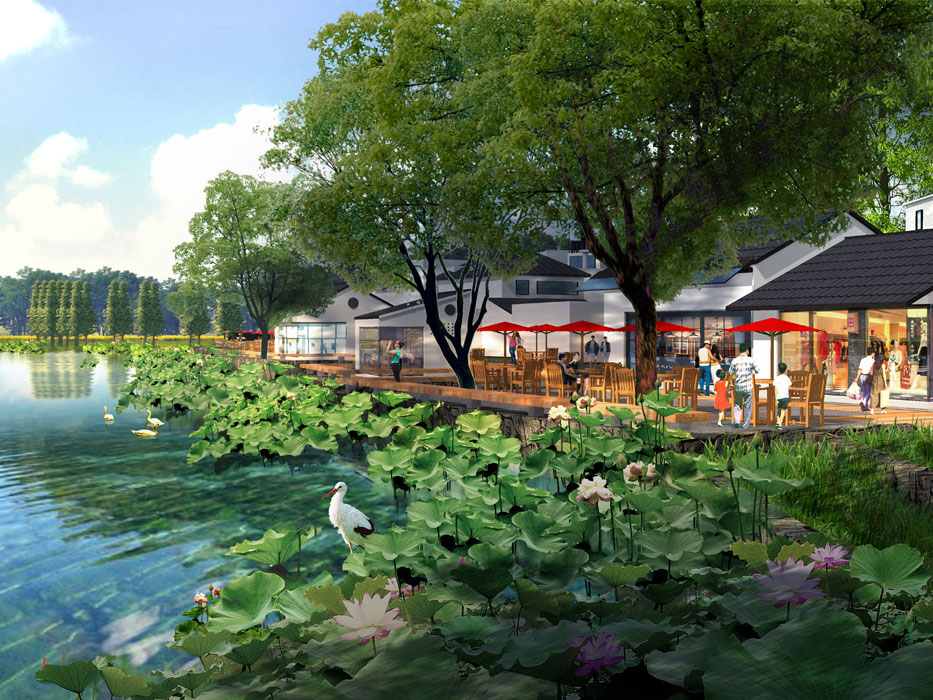
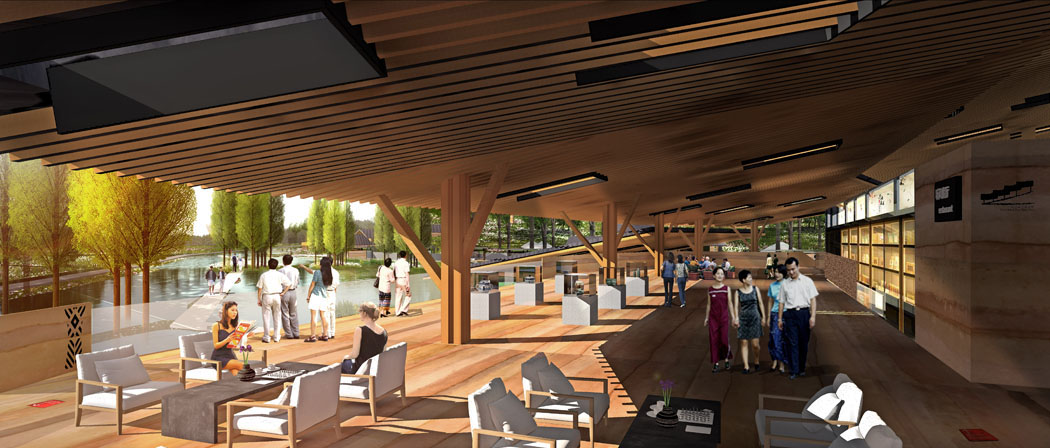
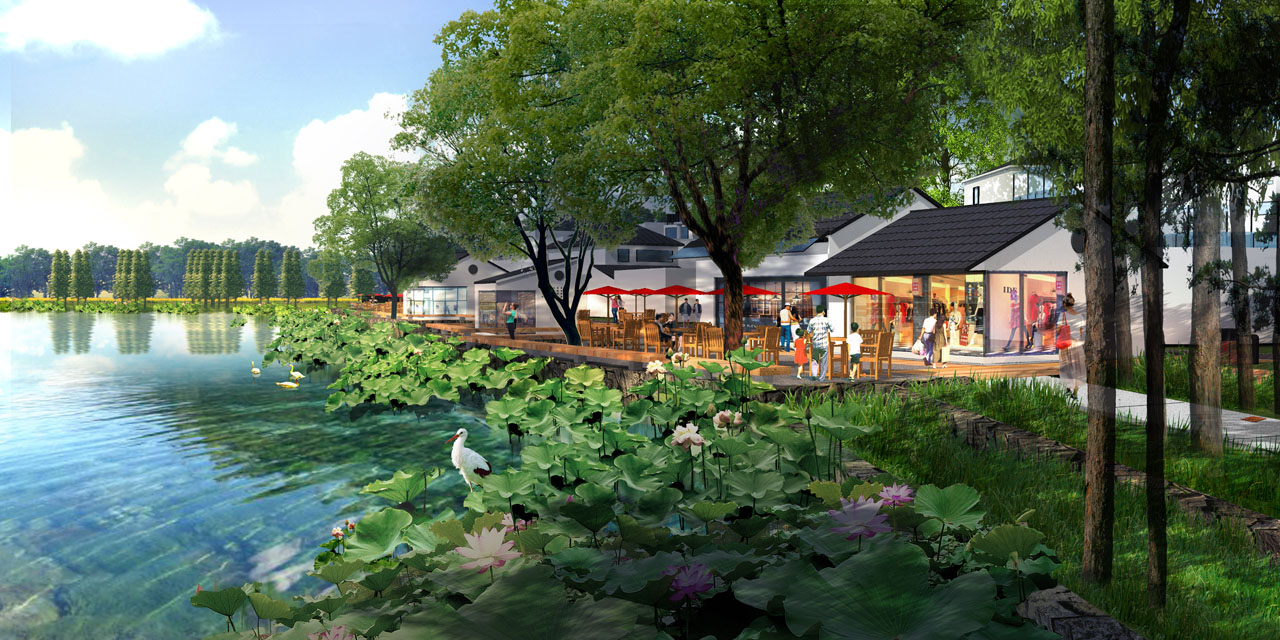
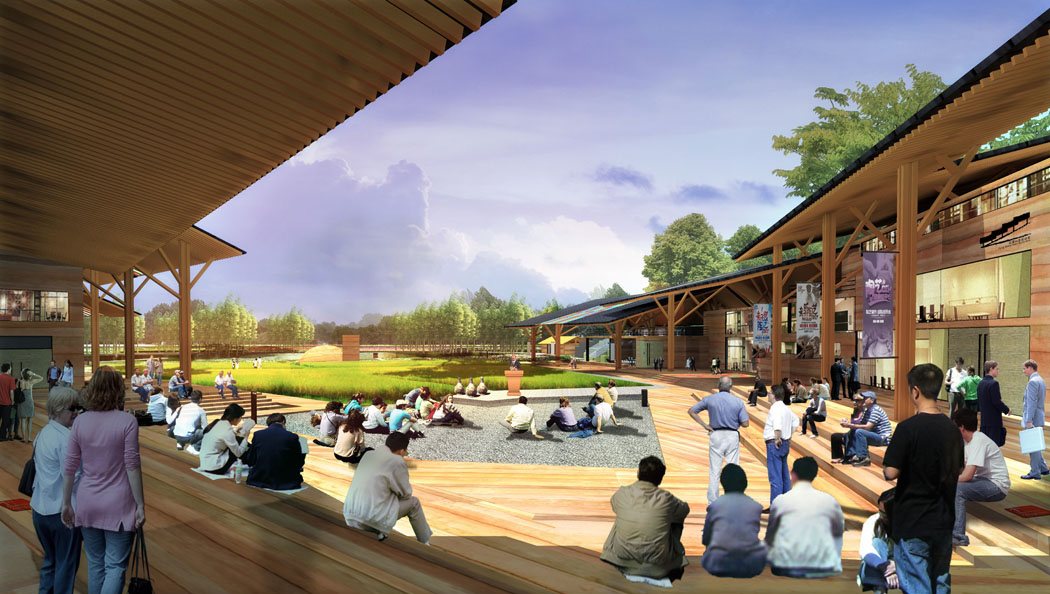
Building design is divided into new and renovated structures. New buildings include the Celadon Academy, Ceramic Workshop, Ceramic Experience Hall, and future ceramic-themed hotel designs. Renovated buildings include scattered existing structures and waterfront buildings in the southwest village, changing their use to tea bars, book houses, service rooms, restrooms, and management facilities.
(4) Public Open Spaces
Public open spaces are designed in conjunction with buildings, water bodies, farmland, mountains, open views, and kiln sites, utilizing existing hydraulic structures (like floodgates) in the layout.
- Spaces near buildings include gathering squares, outdoor tea areas, and leisure platforms.
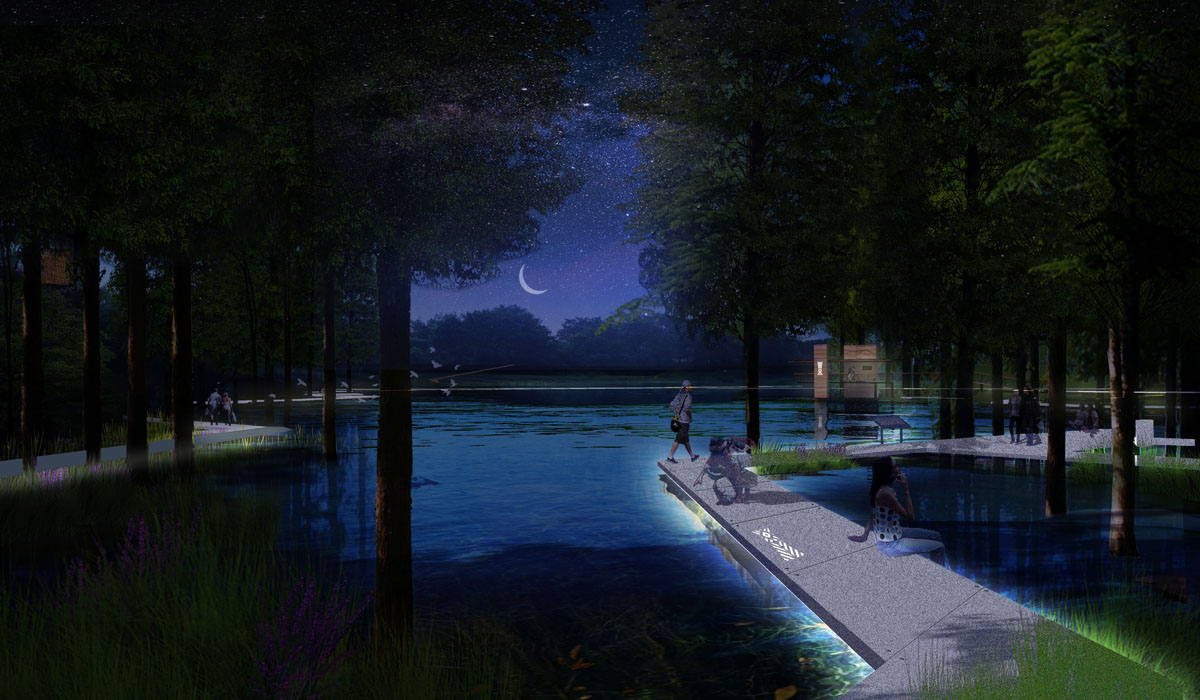
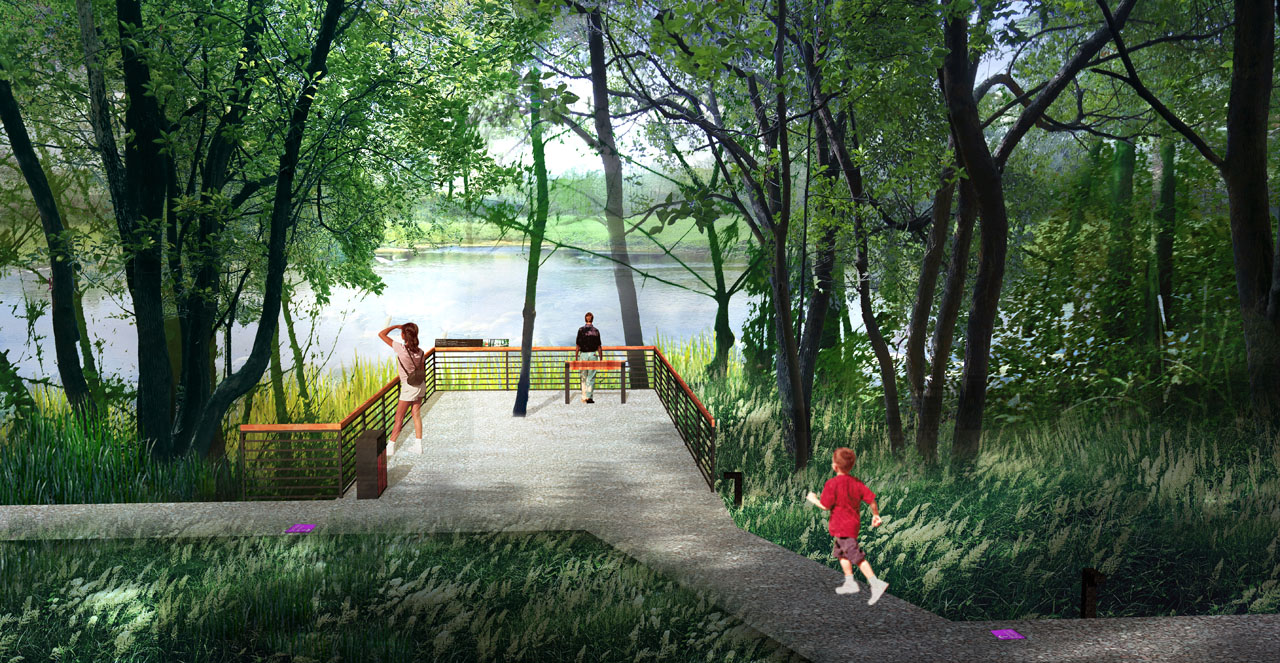
- Spaces near water bodies include waterfront walkways, platforms, boat docks, and piers, with waterfront structures as visual focal points.
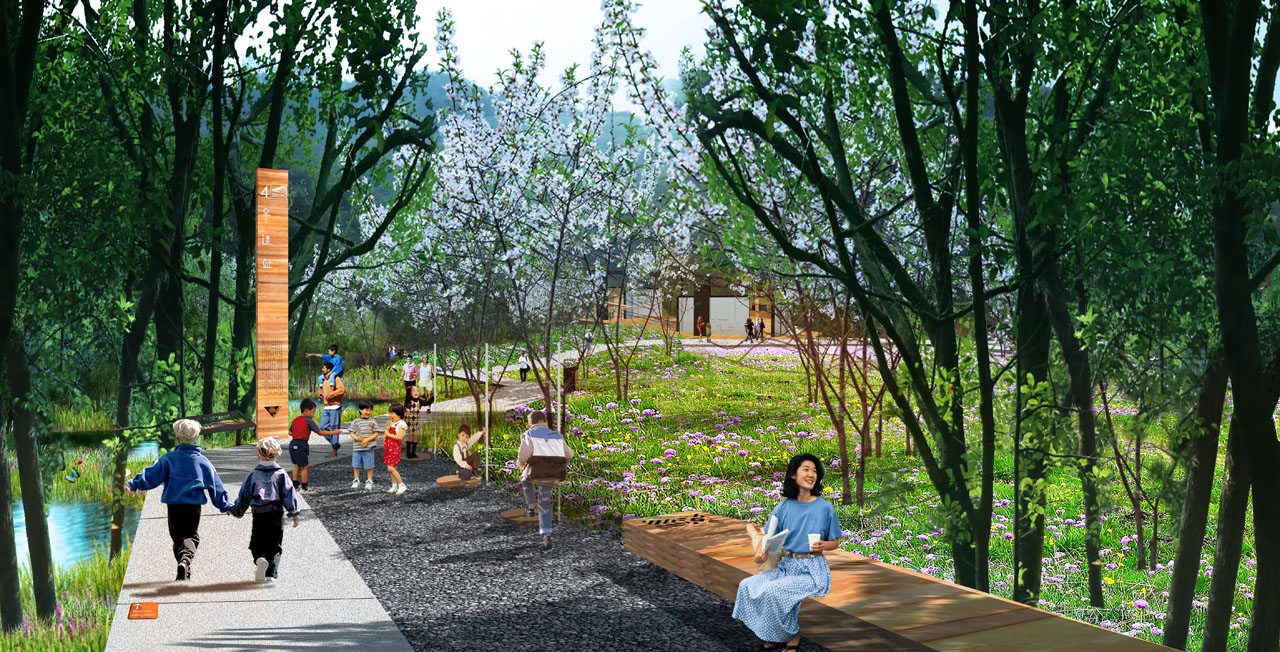
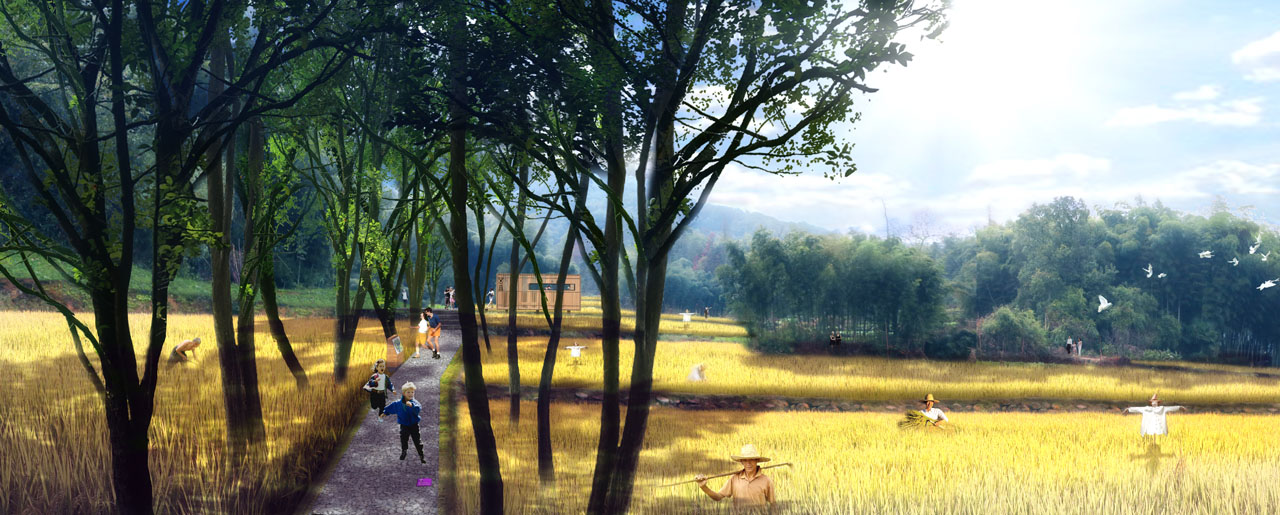
- Spaces near farmland, mountains, and open views feature leisure platforms, walkways, and pavilions for overlooking the lake area.
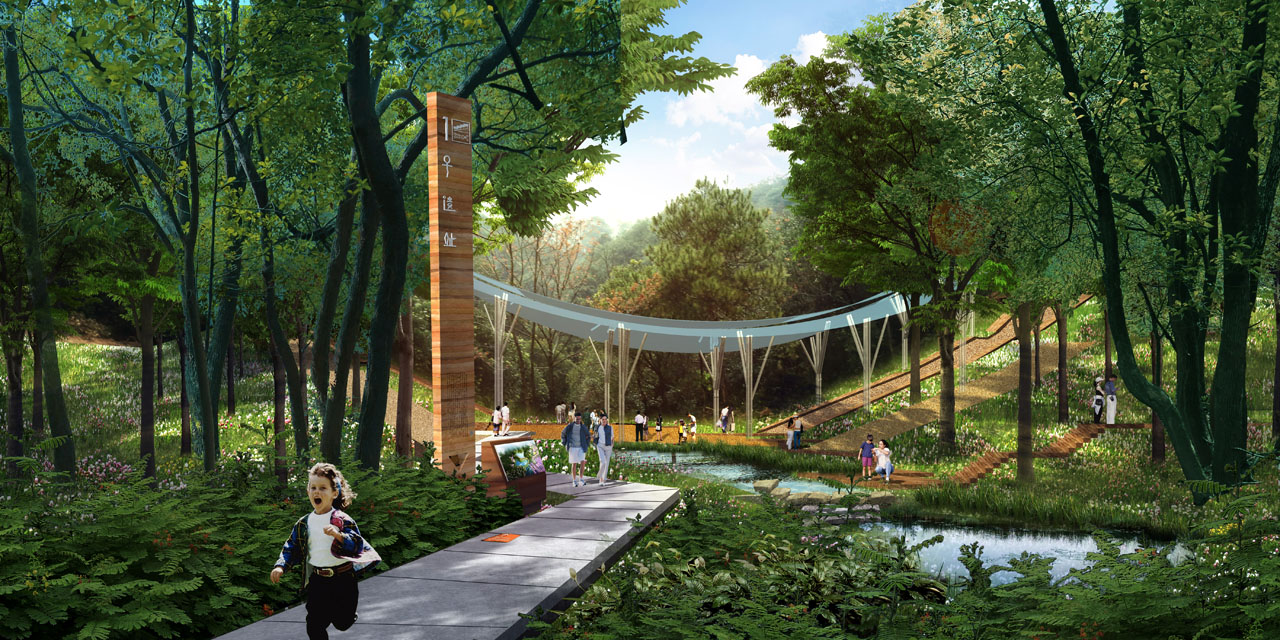
- Kiln sites feature special pavilions and display structures to enhance cultural characteristics.
- Existing floodgates are used to create quiet walking paths, showcasing facility use.
(5) Vegetation
Vegetation design retains healthy existing trees, supplements plants near water, aquatic plants, and ecologically treats existing concrete embankments and farmland. Waterfront plants include pond cypress and bald cypress, with layered aquatic plants according to water depth to enhance diversity. Existing concrete embankments are covered with eco-friendly planting grids and native herbaceous plants. Crop rotation in farmland ensures plant diversity throughout the year with proper timing.
4. Conclusion
The overall plan uses roads as the framework to enhance the site's system, arranges functional buildings and public spaces to add vitality, and employs vegetation design to increase the site's comfort and ecological value.